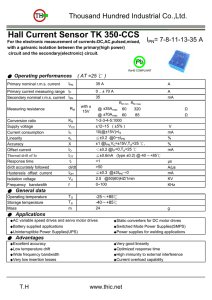
김 해 천
... System calls for device-specific input/output operations (ioctl) have a low overhead and are easily extensible using the request code parameter. The interface of the TURBO driver (trb) is based on ioctl, while the Linux MSR driver (msr) uses a file-based interface that can be accessed most efficien ...
... System calls for device-specific input/output operations (ioctl) have a low overhead and are easily extensible using the request code parameter. The interface of the TURBO driver (trb) is based on ioctl, while the Linux MSR driver (msr) uses a file-based interface that can be accessed most efficien ...
Line filter, SK HLD 110
... Only qualified electricians are allowed to install and commission the module. An electrician is a person who, because of their technical training and experience, has sufficient knowledge with regard to ...
... Only qualified electricians are allowed to install and commission the module. An electrician is a person who, because of their technical training and experience, has sufficient knowledge with regard to ...
EE311: Junior EE Lab Phase Locked Loop
... 3. With the input signal on oscilloscope channel 1, and the VCO signal on oscilloscope channel 2, describe the expected traces when (a) the PLL is in locked mode and (b) the PLL is in the unlocked mode. Assume that the oscilloscope is triggered from the channel 1 signal. 4. Compute a value for C1 th ...
... 3. With the input signal on oscilloscope channel 1, and the VCO signal on oscilloscope channel 2, describe the expected traces when (a) the PLL is in locked mode and (b) the PLL is in the unlocked mode. Assume that the oscilloscope is triggered from the channel 1 signal. 4. Compute a value for C1 th ...
Electromagnetic compatibility consideration and
... band allocated for communications, or if these switching frequencies are close to possible network resonance points. • Always consider harmonic resonance, even when applying small power rated equipment with power electronics. High harmonic order resonances can be especially troublesome, because of s ...
... band allocated for communications, or if these switching frequencies are close to possible network resonance points. • Always consider harmonic resonance, even when applying small power rated equipment with power electronics. High harmonic order resonances can be especially troublesome, because of s ...
UMZ-837-D16-G 数据资料DataSheet下载
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
MTS-4A - Meyer Sound
... surge suppression and dual circuit breakers. The dual-fan cooling system forces air over the heatsinks only, not over the electronics, avoiding residue buildup that can shorten component life. All four amplifier channels operate class AB/H and employ complementary power MOSFET output stages. For max ...
... surge suppression and dual circuit breakers. The dual-fan cooling system forces air over the heatsinks only, not over the electronics, avoiding residue buildup that can shorten component life. All four amplifier channels operate class AB/H and employ complementary power MOSFET output stages. For max ...
Utility frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in an electric power grid transmitted from a power plant to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains power around the world.During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one over the other and no apparent desire for complete worldwide standardization.Unless specified by the manufacturer to operate on both 50 and 60 Hz, appliances may not operate efficiently or even safely if used on anything other than the intended frequency.







![Shrink wrapping machines [Wrapping machines]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007801888_1-84776953c7681328cc8dd8cfe7cb0bc2-300x300.png)