Basic Microwave Measurements
... Transmission lines carry microwave signals from one point to another They are important because the wavelength is much smaller than the length of typical T-lines used in the lab You have to look at them as distributed circuits, rather than lumped circuits ...
... Transmission lines carry microwave signals from one point to another They are important because the wavelength is much smaller than the length of typical T-lines used in the lab You have to look at them as distributed circuits, rather than lumped circuits ...
example abstract
... Transformer is a static electrical device that alternates the voltage applied to one of its coils through electromagnetic induction, thus enabling us to obtain different voltage and current values at the same frequency and power from the other coils. Transformers are widely used in energy transmissi ...
... Transformer is a static electrical device that alternates the voltage applied to one of its coils through electromagnetic induction, thus enabling us to obtain different voltage and current values at the same frequency and power from the other coils. Transformers are widely used in energy transmissi ...
Pax Presentation
... is rapidly growing and numerous papers on the method and technology are presented at international conferences 2004; CIGRE report 254, ”Dielectric Response Methods for Diagnostics of Power Transformers” is published 2006; Project REDIATOOL reported at CIGRE, recommending DFR as a preferred method fo ...
... is rapidly growing and numerous papers on the method and technology are presented at international conferences 2004; CIGRE report 254, ”Dielectric Response Methods for Diagnostics of Power Transformers” is published 2006; Project REDIATOOL reported at CIGRE, recommending DFR as a preferred method fo ...
Frequency response I
... Frequency response I • As the frequency of the processed signals increases, the effects of parasitic capacitance in (BJT/MOS) transistors start to manifest • The gain of the amplifier circuits is frequency dependent, usually decrease with the frequency increase of the input signals • Computing by ha ...
... Frequency response I • As the frequency of the processed signals increases, the effects of parasitic capacitance in (BJT/MOS) transistors start to manifest • The gain of the amplifier circuits is frequency dependent, usually decrease with the frequency increase of the input signals • Computing by ha ...
resonance experiment
... and –1.5. The quality factor was 10.8 for R1 33 ohms and 2.3 for R1 330 ohms. The circuit behaved as expected. ...
... and –1.5. The quality factor was 10.8 for R1 33 ohms and 2.3 for R1 330 ohms. The circuit behaved as expected. ...
CircuitI_exp071411496961
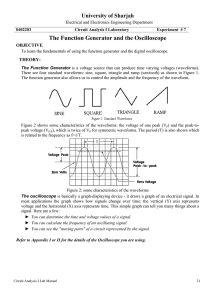
... Figure 2: some characteristics of the waveforms The oscilloscope is basically a graph-displaying device - it draws a graph of an electrical signal. In most applications the graph shows how signals change over time: the vertical (Y) axis represents voltage and the horizontal (X) axis represents time. ...
... Figure 2: some characteristics of the waveforms The oscilloscope is basically a graph-displaying device - it draws a graph of an electrical signal. In most applications the graph shows how signals change over time: the vertical (Y) axis represents voltage and the horizontal (X) axis represents time. ...
Free research poster template
... because the proposed compensating inverter did not complete transition when the node is flipped back by the main driver. As a consequence, the frequency of a ring oscillator with the proposed compensator can operate at higher frequency. The smaller the compensator is, the faster the speed is, if it ...
... because the proposed compensating inverter did not complete transition when the node is flipped back by the main driver. As a consequence, the frequency of a ring oscillator with the proposed compensator can operate at higher frequency. The smaller the compensator is, the faster the speed is, if it ...
******* 1
... There is also a sample rate – multi vibrate , which can be adjusted by front panel , controlling rate from few cycles per second , to as high as 1000 ‘cycle per sec’ and grater . ...
... There is also a sample rate – multi vibrate , which can be adjusted by front panel , controlling rate from few cycles per second , to as high as 1000 ‘cycle per sec’ and grater . ...
Technician Licensing Class - Department of Electrical, Computer
... A. All transceivers use the same microphone connector type B. Some connectors include push-to-talk and voltages for powering the microphone C. All transceivers using the same connector type are wired identically D. Un-keyed connectors allow any microphone to be connected ...
... A. All transceivers use the same microphone connector type B. Some connectors include push-to-talk and voltages for powering the microphone C. All transceivers using the same connector type are wired identically D. Un-keyed connectors allow any microphone to be connected ...
Utility frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in an electric power grid transmitted from a power plant to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains power around the world.During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one over the other and no apparent desire for complete worldwide standardization.Unless specified by the manufacturer to operate on both 50 and 60 Hz, appliances may not operate efficiently or even safely if used on anything other than the intended frequency.