Lecture 22
... Two “hoses” one skinny, one fat, which one allows more water to flow through? More flow = less resistance [more conductance] ...
... Two “hoses” one skinny, one fat, which one allows more water to flow through? More flow = less resistance [more conductance] ...
2SB1705
... The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Upon actual use, therefore, please request that specifications to be separately delivered. Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants cont ...
... The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Upon actual use, therefore, please request that specifications to be separately delivered. Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants cont ...
SP222 RC Circuits Lab
... We will measure the voltage across the capacitor and the current in the resistor for both the charging capacitor and the discharging capacitor. Procedure 1. Construct the circuit shown in the next diagram. (Note: The switch style used here is called a knife-switch and it looks like something out of ...
... We will measure the voltage across the capacitor and the current in the resistor for both the charging capacitor and the discharging capacitor. Procedure 1. Construct the circuit shown in the next diagram. (Note: The switch style used here is called a knife-switch and it looks like something out of ...
The 6LE8 One Tube Broadcaster
... ARE NOT SURE WHAT YOU ARE DOING, DON’T DO IT! For safety reasons it is best to use a three wire mains (AC) cord. The safety capacitors C1 and C2 are optional but they help to reduce unwanted interference from the mains (power line) which may cause hum. C1 and C2 must be special Y-type safety capacit ...
... ARE NOT SURE WHAT YOU ARE DOING, DON’T DO IT! For safety reasons it is best to use a three wire mains (AC) cord. The safety capacitors C1 and C2 are optional but they help to reduce unwanted interference from the mains (power line) which may cause hum. C1 and C2 must be special Y-type safety capacit ...
batteries, interference and grounding
... As the number of electronic devices continues to increase so does the possibility of interference between them and your amateur station. Radio frequency interference (RFI) RFI can occur in either direction---to or from the Amateur radio equipment ...
... As the number of electronic devices continues to increase so does the possibility of interference between them and your amateur station. Radio frequency interference (RFI) RFI can occur in either direction---to or from the Amateur radio equipment ...
US6T5
... The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Upon actual use, therefore, please request that specifications to be separately delivered. Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants cont ...
... The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Upon actual use, therefore, please request that specifications to be separately delivered. Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants cont ...
Worksheet 8.7 - Transformers
... 102 V power line, and the current in the secondary coil is 5.00 A. what is the current in the primary coil? 3) Near your home the voltage pf the power line is 3.6 x 103 V. The transformer between your home and the line reduces this voltage to 1.20 x 102 V. If the transformer is to deliver 2.4 x 103 ...
... 102 V power line, and the current in the secondary coil is 5.00 A. what is the current in the primary coil? 3) Near your home the voltage pf the power line is 3.6 x 103 V. The transformer between your home and the line reduces this voltage to 1.20 x 102 V. If the transformer is to deliver 2.4 x 103 ...
CAT IV or CAT III?
... The basic standard for electrical installation IEC/EN 60364 includes the definition of overvoltage categories in chapter 44 (Protection against voltage disturbances and electromagnetic disturbances). According to the installation impedances, proximity to the origin of the installation and installed ...
... The basic standard for electrical installation IEC/EN 60364 includes the definition of overvoltage categories in chapter 44 (Protection against voltage disturbances and electromagnetic disturbances). According to the installation impedances, proximity to the origin of the installation and installed ...
UMZ16N
... The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Upon actual use, therefore, please request that specifications to be separately delivered. Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants cont ...
... The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Upon actual use, therefore, please request that specifications to be separately delivered. Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants cont ...
III. Substation Bus Configurations and Substation Design
... performed. Each Transmission lines and Transformer must be equipped with a switch to isolate it from the substation such that the station bay or ring bus can be re-energized during maintenance of that Transmission lines or Transformer. Electrical equipment must be arranged with adequate clearances s ...
... performed. Each Transmission lines and Transformer must be equipped with a switch to isolate it from the substation such that the station bay or ring bus can be re-energized during maintenance of that Transmission lines or Transformer. Electrical equipment must be arranged with adequate clearances s ...
AD4C212 - ssousa.com
... The AD4C212 is a bi-directional, double-pole, single-throw, normally closed multipurpose solid-state relay. It is designed to replace electromechanical relays in general purpose switching applications. The relay consists of two integrated circuits, each driving a pair of rugged source-to-source depl ...
... The AD4C212 is a bi-directional, double-pole, single-throw, normally closed multipurpose solid-state relay. It is designed to replace electromechanical relays in general purpose switching applications. The relay consists of two integrated circuits, each driving a pair of rugged source-to-source depl ...
Introduction to Electronics
... provided on the next page, compute and record the theoretical resistance (and error) of each resistor. Convert the percentage error to an absolute error. 2) Use the digital multi-meter as an ohmmeter (see instructions on the next page) to measure and record the experimental resistance (and error; be ...
... provided on the next page, compute and record the theoretical resistance (and error) of each resistor. Convert the percentage error to an absolute error. 2) Use the digital multi-meter as an ohmmeter (see instructions on the next page) to measure and record the experimental resistance (and error; be ...
A connected circuit that consists of e elements connected to each
... We can measure the current of any circuit element by adding an ammeter in series with that element. An ideal ammeter is equivalent to a short circuit and does not change the value of the current. ...
... We can measure the current of any circuit element by adding an ammeter in series with that element. An ideal ammeter is equivalent to a short circuit and does not change the value of the current. ...
phase shift - Controlled Power Company
... magnetic shunts in their design to obtain substantial values of leakage inductance between the primary and secondary circuits. The leakage inductance isolates the primary from secondary load variations, providing excellent regulation. The magnetic shunts also represent a parallel path for the power ...
... magnetic shunts in their design to obtain substantial values of leakage inductance between the primary and secondary circuits. The leakage inductance isolates the primary from secondary load variations, providing excellent regulation. The magnetic shunts also represent a parallel path for the power ...
Partial Discharges in Electrical Insulation
... between the two conductors • The conductors must have a high voltage between them, creating an electric stress • If the electric stress in the gas exceeds 3 kV/mm of spacing (for most dry gases at 100 kPa), then electrons are stripped from the gas atoms • The electric strength of most solid and liqu ...
... between the two conductors • The conductors must have a high voltage between them, creating an electric stress • If the electric stress in the gas exceeds 3 kV/mm of spacing (for most dry gases at 100 kPa), then electrons are stripped from the gas atoms • The electric strength of most solid and liqu ...
MS Word
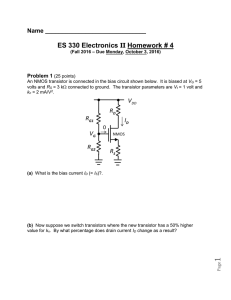
... drain node. Simplifying assumption: Take the AC signal voltage on the source node to be essentially zero (i.e., meaning it remains at the DC terminal voltage you caluclated when determining VGS). Thus, the minimum drain node voltage vDrain will be 1 volt in magnitude in meeting the 2-V peak-to-peak ...
... drain node. Simplifying assumption: Take the AC signal voltage on the source node to be essentially zero (i.e., meaning it remains at the DC terminal voltage you caluclated when determining VGS). Thus, the minimum drain node voltage vDrain will be 1 volt in magnitude in meeting the 2-V peak-to-peak ...
Voltage - Electromotive Force
... 2. The reference terminal from which the voltage is measured 3. Two points in the circuit between which the voltage is measured All the above information is commonly conveyed by placing a set of plus (+) or minus (-) signs directly adjacent to the points of interest with the magnitude of the voltage ...
... 2. The reference terminal from which the voltage is measured 3. Two points in the circuit between which the voltage is measured All the above information is commonly conveyed by placing a set of plus (+) or minus (-) signs directly adjacent to the points of interest with the magnitude of the voltage ...
Safety - G0MWT
... • The static charge can ionise the air to form a low resistance path to ground allowing a very high current to flow as a lightning strike ...
... • The static charge can ionise the air to form a low resistance path to ground allowing a very high current to flow as a lightning strike ...
September 2009 - 3mm × 3mm, 16-Bit ADC Brings Accurate, Precise High Side Current Sensing to Tight Spaces
... Power monitoring circuits are increasingly used throughout automotive, industrial, communications and computing applications as electronics designers strive to continually improve thermal performance, increase efficiency and generally make their products more “green.” The problem is that power monit ...
... Power monitoring circuits are increasingly used throughout automotive, industrial, communications and computing applications as electronics designers strive to continually improve thermal performance, increase efficiency and generally make their products more “green.” The problem is that power monit ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.