A. M. Zayed1 BENEFICIATION OF AKTAS QUARTZ DEPOSITS
... The demand for the raw material quartz is increasing worldwide, in particular, the demand for high-purity quartz (HPQ; e.g. [1,2]). Therefore, quartz has been recently considered as a strategic mineral because it represents the raw material for special applications in high-tech industry. The trace-e ...
... The demand for the raw material quartz is increasing worldwide, in particular, the demand for high-purity quartz (HPQ; e.g. [1,2]). Therefore, quartz has been recently considered as a strategic mineral because it represents the raw material for special applications in high-tech industry. The trace-e ...
Geological Survey of Finland
... Extensive primary halos are associated with the porphyry-type occurrences in southern Finland. The halo patterns are variable in shape, size and associated elements in and around each occurrence, depending on local conditions, but the halos exhibit a general zoning towards the core: Zn( ± Pb) - Au( ...
... Extensive primary halos are associated with the porphyry-type occurrences in southern Finland. The halo patterns are variable in shape, size and associated elements in and around each occurrence, depending on local conditions, but the halos exhibit a general zoning towards the core: Zn( ± Pb) - Au( ...
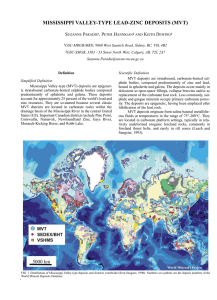
and limestone- hosted Zn-Pb-Ag-(Cu-Au)
... stratified felsic volcanic rocks with abundant limestone interbeds and ore deposits, in turn overlain by argillite-turbidite sedimentary rocks. This cycle has been attributed to a first order volcanotectonic evolution from intense volcanism and crustal extension, through waning volcanism and continu ...
... stratified felsic volcanic rocks with abundant limestone interbeds and ore deposits, in turn overlain by argillite-turbidite sedimentary rocks. This cycle has been attributed to a first order volcanotectonic evolution from intense volcanism and crustal extension, through waning volcanism and continu ...
Sillitoe Hedenquist Linkages between volcanotectonic settings Soc
... deposits. Low-sulfidation deposits genetically linked to bimodal volcanism are formed from extremely dilute fluids, whereas modestly saline contributions account for the low-sulfidation deposits in alkaline centers. Early lithocap-forming and high-sulfidation fluids, as well as low-sulfidation fluid ...
... deposits. Low-sulfidation deposits genetically linked to bimodal volcanism are formed from extremely dilute fluids, whereas modestly saline contributions account for the low-sulfidation deposits in alkaline centers. Early lithocap-forming and high-sulfidation fluids, as well as low-sulfidation fluid ...
Figs 3.4 - Geoscience Australia
... of the Northern Territory could have been derived from a carbonatite or alkaline magmatic source at depth that has so far not been recognised in geophysical surveys. Alkaline rock complexes with REE resources feature in the Halls Creek Orogen (Brockman) and in the Tasman Orogen (Toongi, Narraburra) ...
... of the Northern Territory could have been derived from a carbonatite or alkaline magmatic source at depth that has so far not been recognised in geophysical surveys. Alkaline rock complexes with REE resources feature in the Halls Creek Orogen (Brockman) and in the Tasman Orogen (Toongi, Narraburra) ...
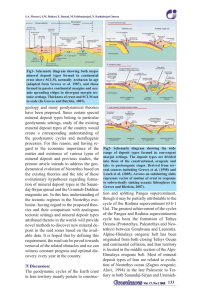
mississippi valley-type lead-zinc deposits (mvt)
... Summary of Economic Characteristics MVT deposits account for approximately 25 percent of the world's lead and zinc resources, and they are dispersed throughout the world (Fig. 1). A large proportion of Pb and Zn production comes from several classic MVT districts located in the drainage basin of the ...
... Summary of Economic Characteristics MVT deposits account for approximately 25 percent of the world's lead and zinc resources, and they are dispersed throughout the world (Fig. 1). A large proportion of Pb and Zn production comes from several classic MVT districts located in the drainage basin of the ...
Revisitied - New Mexico Geological Society
... basalt, turquoise, malachite, azurite, and possibly fluorite for ornaments and stone tools. The major types of deposits in the Zuni Mountains include 1) veins and replacements in Proterozoic rocks, 2) stratabound, sedimentary-copper deposits, and 3) fluorite veins, although 4) REE (rare earth elemen ...
... basalt, turquoise, malachite, azurite, and possibly fluorite for ornaments and stone tools. The major types of deposits in the Zuni Mountains include 1) veins and replacements in Proterozoic rocks, 2) stratabound, sedimentary-copper deposits, and 3) fluorite veins, although 4) REE (rare earth elemen ...
AZTEC QUADRANGLE NEW MEXICO AND COLORADO
... process disclosed in this report, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference therein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommenda ...
... process disclosed in this report, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference therein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommenda ...
the basic mineralogic, paragenetic and genetic
... Volcanic-sedimentary sulphide minerals weie precipitated contemporaneously with the host rocks, notably with rhyolitic or rhyodacitic pyroclasts, whereas the second-phase minerals in this type of deposits were segregated under hydrothermal conditions, but within the host rocks. These hydrothermal su ...
... Volcanic-sedimentary sulphide minerals weie precipitated contemporaneously with the host rocks, notably with rhyolitic or rhyodacitic pyroclasts, whereas the second-phase minerals in this type of deposits were segregated under hydrothermal conditions, but within the host rocks. These hydrothermal su ...
投影片 1
... The mineralizing fluids are conducted upwards within sedimentary units toward basin-bounding faults. The fluids move upwards due to thermal ascent and pressure of the underlying reservoir. Faults which host the hydrothermal flow can show evidence of this flow due to development of massive sulfide ve ...
... The mineralizing fluids are conducted upwards within sedimentary units toward basin-bounding faults. The fluids move upwards due to thermal ascent and pressure of the underlying reservoir. Faults which host the hydrothermal flow can show evidence of this flow due to development of massive sulfide ve ...
Vol. 17. No.1 2008
... sedimentary deposits in passive continental margins (e.g. beach sand deposits and MVT), sedimentary deposits such as Mn deposits, Banded Iron Formation (BIF) and all magmatic deposits including podifrom magmatic chromites and volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. Since preservation of these mineral ...
... sedimentary deposits in passive continental margins (e.g. beach sand deposits and MVT), sedimentary deposits such as Mn deposits, Banded Iron Formation (BIF) and all magmatic deposits including podifrom magmatic chromites and volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. Since preservation of these mineral ...
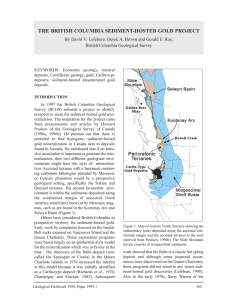
the british columbia sediment-hosted gold project
... In 1997 the British Columbia Geological Survey (BCGS) initiated a project to identify prospective areas for sediment-hosted gold mineralization. The inspiration for the project came from presentations and articles by Howard Poulsen of the Geological Survey of Canada (1996a, 1996b). He pointed out th ...
... In 1997 the British Columbia Geological Survey (BCGS) initiated a project to identify prospective areas for sediment-hosted gold mineralization. The inspiration for the project came from presentations and articles by Howard Poulsen of the Geological Survey of Canada (1996a, 1996b). He pointed out th ...
Rare earth elements in Québec, Canada: Main deposit
... Rare earth elements (REE) are strategic metals vital to global economic growth because they are used in a wide range of high-technology industries (e.g., energy, transport, and telecommunications; Walters et al., 2011). The world production and reserves are mainly owned by China. In 2008, the Chines ...
... Rare earth elements (REE) are strategic metals vital to global economic growth because they are used in a wide range of high-technology industries (e.g., energy, transport, and telecommunications; Walters et al., 2011). The world production and reserves are mainly owned by China. In 2008, the Chines ...
Exploring for molybdenum in Quebec
... Rift-type porphyry Mo deposits Rift-type porphyry Mo deposits constitute a relatively well- understood deposit type in terms of their characteristics and genetic model. Deposits of this type are clearly associated with highly differentiated intrusions (more than 75% SiO2), are rich in fluorine, and ...
... Rift-type porphyry Mo deposits Rift-type porphyry Mo deposits constitute a relatively well- understood deposit type in terms of their characteristics and genetic model. Deposits of this type are clearly associated with highly differentiated intrusions (more than 75% SiO2), are rich in fluorine, and ...
Gold Deposits and Their Geological Classification
... stratiform layers (bankets) of auriferous quartz-pebble conglomerate, pebbly quartz arenite and cross-bedded arenite, with gold locally enriched in thin carbonaceous seams. The deposits occur in mature fluviatile to deltaic facies rocks in extensive cratonic sedimentary basins. The most significant ...
... stratiform layers (bankets) of auriferous quartz-pebble conglomerate, pebbly quartz arenite and cross-bedded arenite, with gold locally enriched in thin carbonaceous seams. The deposits occur in mature fluviatile to deltaic facies rocks in extensive cratonic sedimentary basins. The most significant ...
(VMS) Deposits - Department of Natural Resources
... nearly 100% sulphides within volcanic host rocks. Pyrite is generally the most abundant sulphide, though many non-Newfoundland deposits contain significant pyrrhotite. The base metals zinc (from sphalerite) and copper (from chalcopyrite) are the two most important commodities produced from most VMS ...
... nearly 100% sulphides within volcanic host rocks. Pyrite is generally the most abundant sulphide, though many non-Newfoundland deposits contain significant pyrrhotite. The base metals zinc (from sphalerite) and copper (from chalcopyrite) are the two most important commodities produced from most VMS ...
PDF
... minerals a.a. The deposits of this type are of particular importance in Banat, Romania (Ianovici and Borcos, 1982 see also Jenchenoaeva 1997 this issue). 2. Pornhyry copper deposits: several major porphyry copper deposits have been discovered since 1950 in the Carpatho-Balkanides (Majdanpek a.a. in ...
... minerals a.a. The deposits of this type are of particular importance in Banat, Romania (Ianovici and Borcos, 1982 see also Jenchenoaeva 1997 this issue). 2. Pornhyry copper deposits: several major porphyry copper deposits have been discovered since 1950 in the Carpatho-Balkanides (Majdanpek a.a. in ...
Sedimentary Phosphate Deposits Mineral Deposit Profile F07
... frequency through time. Individual phosphorite deposits delimited by drilling may measure from a few hundreds of metres to tens of kilometres in their longest dimension. Phosphorite deposits commonly occur in belts. TEXTURE / STRUCTURE ...
... frequency through time. Individual phosphorite deposits delimited by drilling may measure from a few hundreds of metres to tens of kilometres in their longest dimension. Phosphorite deposits commonly occur in belts. TEXTURE / STRUCTURE ...
ES3210 - Gold Deposits
... Ore deposition provoked by marked changes in physicochemical conditions of ore-forming fluids over short distances (meter scale) ...
... Ore deposition provoked by marked changes in physicochemical conditions of ore-forming fluids over short distances (meter scale) ...
ARSENIDE VEIN SILVER, URANIUM
... thickness from a few centimetres to two or three decimetres. The metallic minerals occur in irregular lenses of high grade ore surrounded by aureoles of low grade material (Fig. 14.1-4). Arsenides, sulpharsenides, and antimonides of nickel, cobalt, and iron in various proportions, as well as ...
... thickness from a few centimetres to two or three decimetres. The metallic minerals occur in irregular lenses of high grade ore surrounded by aureoles of low grade material (Fig. 14.1-4). Arsenides, sulpharsenides, and antimonides of nickel, cobalt, and iron in various proportions, as well as ...
Structural and biological control of the Cenozoic epithermal uranium
... ignimbritic rocks in this area are highly fractured, kaolinized, and silicified. Voids and fractures are commonly lined with iron oxides, especially at the vicinity of sulfide-rich silicified bodies (Fig. 3f). Uranium is not only found in brecciated zone but also disseminated in the volcanic groundm ...
... ignimbritic rocks in this area are highly fractured, kaolinized, and silicified. Voids and fractures are commonly lined with iron oxides, especially at the vicinity of sulfide-rich silicified bodies (Fig. 3f). Uranium is not only found in brecciated zone but also disseminated in the volcanic groundm ...
Mapping of Structurally Controlled Uranium Mineralization in
... uranium (Fig. 8), except in the part that has less alkalinity in the center of the pluton. Over the whole batholith, both K and U increase northwards. The potassium contents range between 2 and 5% (Fig. 8). Secondary potassic alteration zones in the northern part of the pluton are suggested by low t ...
... uranium (Fig. 8), except in the part that has less alkalinity in the center of the pluton. Over the whole batholith, both K and U increase northwards. The potassium contents range between 2 and 5% (Fig. 8). Secondary potassic alteration zones in the northern part of the pluton are suggested by low t ...
Uranium in the Niger-Nigeria Younger Granite Province
... FIG. 1. Arlit uranium pit showing overlying Permian Izegouande arkosic sandstone (upper 3 levels) resting unconformably on lower Carboniferous shales and sandstones. There is a thin series of finely bedded shales and siltstones forming a barren horizon above the deltaic carbonaceous sandstones in wh ...
... FIG. 1. Arlit uranium pit showing overlying Permian Izegouande arkosic sandstone (upper 3 levels) resting unconformably on lower Carboniferous shales and sandstones. There is a thin series of finely bedded shales and siltstones forming a barren horizon above the deltaic carbonaceous sandstones in wh ...
EPITHERMAL Au
... AGE OF MINERALIZATION: Any age. Tertiary deposits are most abundant; in B.C. Jurassic deposits are important. Deposits of Paleozoic age are described in Australia. Closely related to the host volcanic rocks but invariably slightly younger in age (0.5 to 1 Ma, more or less). HOST/ASSOCIATED ROCK TYPE ...
... AGE OF MINERALIZATION: Any age. Tertiary deposits are most abundant; in B.C. Jurassic deposits are important. Deposits of Paleozoic age are described in Australia. Closely related to the host volcanic rocks but invariably slightly younger in age (0.5 to 1 Ma, more or less). HOST/ASSOCIATED ROCK TYPE ...
12 ABSTRACT Uranium is one of the most abundant element found
... The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA, 1996) assigns uranium deposits to 15 main categories of deposit types, according to their geological setting and genesis of mineralization, arranged according to their approximate economic significance. 1. Unconformity-related deposits ...
... The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA, 1996) assigns uranium deposits to 15 main categories of deposit types, according to their geological setting and genesis of mineralization, arranged according to their approximate economic significance. 1. Unconformity-related deposits ...
Uranium ore
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within the Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the more common elements in the Earth's crust, some 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than gold. It can be found almost everywhere in rock, soil, rivers, and oceans. The challenge is to find those areas where the concentrations are adequate to form an economically viable deposit.Globally, the distribution of uranium ore deposits is widespread on all continents, with the largest deposits found in Australia, Kazakhstan, and Canada. To date, high-grade deposits are only found in the Athabasca Basin region of Canada.Uranium deposits are generally classified based on host rocks, structural setting, and mineralogy of the deposit. The most widely used classification scheme was developed by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and subdivides deposits into 15 categories.