Histones Differentially Modulate the Anticoagulant and
... family of glycosaminoglycans that accelerate antithrombinmediated inhibition of activated clotting factors [mainly thrombin and factor Xa (FXa)]. The family progenitor is unfractionated heparin (UFH), whereas low-molecular-weight heparins (LMWHs) are derived from the chemical or enzymatic depolymeri ...
... family of glycosaminoglycans that accelerate antithrombinmediated inhibition of activated clotting factors [mainly thrombin and factor Xa (FXa)]. The family progenitor is unfractionated heparin (UFH), whereas low-molecular-weight heparins (LMWHs) are derived from the chemical or enzymatic depolymeri ...
Mapping the Heparin-binding Sites on Type I Collagen Monomers
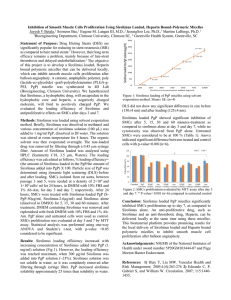
... migration patterns within ACE gels were obtained using a phosphorimager (Molecular Dynamics). From these electrophoretograms, the dissociation constant (Kd) Can be estimated from the protein concentration at which the heparin is half-shifted from being fully mobile at very low protein concentrations ...
... migration patterns within ACE gels were obtained using a phosphorimager (Molecular Dynamics). From these electrophoretograms, the dissociation constant (Kd) Can be estimated from the protein concentration at which the heparin is half-shifted from being fully mobile at very low protein concentrations ...
Inhibition of Smooth Muscle Cells Proliferation Using Sirolimus
... significantly popular for reducing in-stent restenosis (ISR) as compared to bare metal stents.1 However, their long term efficacy remains a problem, mainly because of late-stent thrombosis and delayed endothelialization.2 The objective of this project is to develop a Sirolimus loaded, Heparin bound ...
... significantly popular for reducing in-stent restenosis (ISR) as compared to bare metal stents.1 However, their long term efficacy remains a problem, mainly because of late-stent thrombosis and delayed endothelialization.2 The objective of this project is to develop a Sirolimus loaded, Heparin bound ...
Pharmacology of Hemostasis and Thrombosis
... Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to tissues and takes metabolic waste products away from tissues. Humans have developed a well-regulated system of hemostasis to keep the blood fluid and clot-free in normal vessels and to form a localized plug rapidly in injured vessels. Thrombosis describes a path ...
... Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to tissues and takes metabolic waste products away from tissues. Humans have developed a well-regulated system of hemostasis to keep the blood fluid and clot-free in normal vessels and to form a localized plug rapidly in injured vessels. Thrombosis describes a path ...
Reversal of Anticoagulants at UCDMC
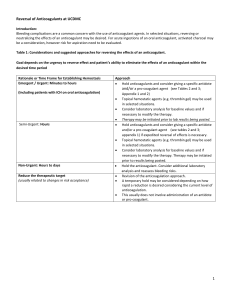
... If life threatening LMWH bleeding persists or significant renal impairment is present, a repeat dose of 0.5mg protamine per 100 anti-Xa units LMWH (~1mg Enoxaparin) can be considered. If bleeding persists in an eminent life threatening event, FEIBA 8 to 25 units/kg can be considered. ...
... If life threatening LMWH bleeding persists or significant renal impairment is present, a repeat dose of 0.5mg protamine per 100 anti-Xa units LMWH (~1mg Enoxaparin) can be considered. If bleeding persists in an eminent life threatening event, FEIBA 8 to 25 units/kg can be considered. ...
Media Kit - Perosphere Inc.
... drawn from healthy human volunteers. Plasma was immediately collected and spiked with rivaroxaban or apixaban at 1x and 2x the therapeutic Cmax. Factor Xa activity was measured before and after PER977 addition using a chromogenic anti-Xa kit (Hyphen-BioMed, France). PER977 completely reversed the an ...
... drawn from healthy human volunteers. Plasma was immediately collected and spiked with rivaroxaban or apixaban at 1x and 2x the therapeutic Cmax. Factor Xa activity was measured before and after PER977 addition using a chromogenic anti-Xa kit (Hyphen-BioMed, France). PER977 completely reversed the an ...
Theranostics Polysaccharide Nanosystems for Future Progress in
... player in coagulation process. At concentrations present in blood, antithrombin slowly inhibits blood clotting because it exists in a low reactivity state. When heparin binds to antithrombin, it induces a conformational change in the molecule which results in a greatly accelerated reaction with thro ...
... player in coagulation process. At concentrations present in blood, antithrombin slowly inhibits blood clotting because it exists in a low reactivity state. When heparin binds to antithrombin, it induces a conformational change in the molecule which results in a greatly accelerated reaction with thro ...
pharm chapter 22 [9-2
... initiated by tissue factor (lipoprotein expressed by activated leukocytes and microparticles derived from activated leukocytes) – tissue factor forms complex with factor VIIa, and complex activates factor IX, which leads to proteolytic cascade that results in generation of thrombin (factor IIa), a m ...
... initiated by tissue factor (lipoprotein expressed by activated leukocytes and microparticles derived from activated leukocytes) – tissue factor forms complex with factor VIIa, and complex activates factor IX, which leads to proteolytic cascade that results in generation of thrombin (factor IIa), a m ...
Clotting Factors
... Warfarin is a vitamin K antagonist and is administered orally. It blocks the function of the vitamin K dependent clotting factors (II, VII, IX, X). Thus large doses of Warfarin affects both the intrinsic and the extrinsic pathways. It takes 916 hours for Warfarin effects to show up in the blood afte ...
... Warfarin is a vitamin K antagonist and is administered orally. It blocks the function of the vitamin K dependent clotting factors (II, VII, IX, X). Thus large doses of Warfarin affects both the intrinsic and the extrinsic pathways. It takes 916 hours for Warfarin effects to show up in the blood afte ...
Media Kit - Perosphere
... drawn from healthy human volunteers. Plasma was immediately collected and spiked with rivaroxaban or apixaban at 1x and 2x the therapeutic Cmax. Factor Xa activity was measured before and after PER977 addition using a chromogenic anti-Xa kit (Hyphen-BioMed, France). PER977 completely reversed the an ...
... drawn from healthy human volunteers. Plasma was immediately collected and spiked with rivaroxaban or apixaban at 1x and 2x the therapeutic Cmax. Factor Xa activity was measured before and after PER977 addition using a chromogenic anti-Xa kit (Hyphen-BioMed, France). PER977 completely reversed the an ...
guidelines for antithrombin use at ucdmc
... D. Antithrombin is administered by intravenous infusion over 10-20 minutes. The drug should be administered within three hours of reconstitution. VI. ANTICOAGULATION THERAPY In patients with AT deficiency requiring anticoagulation therapy, indirect anticoagulants such as unfractionated heparin. low ...
... D. Antithrombin is administered by intravenous infusion over 10-20 minutes. The drug should be administered within three hours of reconstitution. VI. ANTICOAGULATION THERAPY In patients with AT deficiency requiring anticoagulation therapy, indirect anticoagulants such as unfractionated heparin. low ...
Therapeutic Interchange Program: H2 Receptor Antagonist TABLE
... complications/hemorrhage, consider use of protamine sulfate and/or blood products (fresh frozen plasma, platelets, etc.). ...
... complications/hemorrhage, consider use of protamine sulfate and/or blood products (fresh frozen plasma, platelets, etc.). ...
Anticoagulant Dosing Management
... For at least 24 hours before surgery or procedures for a low risk of bleeding or 48 hours for elective surgery or procedures with a moderate or high risk of clinically significant bleeding For mild to moderate bleeding consider prothrombin complex concentrate, 30-50 micrograms/kg Urgent or Emerg ...
... For at least 24 hours before surgery or procedures for a low risk of bleeding or 48 hours for elective surgery or procedures with a moderate or high risk of clinically significant bleeding For mild to moderate bleeding consider prothrombin complex concentrate, 30-50 micrograms/kg Urgent or Emerg ...
Pharmacotherapy of Angina Pectoris
... VIII. Agents that Prevent or Remove Thrombus A. Activators of antithrombin (also called antithrombin III) • Expose active sites on AT-III, OK in pregnancy • Increase rate of thrombin inactivation by antithrombin 1. Unfractionated Heparin (12,000-30,000MW) • highly-sulfated glycosaminoglycan, high -v ...
... VIII. Agents that Prevent or Remove Thrombus A. Activators of antithrombin (also called antithrombin III) • Expose active sites on AT-III, OK in pregnancy • Increase rate of thrombin inactivation by antithrombin 1. Unfractionated Heparin (12,000-30,000MW) • highly-sulfated glycosaminoglycan, high -v ...
Heparin by Wikipedia
... anticoagulant, preventing the formation of clots and extension of existing clots within the blood. While heparin does not break down clots that have already formed (unlike tissue plasminogen activator), it allows the body's natural clot lysis mechanisms to work normally to break down clots that have ...
... anticoagulant, preventing the formation of clots and extension of existing clots within the blood. While heparin does not break down clots that have already formed (unlike tissue plasminogen activator), it allows the body's natural clot lysis mechanisms to work normally to break down clots that have ...
Antithrombotic agents: Implications in dentistry ORAL MEDICINE
... and Homeostasis requested that all lots of thromboplastin have their international sensitivity index (ISI) indicated.6 The ISI establishes the reference standard of 1.0 based on human brain-derived thromboplastin. An ISI greater than 1.0 designates a less sensitive thromboplastin, whereas a value le ...
... and Homeostasis requested that all lots of thromboplastin have their international sensitivity index (ISI) indicated.6 The ISI establishes the reference standard of 1.0 based on human brain-derived thromboplastin. An ISI greater than 1.0 designates a less sensitive thromboplastin, whereas a value le ...
Rapid Reversal of Anticoagulation in Trauma Patients
... • • Atrial fibrillation • • Deep vein thrombosis • • Mechanical heart valves • • Stroke prevention ...
... • • Atrial fibrillation • • Deep vein thrombosis • • Mechanical heart valves • • Stroke prevention ...
VEGF exists in different isoforms
... Different models of Morphogen Action a) Morphogen Diffusion b) Morphogen inhibitor diffusion c) Cytoneme function a) Close physical interaction b) Cytoplasmic diffusion. ...
... Different models of Morphogen Action a) Morphogen Diffusion b) Morphogen inhibitor diffusion c) Cytoneme function a) Close physical interaction b) Cytoplasmic diffusion. ...
Intentional low-molecular-weight heparin overdose: a case report
... similar to that of our patient. Due to incomplete reversal with protamine, rFVIIa has been used in a small number of patients. Three patients, all with known underlying hypercoagulable disorders, developed bleeding while on LMWH. In all three cases, the patients were treated with rFVIIa with reporte ...
... similar to that of our patient. Due to incomplete reversal with protamine, rFVIIa has been used in a small number of patients. Three patients, all with known underlying hypercoagulable disorders, developed bleeding while on LMWH. In all three cases, the patients were treated with rFVIIa with reporte ...
DVT and PE Pharmacotherapy Teaching Slides
... (Grade 1A) • longer duration of UFH or LMWH if massive PE • Should overlap with warfarin for at least 4-5 days. – D/C after 2 consecutive days of therapeutic INR ...
... (Grade 1A) • longer duration of UFH or LMWH if massive PE • Should overlap with warfarin for at least 4-5 days. – D/C after 2 consecutive days of therapeutic INR ...
coagulation final 2
... Heparin: variable anticoagulant effect • Variable protein binding • Clearance varies with chain length • Therefore, anticoagulant response monitored by activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) • Target 1.5 – 2.5 times control ...
... Heparin: variable anticoagulant effect • Variable protein binding • Clearance varies with chain length • Therefore, anticoagulant response monitored by activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) • Target 1.5 – 2.5 times control ...
Coagulation
... - antithrombin III inhibits clotting factor proteases, Thrombin (IIa), IXa, Xa, XIa and XIIa, by forming stable complexes - heparin binds to AT-III and causes a conformational change thereby activating AT-III ...
... - antithrombin III inhibits clotting factor proteases, Thrombin (IIa), IXa, Xa, XIa and XIIa, by forming stable complexes - heparin binds to AT-III and causes a conformational change thereby activating AT-III ...
Disorders of Hemostasis Hereditary Disorders of Hemostasis Von
... Heparin should be stopped at least 6 hours before surgery, and restarted about 12 hours after surgery. ...
... Heparin should be stopped at least 6 hours before surgery, and restarted about 12 hours after surgery. ...
Heparin

Heparin (from Ancient Greek ἧπαρ (hêpar), ""liver""), a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is widely used as an injectable anticoagulant, and has the highest negative charge density of any known biological molecule. It can also be used to form an inner anticoagulant surface on various experimental and medical devices such as test tubes and renal dialysis machines.Although it is used principally in medicine for anticoagulation, its true physiological role in the body remains unclear, because blood anticoagulation is achieved mostly by heparan sulfate proteoglycans derived from endothelial cells. Heparin is usually stored within the secretory granules of mast cells and released only into the vasculature at sites of tissue injury. It has been proposed that, rather than anticoagulation, the main purpose of heparin is defense at such sites against invading bacteria and other foreign materials. In addition, it is observed across a number of widely different species, including some invertebrates that do not have a similar blood coagulation system.In nature, heparin is a polymer of varying chain size. Unfractionated heparin as a pharmaceutical is heparin that has not been fractionated to sequester the fraction of molecules with low molecular weight. In contrast, low-molecular-weight heparin has undergone fractionation for the purpose of making its pharmacodynamics more predictable.Heparin is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, a list of the most important medications needed in a basic health system.