Domain Bacteria - Crossroads Academy
... The Domain Bacteria, has a wide variety of single celled organisms. They are o9en called prokaryotes because they have no nuclei. The term prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό-‐ (pro-‐) "before" + κ ...
... The Domain Bacteria, has a wide variety of single celled organisms. They are o9en called prokaryotes because they have no nuclei. The term prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό-‐ (pro-‐) "before" + κ ...
Section 9.1 – The Structure of DNA
... 2. Describe how Avery’s experiment supplied evidence that DNA, and not protein, is the genetic material. Avery showed that DNA–destroying enzymes but not protein–destroying enzymes, prevented transformation. 3. Describe the contributions of Hershey and Chase to the understanding that DNA is the gene ...
... 2. Describe how Avery’s experiment supplied evidence that DNA, and not protein, is the genetic material. Avery showed that DNA–destroying enzymes but not protein–destroying enzymes, prevented transformation. 3. Describe the contributions of Hershey and Chase to the understanding that DNA is the gene ...
File
... 18) The purpose of a mordant in the Gram stain is _________. 19) Which microscope is most useful for visualizing a biofilm? 20) What Gram reaction do you expect from acid-fast bacteria? 21) What is the total magnification of a chloroplast viewed with a 10x ocular lens and a 45x objective len ...
... 18) The purpose of a mordant in the Gram stain is _________. 19) Which microscope is most useful for visualizing a biofilm? 20) What Gram reaction do you expect from acid-fast bacteria? 21) What is the total magnification of a chloroplast viewed with a 10x ocular lens and a 45x objective len ...
Biofilm exopolysaccharides
... Another result may be the formation of strong or weak gels. The polysaccharides can thus form various types of structures within a biofilm. However, in biofilms the polysaccharides do not exist alone but may interact with a wide range of other molecular species, including lectins, proteins, lipids e ...
... Another result may be the formation of strong or weak gels. The polysaccharides can thus form various types of structures within a biofilm. However, in biofilms the polysaccharides do not exist alone but may interact with a wide range of other molecular species, including lectins, proteins, lipids e ...
Bacteria pretest review
... 29. What to they bind to on the cell? __________________________ 30. Viruses are general or highly specific to the cell they can infect? ______________________ 32. What is this generalized or specific relationship to the host cell called 31. What is the main way that viruses replicate? _____________ ...
... 29. What to they bind to on the cell? __________________________ 30. Viruses are general or highly specific to the cell they can infect? ______________________ 32. What is this generalized or specific relationship to the host cell called 31. What is the main way that viruses replicate? _____________ ...
The Truth About Antibiotics
... The Truth About Antibiotics From a Medical Perspective Amanda Anderson Clinic Worker ...
... The Truth About Antibiotics From a Medical Perspective Amanda Anderson Clinic Worker ...
Microbial biofilms: case reviews of bacterial and fungal pathogens
... Viable bacteria and fungi have been recovered from environmental fomites and medical surfaces after numerous cleansing treatments, where they have been shown to possess the genes for virulence factors associated with incidence of human disease. These organisms exploit an advantage unique to microbia ...
... Viable bacteria and fungi have been recovered from environmental fomites and medical surfaces after numerous cleansing treatments, where they have been shown to possess the genes for virulence factors associated with incidence of human disease. These organisms exploit an advantage unique to microbia ...
Review - Wound Infection Institute
... Using four different antibiotic groups, Koseoglu et al (2006) found that development of E coli biofilms on urethral catheters could only be delayed, not prevented.[35] The polymeric barrier is also effective against reactive species, such as hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide which are produced by p ...
... Using four different antibiotic groups, Koseoglu et al (2006) found that development of E coli biofilms on urethral catheters could only be delayed, not prevented.[35] The polymeric barrier is also effective against reactive species, such as hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide which are produced by p ...
Abstract(English)
... methanogens. All these conditions result in 60% removal for COD which is lower than other studies done at the same conditions and achieved 88% COD removal for domestic wastewater. The chemical analysis of the UASB shows that the reactor removal efficiency for COD is 60% and that for BOD is 56%. The ...
... methanogens. All these conditions result in 60% removal for COD which is lower than other studies done at the same conditions and achieved 88% COD removal for domestic wastewater. The chemical analysis of the UASB shows that the reactor removal efficiency for COD is 60% and that for BOD is 56%. The ...
Chapter 3,
... Exchange rates across the surface of a cell and surface-to-volume ratios are considered major factors that put limits on cell size. Eukaryotic cells have extensive internal membranes, particularly the endoplasmic reticulum, that function to vastly increase the functional surface area of the cell. Ma ...
... Exchange rates across the surface of a cell and surface-to-volume ratios are considered major factors that put limits on cell size. Eukaryotic cells have extensive internal membranes, particularly the endoplasmic reticulum, that function to vastly increase the functional surface area of the cell. Ma ...
Risk Reduction in Drinking Water Distribution Systems by On
... Studies involving the blue-fluorescent strain Legionella bozemanii were initiated in the fourth quarter of this year (Objective 6). Biofilm formation was monitored on-line using the bacterial autofluorescence which was more sensitive than tryptophan fluorescence. Preliminary results demonstrated tha ...
... Studies involving the blue-fluorescent strain Legionella bozemanii were initiated in the fourth quarter of this year (Objective 6). Biofilm formation was monitored on-line using the bacterial autofluorescence which was more sensitive than tryptophan fluorescence. Preliminary results demonstrated tha ...
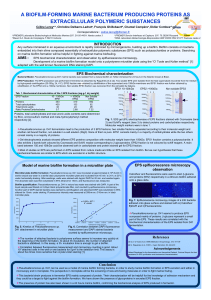
A biofilm-forming marine bacterium producing proteins
... Any surface immersed in an aqueous environment is rapidly colonized by microorganisms, building up a biofilm. Biofilm consists on bacteria embedded into their slime composed essentially of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) such as polysaccharides or proteins. Searching on marine biofilm forma ...
... Any surface immersed in an aqueous environment is rapidly colonized by microorganisms, building up a biofilm. Biofilm consists on bacteria embedded into their slime composed essentially of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) such as polysaccharides or proteins. Searching on marine biofilm forma ...
Microbiology of Periodontal Diseases
... Matrix-enclosed bacterial populations adherent to each other and/or to surfaces or interfaces May form on a wide variety of surfaces, living tissues, indwelling medical devices, water system piping, natural aquatic systems Prevailing microbial lifestyle (vs. planktonic) Like a complex, highly differ ...
... Matrix-enclosed bacterial populations adherent to each other and/or to surfaces or interfaces May form on a wide variety of surfaces, living tissues, indwelling medical devices, water system piping, natural aquatic systems Prevailing microbial lifestyle (vs. planktonic) Like a complex, highly differ ...
Exam Questions for Lesson 1
... Some white blood cells are phagocytic. Describe how these phagocytic white blood cells destroy bacteria. ...
... Some white blood cells are phagocytic. Describe how these phagocytic white blood cells destroy bacteria. ...
Microbiology Test Review
... (Test Wednesday March 30th or Thursday March 31st) 1. What are the two basic components of a virus? 2. Describe the structure of bacteria. ( Be sure to discuss: cell wall, flagellum, pili, DNA) ...
... (Test Wednesday March 30th or Thursday March 31st) 1. What are the two basic components of a virus? 2. Describe the structure of bacteria. ( Be sure to discuss: cell wall, flagellum, pili, DNA) ...
Association with disease severity in contact lens related keratitis
... groups exhibited more bacterial types than the controls (Mann-Whitney U test, p=0.0013). Presenting visual acuity was correlated with number of bacteria identified (p=0.011). Achromobacter and Stenotrophomonas were predominant isolates. ...
... groups exhibited more bacterial types than the controls (Mann-Whitney U test, p=0.0013). Presenting visual acuity was correlated with number of bacteria identified (p=0.011). Achromobacter and Stenotrophomonas were predominant isolates. ...
Major Contributing Factor in Increased Antibiotic Resistance
... formation of biofilms is an example of a phenotypic change that results in increased antibiotic resistance. Biofilms, or aggregations of sessile bacteria surrounded by a polymeric matrix (2), are a leading cause of chronic nosocomial infections. Diseases such as endocarditis, osteomyelitis and medic ...
... formation of biofilms is an example of a phenotypic change that results in increased antibiotic resistance. Biofilms, or aggregations of sessile bacteria surrounded by a polymeric matrix (2), are a leading cause of chronic nosocomial infections. Diseases such as endocarditis, osteomyelitis and medic ...
Document
... DNA. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more advanced, having a nucleus, ER, golgi, etc. Viruses are not classified as cells. They have only a protein coat and a piece of DNA or RNA. They are unable to reproduce without a host cell. ...
... DNA. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more advanced, having a nucleus, ER, golgi, etc. Viruses are not classified as cells. They have only a protein coat and a piece of DNA or RNA. They are unable to reproduce without a host cell. ...
Biofilm

A biofilm is any group of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other on a surface. These adherent cells are frequently embedded within a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS). Biofilm extracellular polymeric substance, which is also referred to as slime (although not everything described as slime is a biofilm), is a polymeric conglomeration generally composed of extracellular DNA, proteins, and polysaccharides. Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial and hospital settings. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single-cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium.Microbes form a biofilm in response to many factors, which may include cellular recognition of specific or non-specific attachment sites on a surface, nutritional cues, or in some cases, by exposure of planktonic cells to sub-inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics. When a cell switches to the biofilm mode of growth, it undergoes a phenotypic shift in behavior in which large suites of genes are differentially regulated.