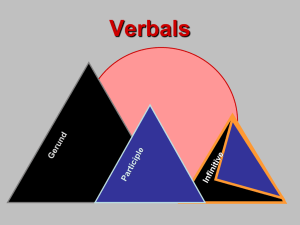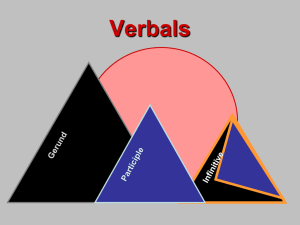
Verbals Powerpoint - Grass Lake Community Schools
... • His sister was dancing in the show. (not a gerund, verb phrase) • I hate practicing the piano. (DO) • I gave my mom’s cooking a perfect 10. (IO) • Sitting by the pool is quite relaxing. (S) ...
... • His sister was dancing in the show. (not a gerund, verb phrase) • I hate practicing the piano. (DO) • I gave my mom’s cooking a perfect 10. (IO) • Sitting by the pool is quite relaxing. (S) ...
Verbals
... • His sister was dancing in the show. (not a gerund, verb phrase) • I hate practicing the piano. (DO) • I gave my mom’s cooking a perfect 10. (IO) • Sitting by the pool is quite relaxing. (S) ...
... • His sister was dancing in the show. (not a gerund, verb phrase) • I hate practicing the piano. (DO) • I gave my mom’s cooking a perfect 10. (IO) • Sitting by the pool is quite relaxing. (S) ...
PAST PARTICIPLES AND THE PERFECT TENSES
... PAST PARTICIPLES • In Spanish, past participles are formed by dropping the “-ar” and adding –ado, or the “-er,” “-ir” and adding -ido Examples: comer (to eat) comido (eaten) hablar (to speak) hablado (spoken) ...
... PAST PARTICIPLES • In Spanish, past participles are formed by dropping the “-ar” and adding –ado, or the “-er,” “-ir” and adding -ido Examples: comer (to eat) comido (eaten) hablar (to speak) hablado (spoken) ...
The Writing Center Presents: - Prairie View A&M University
... A preposition should always come in front of the prepositional phrase. Preposition + Optional modifiers (i.e.. A, the, etc.) + Object (Noun, pronoun or gerund). Some prepositions can also acts as subordinating conjunctions. These prepositions will be followed by a subject and a verb. ...
... A preposition should always come in front of the prepositional phrase. Preposition + Optional modifiers (i.e.. A, the, etc.) + Object (Noun, pronoun or gerund). Some prepositions can also acts as subordinating conjunctions. These prepositions will be followed by a subject and a verb. ...
Chapter 8 Other verb
... structurally, and semantically one of their constituent members modifies the other in some ways, hence their constituent members vary and belong to different semantic fields. Verbal compounds, on the other hand, are mono-clausal and semantically they refer to one single activity or state. However, s ...
... structurally, and semantically one of their constituent members modifies the other in some ways, hence their constituent members vary and belong to different semantic fields. Verbal compounds, on the other hand, are mono-clausal and semantically they refer to one single activity or state. However, s ...
Verb tenses 1 - TP Publications
... The subject is usually the ‘doer’, or the person/thing described. The predicate means ‘the rest of the sentence’ to put it crudely but simply. The verb conveys an action or state. The OBJECT is the person/thing at the receiving end of the action, hence music is the object of the verb makes. Noun, ve ...
... The subject is usually the ‘doer’, or the person/thing described. The predicate means ‘the rest of the sentence’ to put it crudely but simply. The verb conveys an action or state. The OBJECT is the person/thing at the receiving end of the action, hence music is the object of the verb makes. Noun, ve ...
WHAT ARE PRONOUNS and what do they do?
... REFLEXlVEIINTENSIVE PRONOUNS: Pronouns with -selfor -selves can be used in two ways: as reflexives or as intensives. DO NOT use reflexive or intensive pronouns as substitutes for the subject of a sentence or in the place of a simple pronoun. ...
... REFLEXlVEIINTENSIVE PRONOUNS: Pronouns with -selfor -selves can be used in two ways: as reflexives or as intensives. DO NOT use reflexive or intensive pronouns as substitutes for the subject of a sentence or in the place of a simple pronoun. ...
the structure of auxiliaries within the complex verbal groups
... its Head. Lexical verbs are those verbs which belong to the general vocabulary of a language. The lexical Head always appears last in the Verbal Groups. The lexical Head Verb may or may not be modified by auxiliary verbs. A Verbal group consisting only of a Head verb (without auxiliaries) is called ...
... its Head. Lexical verbs are those verbs which belong to the general vocabulary of a language. The lexical Head always appears last in the Verbal Groups. The lexical Head Verb may or may not be modified by auxiliary verbs. A Verbal group consisting only of a Head verb (without auxiliaries) is called ...
Morphology and cross dependencies in the synthesis of
... These four steps imply that both the direct object and the verb are checked over twice. Note that this is only for the synthesis of these two elements. The cross dependencies that arise from other elements imply that the direct object and the verb are checked over more thant twice. Generally speakin ...
... These four steps imply that both the direct object and the verb are checked over twice. Note that this is only for the synthesis of these two elements. The cross dependencies that arise from other elements imply that the direct object and the verb are checked over more thant twice. Generally speakin ...
Chapter 1 Been There, Done That: Passé Proche and Passé Composé
... Chapter 1: Been There, Done That: Passé Proche and Passé Composé example, ask yourself whether the verb prévenir introduces a person like Jean directly or with the preposition à. In other words, is the sentence saying Ils ont prévenu à Jean or Ils ont prévenu Jean? The fact that the correct sentenc ...
... Chapter 1: Been There, Done That: Passé Proche and Passé Composé example, ask yourself whether the verb prévenir introduces a person like Jean directly or with the preposition à. In other words, is the sentence saying Ils ont prévenu à Jean or Ils ont prévenu Jean? The fact that the correct sentenc ...
The Phrase Self-Quiz
... Pirouetting on her toes is not the subject of the sentence. “Who completed?” The ballerina completed; therefore, ballerina is the subject. What does Pirouetting on her toes answer? Not what she does. Completed tells that. Pirouetting on her toes gives more description of the ballerina. To double che ...
... Pirouetting on her toes is not the subject of the sentence. “Who completed?” The ballerina completed; therefore, ballerina is the subject. What does Pirouetting on her toes answer? Not what she does. Completed tells that. Pirouetting on her toes gives more description of the ballerina. To double che ...
The Infinitive and the Infinitive Phrase
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
... 2. Find the verb 3. If the verb is an action verb (it can be done DO), ask “WHAT” after the verb. 4. If the infinitive phrase makes sense, you have a DO. The band and choir try (verb) to work together during the musical. (try what? To work together during the musical) ...
The Grammar Aquarium Guide to Grammatical Terms
... A verb is an action, doing or being word. The same verb can take different forms. This will depend on how many people, or things are doing it and when it happened. A sentence will normally contain at least one verb. ...
... A verb is an action, doing or being word. The same verb can take different forms. This will depend on how many people, or things are doing it and when it happened. A sentence will normally contain at least one verb. ...
Countable Nouns
... "Will" often suggests that a speaker will do something voluntarily. A voluntary action is one the speaker offers to do for someone else. Often, we use "will" to respond to someone else's complaint or request for help. We also use "will" when we request that someone help us or volunteer to do somethi ...
... "Will" often suggests that a speaker will do something voluntarily. A voluntary action is one the speaker offers to do for someone else. Often, we use "will" to respond to someone else's complaint or request for help. We also use "will" when we request that someone help us or volunteer to do somethi ...
possessive constructions in nganasan - slm.uni
... Apart from the negative existential verb, negation can also be expressed by means of a caritive/abessive formative suffix. In this case two structures can be differentiated. The NP with the caritive/abessive suffix can stand either with an affirmative form, or with the negative existential verb. The ...
... Apart from the negative existential verb, negation can also be expressed by means of a caritive/abessive formative suffix. In this case two structures can be differentiated. The NP with the caritive/abessive suffix can stand either with an affirmative form, or with the negative existential verb. The ...
Neuter dobré dobré
... Animate and Inanimate), and then by their ending in the Nominative -- hard or soft. So a given word might be a “hard masculine noun or “soft feminine adjective” etc. These categories are represented by chosen words called paradigms. How to tell the Gender: Nouns ending in -o and -í are Neuter. Nouns ...
... Animate and Inanimate), and then by their ending in the Nominative -- hard or soft. So a given word might be a “hard masculine noun or “soft feminine adjective” etc. These categories are represented by chosen words called paradigms. How to tell the Gender: Nouns ending in -o and -í are Neuter. Nouns ...
Grammar essentials - Branson Public Schools
... Rule #2: Use an apostrophe and s to form the possessive of a plural noun that does not end in s. Examples: men’s, women’s, oxen’s, geese’s Rule #3: Use an apostrophe alone to form the possessive of a plural noun that ends in s. Examples: boys’, babies’, Thompsons’ ...
... Rule #2: Use an apostrophe and s to form the possessive of a plural noun that does not end in s. Examples: men’s, women’s, oxen’s, geese’s Rule #3: Use an apostrophe alone to form the possessive of a plural noun that ends in s. Examples: boys’, babies’, Thompsons’ ...
Campus Academic Resource Program
... What is a participle: According to the Purdue Online Writing Lab, the definition of a participle is: “…a verbal that is used as an adjective, modifying a noun or pronoun,” (for a definition of verbal, see the glossary section at the end of this handout). Additionally, a participial phrase can be use ...
... What is a participle: According to the Purdue Online Writing Lab, the definition of a participle is: “…a verbal that is used as an adjective, modifying a noun or pronoun,” (for a definition of verbal, see the glossary section at the end of this handout). Additionally, a participial phrase can be use ...
Agreement: Matching Sentence Parts
... 6. Two or more singular subjects joined by or or nor must have a singular verb. This makes perfect sense: You are making a choice between two singular subjects. The or shows that you are only choosing one. Either the dog or the cat has to go. sing. subject. or sing. subject sing. verb Only one pet w ...
... 6. Two or more singular subjects joined by or or nor must have a singular verb. This makes perfect sense: You are making a choice between two singular subjects. The or shows that you are only choosing one. Either the dog or the cat has to go. sing. subject. or sing. subject sing. verb Only one pet w ...
Document
... A linking verb links its subject to a word in the predicate. The linking verbs include: be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being appear, become, feel, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, sound, taste Go back to home ...
... A linking verb links its subject to a word in the predicate. The linking verbs include: be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being appear, become, feel, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, sound, taste Go back to home ...
ComparativesSuperlatives
... 1. What case is X in? Why is X in this case? - Dative after persuadeo / verb of giving-showing-preparing-talking - Accusative after preposition taking accusative - Ablative after preposition taking ablative 2. Give the nominative singular of X. (= what is the basic form of this noun) 3. What gender ...
... 1. What case is X in? Why is X in this case? - Dative after persuadeo / verb of giving-showing-preparing-talking - Accusative after preposition taking accusative - Ablative after preposition taking ablative 2. Give the nominative singular of X. (= what is the basic form of this noun) 3. What gender ...
Verbs Part II - Ms. Kitchens` Corner
... Have you seen the cat’s ________________? On Friday all the _____________ quit their jobs. I do not believe those ____________. Otto __________food to the squirrels. ...
... Have you seen the cat’s ________________? On Friday all the _____________ quit their jobs. I do not believe those ____________. Otto __________food to the squirrels. ...
CEP 811: StAIR Project
... ADJECTIVES: WATCH THIS VIDEO! Click in the black box to start the video. ...
... ADJECTIVES: WATCH THIS VIDEO! Click in the black box to start the video. ...