Grammar and punctuation terminology for pupils PPTX File
... into a sentence to add more information. • A parenthesis can be placed in brackets or between dashes or commas. Arthur (the dog next door) often barks early in the morning. My son – second from the right - is running in the final at school. Frank, I think, sings brilliantly. • Parenthesis can refer ...
... into a sentence to add more information. • A parenthesis can be placed in brackets or between dashes or commas. Arthur (the dog next door) often barks early in the morning. My son – second from the right - is running in the final at school. Frank, I think, sings brilliantly. • Parenthesis can refer ...
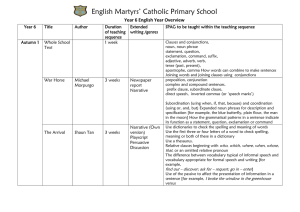
English Martyrs` Catholic Primary School Year 6 English Year
... Subordination (using when, if, that, because) and coordination (using or, and, but) Expanded noun phrases for description and specification [for example, the blue butterfly, plain flour, the man in the moon] How the grammatical patterns in a sentence indicate its function as a statement, question, e ...
... Subordination (using when, if, that, because) and coordination (using or, and, but) Expanded noun phrases for description and specification [for example, the blue butterfly, plain flour, the man in the moon] How the grammatical patterns in a sentence indicate its function as a statement, question, e ...
E155_Mtg9
... There, Their, They’re • There is an adverb meaning "that location." It is sometimes used with the verb to be as an idiom. It is spelled like here which means "this location." – I put the collar right there. (that location) – There are five prime numbers less than ten. (with to be) ...
... There, Their, They’re • There is an adverb meaning "that location." It is sometimes used with the verb to be as an idiom. It is spelled like here which means "this location." – I put the collar right there. (that location) – There are five prime numbers less than ten. (with to be) ...
(2) - cloudfront.net
... subject-verb order is inverted (backwards). Examples: • Will Dad take us to school tomorrow? • Have you completed all of your homework? • Will we walk to the store on Thursday? 4. Conditional: This verb mood indicates a conditional state that will cause something else to happen. Key words that are c ...
... subject-verb order is inverted (backwards). Examples: • Will Dad take us to school tomorrow? • Have you completed all of your homework? • Will we walk to the store on Thursday? 4. Conditional: This verb mood indicates a conditional state that will cause something else to happen. Key words that are c ...
Helping Verbs Primary helping verbs (3 verbs)
... to stand for a main verb in some constructions (He speaks faster than she does.) ...
... to stand for a main verb in some constructions (He speaks faster than she does.) ...
Noun Phrases - Amy Benjamin
... few introductory structures in sentences; between lower case and capitals lacking lead-in from one sentence to the next (lacking awareness of reader needs) ...
... few introductory structures in sentences; between lower case and capitals lacking lead-in from one sentence to the next (lacking awareness of reader needs) ...
MORE ON COMPLEMENTS
... object complements that are noun phrases. Here are some examples: A. Noun phrase subject complements after linking verbs. The man is an idiot. B. Noun phrase object complements – after the direct object of a noun. Often there is an implied “to be” linking these. The agent considered the man a total ...
... object complements that are noun phrases. Here are some examples: A. Noun phrase subject complements after linking verbs. The man is an idiot. B. Noun phrase object complements – after the direct object of a noun. Often there is an implied “to be” linking these. The agent considered the man a total ...
Making Subjects and Verbs Agree EXERCISES A. Underline the
... 2. Workers in the same occupations share stories. 3. People of the same region often share folklore. 4. Across each ethnic group, there is a common folklore. 5. Do students at your school have the same folklore? C. Add a prepositional phrase to each sentence. 1. Cinderella live long ago ____________ ...
... 2. Workers in the same occupations share stories. 3. People of the same region often share folklore. 4. Across each ethnic group, there is a common folklore. 5. Do students at your school have the same folklore? C. Add a prepositional phrase to each sentence. 1. Cinderella live long ago ____________ ...
man - St. Mary School
... A complete subject contains the simple subject and its modifiers. It does not include the verb. The simple subject tells who or what the sentence is about. A kind young man / helped the elderly woman across the street. The complete subject is “A kind young man” and the complete predicate is “helped ...
... A complete subject contains the simple subject and its modifiers. It does not include the verb. The simple subject tells who or what the sentence is about. A kind young man / helped the elderly woman across the street. The complete subject is “A kind young man” and the complete predicate is “helped ...
English grammar basics
... In a sentence, words which are used to describe nouns are called adjectives, and words which are used to describe verbs are called adverbs. If your sentence is (the increasingly complicated) “The sad milkman in the muddy road rapidly and excitedly sends the forgettable banana bread to Morocco.”, the ...
... In a sentence, words which are used to describe nouns are called adjectives, and words which are used to describe verbs are called adverbs. If your sentence is (the increasingly complicated) “The sad milkman in the muddy road rapidly and excitedly sends the forgettable banana bread to Morocco.”, the ...
4th Grade Language Curriculum
... 1. PREPOSITIONS - Common prepositions: about, above, across, after, against, along, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, near, of, off, on, onto, out, outside, over, past, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneat ...
... 1. PREPOSITIONS - Common prepositions: about, above, across, after, against, along, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, near, of, off, on, onto, out, outside, over, past, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneat ...
Active, Middle, and Passive: Understanding Ancient Greek Voice 1
... “middle” but “middle-passive” and indicative of the fact that the grammatical subject is entering into a state or condition or action either on his own initiative or in response to some external stimulus or cause or even spontaneously. In the case of this particular verb it is perhaps worth noting ...
... “middle” but “middle-passive” and indicative of the fact that the grammatical subject is entering into a state or condition or action either on his own initiative or in response to some external stimulus or cause or even spontaneously. In the case of this particular verb it is perhaps worth noting ...
"Painting with Participles" concept.
... (This is the best because instead of just adding participles, a participial phrase was added that gave us even more detail and description. This completed the image in the readers mind.) ...
... (This is the best because instead of just adding participles, a participial phrase was added that gave us even more detail and description. This completed the image in the readers mind.) ...
6. - DadTalk
... 5. I thought there was no rainbow, but, wow, there it is! 6. Yes, I’d love to go to the car show with you. 7. Aha! I thought I saw you creeping up on me. 8. Hey, aren’t you Marcy’s brother? 9. I forgot these boots have holes in them. Good grief! 10. Oh, no, the squirrel is in the birdfeeder again. X ...
... 5. I thought there was no rainbow, but, wow, there it is! 6. Yes, I’d love to go to the car show with you. 7. Aha! I thought I saw you creeping up on me. 8. Hey, aren’t you Marcy’s brother? 9. I forgot these boots have holes in them. Good grief! 10. Oh, no, the squirrel is in the birdfeeder again. X ...
What does an adjective do
... Look at the sentences. What word in (a) becomes “whom” in (b)? a. The students are hard-working. I teach them. b. The students [whom I teach] are hard-working. For people, use whom, who, or that. Which pronoun is the most formal? For things, use which or that. ...
... Look at the sentences. What word in (a) becomes “whom” in (b)? a. The students are hard-working. I teach them. b. The students [whom I teach] are hard-working. For people, use whom, who, or that. Which pronoun is the most formal? For things, use which or that. ...
Grammar Notebook Part One - cathyeagle
... – Passive Voice: The subject does not perform the verb but the verb happens to the subject • The slave is sold by Aurelia. Servus venditur ab Aurelia • The person or thing doing the verb goes into the ablative. – No preposition for things (means), “a, ab” for people (personal ...
... – Passive Voice: The subject does not perform the verb but the verb happens to the subject • The slave is sold by Aurelia. Servus venditur ab Aurelia • The person or thing doing the verb goes into the ablative. – No preposition for things (means), “a, ab” for people (personal ...
sentence analysis - FS: It works!
... 5. A gerund, a gerundial phrase, a gerundial construction. E.g. I like flying/flying by myself/them flying to London. 6. A syntactically indivisible group. E.g. I lost the tread and needle. 7. A quotation. E.g. He called “hello” several times. 8. A prepositional phrase with a noun or gerund. E.g. Do ...
... 5. A gerund, a gerundial phrase, a gerundial construction. E.g. I like flying/flying by myself/them flying to London. 6. A syntactically indivisible group. E.g. I lost the tread and needle. 7. A quotation. E.g. He called “hello” several times. 8. A prepositional phrase with a noun or gerund. E.g. Do ...
SUBJECT-VERB AGREEMENT Adapted from
... 4. Either my shoes or your coat IS always on the floor. 5. George and Tamara DON'T want to see that movie. 6. Benito DOESN'T know the answer. 7. One of my sisters IS GOING on a trip to France. 8. The man with all the birds LIVES on my street. 9. The movie, including all the previews, TAKES about two ...
... 4. Either my shoes or your coat IS always on the floor. 5. George and Tamara DON'T want to see that movie. 6. Benito DOESN'T know the answer. 7. One of my sisters IS GOING on a trip to France. 8. The man with all the birds LIVES on my street. 9. The movie, including all the previews, TAKES about two ...
Year 6 VGP Appendix - Parklands Primary School, Leeds
... Linking ideas across paragraphs using a wider range of cohesive devices: repetition of a word or phrase, grammatical connections [for example, the use of adverbials such as on the other hand, in contrast, or as a consequence], and ellipsis Layout devices [for example, headings, sub-headings, columns ...
... Linking ideas across paragraphs using a wider range of cohesive devices: repetition of a word or phrase, grammatical connections [for example, the use of adverbials such as on the other hand, in contrast, or as a consequence], and ellipsis Layout devices [for example, headings, sub-headings, columns ...
Verb Conjugation Powerpoint
... “to go” we have to conjugate it to make it fit with the subject of the sentence. Sometimes that means we add nothing to it. But sometimes we do add letters or change the word. • I go. You go. He goes. She goes. It goes. We go. Y’all go. They go. ...
... “to go” we have to conjugate it to make it fit with the subject of the sentence. Sometimes that means we add nothing to it. But sometimes we do add letters or change the word. • I go. You go. He goes. She goes. It goes. We go. Y’all go. They go. ...
Nouns
... an action, but says something about its subject linking verb — links, or joins, the subject to a word or words in the predicate. predicate nominative —the word following the linking verb that is in the predicate that renames the subject predicate adjective—the word following the linking verb that is ...
... an action, but says something about its subject linking verb — links, or joins, the subject to a word or words in the predicate. predicate nominative —the word following the linking verb that is in the predicate that renames the subject predicate adjective—the word following the linking verb that is ...
QuickGuidetoCommas
... clauses after nouns are always essential. That clauses following a verb expressing mental action are always essential. 5. Use commas to separate three or more words, phrases, or clauses written in a series. 6. Use commas to separate two or more coordinate adjectives that describe the same noun. Be s ...
... clauses after nouns are always essential. That clauses following a verb expressing mental action are always essential. 5. Use commas to separate three or more words, phrases, or clauses written in a series. 6. Use commas to separate two or more coordinate adjectives that describe the same noun. Be s ...
What is a phrase - Spokane Public Schools
... What is a phrase? A group of words WITHOUT a subject and its predicate that acts like a single part of speech. How do I know how a phrase is functioning? Phrases ...
... What is a phrase? A group of words WITHOUT a subject and its predicate that acts like a single part of speech. How do I know how a phrase is functioning? Phrases ...