Linear Systems Offers Direct Alternative for Analog Devices MAT01
... IC = 100µA, VCE = 5V, BW=200Hz, RG= 10KΩ, f = 1KHz ...
... IC = 100µA, VCE = 5V, BW=200Hz, RG= 10KΩ, f = 1KHz ...
SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS
... circuit. Some amount of current will flow through every path it can take to get to the point of lowest voltage (usually called ground). Using the above circuit as an example, here’s how current would flow as it runs from the battery’s positive terminal to the negative: ...
... circuit. Some amount of current will flow through every path it can take to get to the point of lowest voltage (usually called ground). Using the above circuit as an example, here’s how current would flow as it runs from the battery’s positive terminal to the negative: ...
LAB - 1 - ECE233
... component. Hence it should be connected in parallel with the electrical component. It is also possible to measure the potential (voltage) difference between any two points (nodes) in a circuit. For this purpose, the probes of the multimeter are connected to these two points. Generally it is a conven ...
... component. Hence it should be connected in parallel with the electrical component. It is also possible to measure the potential (voltage) difference between any two points (nodes) in a circuit. For this purpose, the probes of the multimeter are connected to these two points. Generally it is a conven ...
Chapter 11 — Electrical Integration
... system and the AC grounding system must be connected together with a bonding conductor. The array may also require a separate grounding electrode system. ...
... system and the AC grounding system must be connected together with a bonding conductor. The array may also require a separate grounding electrode system. ...
R210-90-5
... In recent years, harmonic loads on distribution systems (in which currents at higher-frequency multiples of the fundamental 60Hz frequency add to the fundamental current) have increased dramatically due to the increased use of ferromagnetic devices (motors, transformers), arcing devised (fluorescent ...
... In recent years, harmonic loads on distribution systems (in which currents at higher-frequency multiples of the fundamental 60Hz frequency add to the fundamental current) have increased dramatically due to the increased use of ferromagnetic devices (motors, transformers), arcing devised (fluorescent ...
Electric Power Distribution
... Household electricity is alternating current (AC) Household voltages are typically 120V or 240V Power is distributed at much higher voltages Power transformers are common around us Power substations are there, but harder to find ...
... Household electricity is alternating current (AC) Household voltages are typically 120V or 240V Power is distributed at much higher voltages Power transformers are common around us Power substations are there, but harder to find ...
UNDERSTANDING AND USING 723VOLTAGE REGULATORS
... The quick charge is not quite as good as more sophisticated circuits which maintain a maximum rate until a set point and then switch to the low rate. The 723 circuit starts out at maximum charge but tapers off as the voltage of the battery pack increases with the level of charge. The quick charge is ...
... The quick charge is not quite as good as more sophisticated circuits which maintain a maximum rate until a set point and then switch to the low rate. The 723 circuit starts out at maximum charge but tapers off as the voltage of the battery pack increases with the level of charge. The quick charge is ...
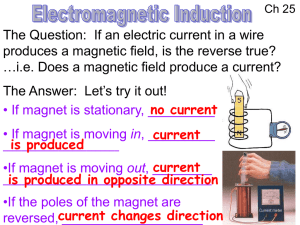
changing magnetic field
... The key to obtaining a current in the secondary coil is to establish a changing magnetic field in the primary coil. Instead of using a battery (DC) and switching the current on/off repeatedly (a little impractical!!) alternating current to accomplish this, _____________________ in the primary coil i ...
... The key to obtaining a current in the secondary coil is to establish a changing magnetic field in the primary coil. Instead of using a battery (DC) and switching the current on/off repeatedly (a little impractical!!) alternating current to accomplish this, _____________________ in the primary coil i ...
Dual impedance digital multimeters— What`s the point?
... today for testing industrial, electrical, and electronic systems have high impedance input circuits greater than 1 megohm. In simple terms this means that when the DMM is placed across a circuit for a measurement, it will have little impact on circuit performance. This is the desired effect for ...
... today for testing industrial, electrical, and electronic systems have high impedance input circuits greater than 1 megohm. In simple terms this means that when the DMM is placed across a circuit for a measurement, it will have little impact on circuit performance. This is the desired effect for ...
Printed-Circuit-Board Layout for Improved
... The supply lines in Figure 1 form loops A–C–D–B and A–E–F–B. The energy the system needs to operate is conducted by these lines. Since the power consumption of the circuit is not constant but depends on its instantaneous state, then all the frequency components generated in the individual parts of t ...
... The supply lines in Figure 1 form loops A–C–D–B and A–E–F–B. The energy the system needs to operate is conducted by these lines. Since the power consumption of the circuit is not constant but depends on its instantaneous state, then all the frequency components generated in the individual parts of t ...
Applying power quality measurements to predictive maintenance
... Taking a single voltage reading tells only part of the story. How is the voltage changing during an hour? During a day? Sags, swells and transients are short-term variations in voltage. The voltage sag (or dip) is the most common and troublesome variety. Sags indicate that a system is having trouble ...
... Taking a single voltage reading tells only part of the story. How is the voltage changing during an hour? During a day? Sags, swells and transients are short-term variations in voltage. The voltage sag (or dip) is the most common and troublesome variety. Sags indicate that a system is having trouble ...
Step Down Transformer By Sultan Salahuddin
... circuits contains a winding, which links it inductively to the other circuits. The windings are wound onto an iron core. The iron core channels the magnetic flux generated by the current flowing around the primary winding, and as much as possible, also links the secondary winding www.BZUpages.com ...
... circuits contains a winding, which links it inductively to the other circuits. The windings are wound onto an iron core. The iron core channels the magnetic flux generated by the current flowing around the primary winding, and as much as possible, also links the secondary winding www.BZUpages.com ...
LabS2004_2 - University of Kentucky College of Engineering
... characterized by transfer functions, differential equations, and/or impulse responses. For linear circuits these characterizations, along with the initial conditions, completely describe the inputoutput relationship. Circuits containing no energy storage elements are referred to as instantaneous or ...
... characterized by transfer functions, differential equations, and/or impulse responses. For linear circuits these characterizations, along with the initial conditions, completely describe the inputoutput relationship. Circuits containing no energy storage elements are referred to as instantaneous or ...
Power Systems for Aerospace, Marine and
... o New motor designs o Moving EPS technology to other automotive applications (e.g. clutch, braking…) + reduces development costs o Sensorless control + lower component count lower cost + higher reliability - low speed - more complex control - audible noise (from carrier signal injection) ...
... o New motor designs o Moving EPS technology to other automotive applications (e.g. clutch, braking…) + reduces development costs o Sensorless control + lower component count lower cost + higher reliability - low speed - more complex control - audible noise (from carrier signal injection) ...
Construction of a Simple Transformer to Illustrate Faraday`s Law of
... In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the property of an electrical conductor by which a change in current flowing through it induces an electromotive force in both the conductor itself and in any nearby conductors by mutual inductance. These effects are derived from two fundamental obs ...
... In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the property of an electrical conductor by which a change in current flowing through it induces an electromotive force in both the conductor itself and in any nearby conductors by mutual inductance. These effects are derived from two fundamental obs ...
Chapter 18: Electric Current and Circuits
... Example (text problem 18.85): A capacitor is charged to an initial voltage of V0 = 9.0 volts. The capacitor is then discharged through a resistor. The current is measured and is shown in the figure. ...
... Example (text problem 18.85): A capacitor is charged to an initial voltage of V0 = 9.0 volts. The capacitor is then discharged through a resistor. The current is measured and is shown in the figure. ...
ac/dc voltage measurements
... 3. Touch the test probe tips across the circuit or part under test. It is best to disconnect one side of the part under test so the rest of the circuit will not interfere with the resistance reading. 4. Read the resistance in the display CONTINUITY CHECK WARNING: To avoid electric shock, never measu ...
... 3. Touch the test probe tips across the circuit or part under test. It is best to disconnect one side of the part under test so the rest of the circuit will not interfere with the resistance reading. 4. Read the resistance in the display CONTINUITY CHECK WARNING: To avoid electric shock, never measu ...
Low voltage fast-switching NPN power transistors
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
DATASHEET: Furman AR-1220
... The 20 amp AR-1220 AC Line Voltage Regulator is intended to protect audio, video, computer and other electronic equipment from problems caused by AC line voltage irregularities—sags, brownouts, or overvoltages that can cause sensitive digital equipment to malfunction, or, in extreme cases, to sustai ...
... The 20 amp AR-1220 AC Line Voltage Regulator is intended to protect audio, video, computer and other electronic equipment from problems caused by AC line voltage irregularities—sags, brownouts, or overvoltages that can cause sensitive digital equipment to malfunction, or, in extreme cases, to sustai ...
Ground (electricity)

In electrical engineering, ground or earth is the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.Electrical circuits may be connected to ground (earth) for several reasons. In mains powered equipment, exposed metal parts are connected to ground to prevent user contact with dangerous voltage if electrical insulation fails. Connections to ground limit the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. In some telegraph and power transmission circuits, the earth itself can be used as one conductor of the circuit, saving the cost of installing a separate return conductor (see single-wire earth return).For measurement purposes, the Earth serves as a (reasonably) constant potential reference against which other potentials can be measured. An electrical ground system should have an appropriate current-carrying capability to serve as an adequate zero-voltage reference level. In electronic circuit theory, a ""ground"" is usually idealized as an infinite source or sink for charge, which can absorb an unlimited amount of current without changing its potential. Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or if large enough will produce an electric shock hazard.The use of the term ground (or earth) is so common in electrical and electronics applications that circuits in portable electronic devices such as cell phones and media players as well as circuits in vehicles may be spoken of as having a ""ground"" connection without any actual connection to the Earth, despite ""common"" being a more appropriate term for such a connection. This is usually a large conductor attached to one side of the power supply (such as the ""ground plane"" on a printed circuit board) which serves as the common return path for current from many different components in the circuit.