Pituitary Disease
... Short- Regular What is a name of an “intermediate acting” insulin? Intermediate- NPH and Lente What is a name of a “long acting” insulin? ...
... Short- Regular What is a name of an “intermediate acting” insulin? Intermediate- NPH and Lente What is a name of a “long acting” insulin? ...
Calcium Homeostasis(1)
... a) Pancreatic hormones -The endocrine cells of the pancreas are present in discrete groups called ‘islets of Langerhan’s’, which are more numerous in the tail than in the body and comprise 1-2% of ...
... a) Pancreatic hormones -The endocrine cells of the pancreas are present in discrete groups called ‘islets of Langerhan’s’, which are more numerous in the tail than in the body and comprise 1-2% of ...
Sickle Cell Disease
... Beta cells- type of cell found in the Islets of Langerhans within the pancreas that make and release insulin. Insulin is a hormone required to move the glucose into cells throughout the body. If no insulin can be produced, the glucose stays in the blood instead, where it can cause serious damage ...
... Beta cells- type of cell found in the Islets of Langerhans within the pancreas that make and release insulin. Insulin is a hormone required to move the glucose into cells throughout the body. If no insulin can be produced, the glucose stays in the blood instead, where it can cause serious damage ...
GLIPIZIDE TABLETS, USP 5 mg and 10 mg Rx Only
... elimination ranges from 2 to 4 hours in normal subjects, whether given intravenously or orally. The metabolic and excretory patterns are similar with the two routes of administration, indicating that first-pass metabolism is not significant. Glipizide does not accumulate in plasma on repeated oral a ...
... elimination ranges from 2 to 4 hours in normal subjects, whether given intravenously or orally. The metabolic and excretory patterns are similar with the two routes of administration, indicating that first-pass metabolism is not significant. Glipizide does not accumulate in plasma on repeated oral a ...
The Adrenomedullary and Glucagon Responses of
... hormone-deficient children compared to a 12- to 13-fold increase in the control and growth hormone-deficient groups. The increments for both groups fall within the range reported in healthy children (5- to 20-fold increase in E). (2). We had expected that ACTH deficiency in children would result in ...
... hormone-deficient children compared to a 12- to 13-fold increase in the control and growth hormone-deficient groups. The increments for both groups fall within the range reported in healthy children (5- to 20-fold increase in E). (2). We had expected that ACTH deficiency in children would result in ...
PowerPoint Slides
... Neurons don’t require insulin, are exposed to high intracellular glucose: – peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy ...
... Neurons don’t require insulin, are exposed to high intracellular glucose: – peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy ...
Growth Hormone Deficiency
... measurements in U.S. children. Pediatric growth charts have been used by pediatricians, nurses, and parents to track the growth of infants, children, and adolescents in the United States since 1977. The 1977 growth charts were developed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) as a clinic ...
... measurements in U.S. children. Pediatric growth charts have been used by pediatricians, nurses, and parents to track the growth of infants, children, and adolescents in the United States since 1977. The 1977 growth charts were developed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) as a clinic ...
How Much Cortisol Do We Need? Chronic Secondary
... Hypopituitarism often results from pituitary or hypothalamic tumor or treatment of the tumor [1]. Other less common causes like infiltrative diseases (Sarcoidosis, hemochromatosis, histiocytosis) [2-4] Sheehan’s syndrome [1], inflammation, infection, head trauma [5-7] and genetic mutations have been ...
... Hypopituitarism often results from pituitary or hypothalamic tumor or treatment of the tumor [1]. Other less common causes like infiltrative diseases (Sarcoidosis, hemochromatosis, histiocytosis) [2-4] Sheehan’s syndrome [1], inflammation, infection, head trauma [5-7] and genetic mutations have been ...
Topics1
... • Glycemic targets and treatments to lower glucose must be individualized according to specific patient characteristics. • The mainstay of any type 2 diabetes treatment program is still diet, exercise, and education. • Metformin is the preferred first-line drug, in the absence of contraindications. ...
... • Glycemic targets and treatments to lower glucose must be individualized according to specific patient characteristics. • The mainstay of any type 2 diabetes treatment program is still diet, exercise, and education. • Metformin is the preferred first-line drug, in the absence of contraindications. ...
Clinical Biochemistry Department GLUCAGON STIMULATION TEST
... Sex Steroid priming In children over 11 years of age or with a bone age of greater than 10 years Stilbestrol should be given (1.0mg b.d.) for 48 hours prior to the test. If necessary, the GH provocation test may need to be rebooked and Primoteston (125mg i.m.) given 5 days before the test. PRECAUTIO ...
... Sex Steroid priming In children over 11 years of age or with a bone age of greater than 10 years Stilbestrol should be given (1.0mg b.d.) for 48 hours prior to the test. If necessary, the GH provocation test may need to be rebooked and Primoteston (125mg i.m.) given 5 days before the test. PRECAUTIO ...
Text Version
... Neurons don’t require insulin, are exposed to high intracellular glucose: – peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy ...
... Neurons don’t require insulin, are exposed to high intracellular glucose: – peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy ...
Diabetes Mellitus
... is important with both cats and dogs. For dogs, this generally means a high-fiber, low-fat diet for controlled release of sugars. For cats, low-carbohydrate, high-protein/fat diets are recommended. Rarely, certain cats can be managed with oral medications and diet alone. What sort of long-term monit ...
... is important with both cats and dogs. For dogs, this generally means a high-fiber, low-fat diet for controlled release of sugars. For cats, low-carbohydrate, high-protein/fat diets are recommended. Rarely, certain cats can be managed with oral medications and diet alone. What sort of long-term monit ...
A chief of endocrinology department, prof. Vlasenko MV
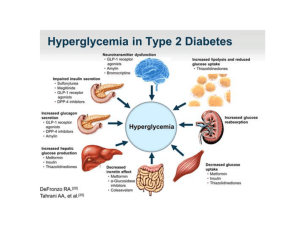
... diet. (Obesity leads to insensitivity of muscle and adipose tissue to insulin, presumable as the result of decreased binding of insulin to its plasma membrane receptor. Hyperglycemia is the face of increased insulin secretion and hyperlipoproteinemia are secondary to this abnormality. The defect in ...
... diet. (Obesity leads to insensitivity of muscle and adipose tissue to insulin, presumable as the result of decreased binding of insulin to its plasma membrane receptor. Hyperglycemia is the face of increased insulin secretion and hyperlipoproteinemia are secondary to this abnormality. The defect in ...
IntroToDMWUinSTLDiabRsrch - 2013-08-05 COLOR
... glucose clearance into insulin-sensitive tissues (e.g., muscle) hyperglycemia. ...
... glucose clearance into insulin-sensitive tissues (e.g., muscle) hyperglycemia. ...
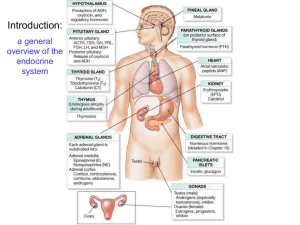
The Endocrine System
... Insulin Promotes Anabolism Insulin lowers plasma glucose by: 1. Increasing glucose transport into most insulin sensitive cells 2. Enhancing cellular utilization and storage of glucose 3. Enhancing utilization of amino acids 4. Promoting fat synthesis ...
... Insulin Promotes Anabolism Insulin lowers plasma glucose by: 1. Increasing glucose transport into most insulin sensitive cells 2. Enhancing cellular utilization and storage of glucose 3. Enhancing utilization of amino acids 4. Promoting fat synthesis ...
Metabolic Changes in DM
... A1C cut-off point of >6.5 % is used to diagnose diabetes. A1C values also correlate with the prevalence of retinopathy Assays for A1C has to be standardized according to the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program (NGSP). ...
... A1C cut-off point of >6.5 % is used to diagnose diabetes. A1C values also correlate with the prevalence of retinopathy Assays for A1C has to be standardized according to the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program (NGSP). ...
Type 2 Diabetes Management Goals
... Signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia Dietary education for improved glycemic control and appreciation of triggers for hypoglycemia Avoiding missed or delayed meals Appropriate self-treatment Understanding of hypoglycemia unawareness Importance of reporting hypoglycemia ...
... Signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia Dietary education for improved glycemic control and appreciation of triggers for hypoglycemia Avoiding missed or delayed meals Appropriate self-treatment Understanding of hypoglycemia unawareness Importance of reporting hypoglycemia ...
glucose
... because the tissues are unable to access the glucose • death occurs shortly after onset unless given injections of insulin ...
... because the tissues are unable to access the glucose • death occurs shortly after onset unless given injections of insulin ...
Control of blood glucose
... 1. Homeostasis of blood glucose (insulin and glucagon, diabetes) 2. Homeostasis of basal metabolic rate (thyroid hormone, goitre and brain development) 3. Homeostasis of appetite (leptin hormone, obesity and OB gene mutations) 4. Management of growth (growth hormone and ...
... 1. Homeostasis of blood glucose (insulin and glucagon, diabetes) 2. Homeostasis of basal metabolic rate (thyroid hormone, goitre and brain development) 3. Homeostasis of appetite (leptin hormone, obesity and OB gene mutations) 4. Management of growth (growth hormone and ...
Hypo and Hyperglycemia, Part 2 of 4
... The body responds hypoglycemia by: Glycogenolysis Glycogen stores (~75g) in liver can be broken down into glucose monomers Can keep the body out of coma for a short period of time ...
... The body responds hypoglycemia by: Glycogenolysis Glycogen stores (~75g) in liver can be broken down into glucose monomers Can keep the body out of coma for a short period of time ...
Endocrine Part 2 Powerpoint
... whenever blood glucose gets high – Signals all cells to absorb additional glucose ...
... whenever blood glucose gets high – Signals all cells to absorb additional glucose ...
Diabetic hypoglycemia
Diabetic hypoglycemia is a low blood glucose level occurring in a person with diabetes mellitus. It is one of the most common types of hypoglycemia seen in emergency departments and hospitals. According to the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System-All Injury Program (NEISS-AIP), and based on a sample examined between 2004 and 2005, an estimated 55,819 cases (8.0% of total admissions) involved insulin, and severe hypoglycemia is likely the single most common event.In general, hypoglycemia occurs when a treatment to lower the elevated blood glucose of diabetes inaccurately matches the body's physiological need, and therefore causes the glucose to fall to a below-normal level.