English/Language Arts Vocabulary Words for K-2
... English/Language Arts Vocabulary for Students in Grades K-2 Students who are in grades K through 2 will be hearing the following English/Language Arts vocabulary terms used in the classroom. Obviously, if your child is in kindergarten, not all of these terms will be presented in class. Kindergarten ...
... English/Language Arts Vocabulary for Students in Grades K-2 Students who are in grades K through 2 will be hearing the following English/Language Arts vocabulary terms used in the classroom. Obviously, if your child is in kindergarten, not all of these terms will be presented in class. Kindergarten ...
Literacy overview y56
... contribute to meaning Discuss and evaluate how authors use language, including figurative language, considering the impact on the reader Distinguish between statements of fact and opinion Retrieve, record and present information from non-fiction Participate in discussions about books that are read t ...
... contribute to meaning Discuss and evaluate how authors use language, including figurative language, considering the impact on the reader Distinguish between statements of fact and opinion Retrieve, record and present information from non-fiction Participate in discussions about books that are read t ...
Year 5 and 6 English Overview
... maintain positive attitudes to reading and understanding of what they read by: continuing to read and discuss an increasingly wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks reading books tha t are structured in different ways and reading for a range of purpo ...
... maintain positive attitudes to reading and understanding of what they read by: continuing to read and discuss an increasingly wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks reading books tha t are structured in different ways and reading for a range of purpo ...
PSSA English Language Arts Glossary Grade 4
... subject-verb agreement - A grammatical rule in which the subject of a sentence must agree with its verb in both number and tense. subordinating conjunctions - (after, because, although) emphasize the importance of one grammatical structure over the other. summarize - To capture all of the most impor ...
... subject-verb agreement - A grammatical rule in which the subject of a sentence must agree with its verb in both number and tense. subordinating conjunctions - (after, because, although) emphasize the importance of one grammatical structure over the other. summarize - To capture all of the most impor ...
Name Language Arts / Five – A – Day
... (person, place, or thing)? punctuation mark: Students will use the rules of the English language in writing and speaking. ...
... (person, place, or thing)? punctuation mark: Students will use the rules of the English language in writing and speaking. ...
Editor`s Nitpicking # 2 - American Journal of Neuroradiology
... its meaning is the same. If used as an adjective, it means something that is characteristic of the current times. The word “now” is short but complex. It can be used as an adverb, noun, adjective, or a conjunction. It generally means at the present time or moment. Less common usages are conjunctiona ...
... its meaning is the same. If used as an adjective, it means something that is characteristic of the current times. The word “now” is short but complex. It can be used as an adverb, noun, adjective, or a conjunction. It generally means at the present time or moment. Less common usages are conjunctiona ...
Basic notions
... the lexeme break: break1 (become not whole) vs break2 (cause become not whole). ...
... the lexeme break: break1 (become not whole) vs break2 (cause become not whole). ...
e30_15-16_7_learning-words-grammar-and
... children make association between words and ideas 5-10 years old. Syntagmatic association: choosing a linking idea in a word from a different part of speech/word classes so it produces from noun cue to verb responses: bark or eat from dog and table. ...
... children make association between words and ideas 5-10 years old. Syntagmatic association: choosing a linking idea in a word from a different part of speech/word classes so it produces from noun cue to verb responses: bark or eat from dog and table. ...
Grades 9-10 Language Standards : Conventions of Standard English
... Essential Vocabulary: phrase and clause, phrase types (noun, verb, adjectival, adverbial, participial, prepositional, absolute), clause types (independent, dependent; noun, relative, adverbial), parallel structure, syntax, conventions, semicolon, conjunctive adverb; dependent (subordinate) clause, c ...
... Essential Vocabulary: phrase and clause, phrase types (noun, verb, adjectival, adverbial, participial, prepositional, absolute), clause types (independent, dependent; noun, relative, adverbial), parallel structure, syntax, conventions, semicolon, conjunctive adverb; dependent (subordinate) clause, c ...
List of Academic Vocabulary Terms absolute phrase adjective
... a short and amusing or interesting story about a real incident or person. ...
... a short and amusing or interesting story about a real incident or person. ...
File
... • used to create a word that describes the complete opposite of its nonnegative form. • When affixing non- to a word, no hyphen is needed unless the stem is a proper noun. • Non- =“absence or lack of”: non-standard. • “not doing, failure to do”: non-accomplishment • If someone has a non-medical back ...
... • used to create a word that describes the complete opposite of its nonnegative form. • When affixing non- to a word, no hyphen is needed unless the stem is a proper noun. • Non- =“absence or lack of”: non-standard. • “not doing, failure to do”: non-accomplishment • If someone has a non-medical back ...
Lexical Studies Lecture 1
... Compare again our formation abso-bloody-lutely from above, where –bloody interrupts the morpheme absolute (the base absolutely consists of course of the two morphemes absolute and -ly). Such intervening affixes are called infixes. we have only encountered complex words that are created by concatenat ...
... Compare again our formation abso-bloody-lutely from above, where –bloody interrupts the morpheme absolute (the base absolutely consists of course of the two morphemes absolute and -ly). Such intervening affixes are called infixes. we have only encountered complex words that are created by concatenat ...
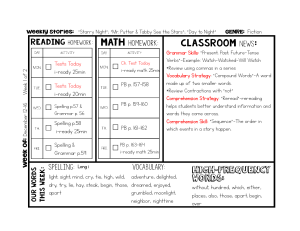
Tests Today i-ready 25min Tests Today i
... Vocabulary Strategy: “Compound Words”-A word made up of two smaller words. PB p. 157-158 *Review Contractions with “not” Comprehension Strategy: “Reread”-rereading PB p. 159-160 helps students better understand information and words they come across. Comprehension Skill: “Sequence”-The order i ...
... Vocabulary Strategy: “Compound Words”-A word made up of two smaller words. PB p. 157-158 *Review Contractions with “not” Comprehension Strategy: “Reread”-rereading PB p. 159-160 helps students better understand information and words they come across. Comprehension Skill: “Sequence”-The order i ...
Open class word and closed class word
... e.g. table---tables talk----talks, talking, talked boy---boy’s The latter studies the rules for word-formation ...
... e.g. table---tables talk----talks, talking, talked boy---boy’s The latter studies the rules for word-formation ...
Chapter 2: Words, sentences, and syntax
... The traditional word classes are the result of classification. Think of classification as the process of sorting a pile of something, eg. fruit, into smaller, uniform piles. Now, what should the result of this sorting be? That depends on its purpose. The crucial thing about classification is that it ...
... The traditional word classes are the result of classification. Think of classification as the process of sorting a pile of something, eg. fruit, into smaller, uniform piles. Now, what should the result of this sorting be? That depends on its purpose. The crucial thing about classification is that it ...
intralinguistic relations of words
... The verb look, is usually treated as a synonym of see, watch, observe, etc., but in another of its meanings it is not synonymous with this group of words but rather with the verbs seem, appear (cf. to look at smb and to look pale). The number of synonymic sets of a polysemantic word tends as a rule ...
... The verb look, is usually treated as a synonym of see, watch, observe, etc., but in another of its meanings it is not synonymous with this group of words but rather with the verbs seem, appear (cf. to look at smb and to look pale). The number of synonymic sets of a polysemantic word tends as a rule ...
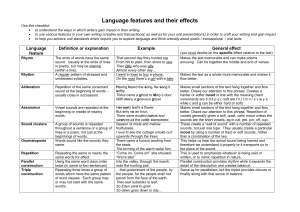
Language features and their effects
... better. Draws our attention to this phrase. Creates a harder or softer mood in line with the meaning (hard consonants are b d k p q t, soft are f h j l m n r s v w y z, while c and g can be either hard or soft) Makes small sections of the text hang together and flow better. Draws our attention to th ...
... better. Draws our attention to this phrase. Creates a harder or softer mood in line with the meaning (hard consonants are b d k p q t, soft are f h j l m n r s v w y z, while c and g can be either hard or soft) Makes small sections of the text hang together and flow better. Draws our attention to th ...
Year Three - Rivington Primary School
... Listening to and discussing a wide range of texts (and listening to what others say) Performing and reading poems and play scripts aloud, showing understanding through intonation, tone, volume and action Discussing their understanding of texts and explaining the meaning of words in context Asking qu ...
... Listening to and discussing a wide range of texts (and listening to what others say) Performing and reading poems and play scripts aloud, showing understanding through intonation, tone, volume and action Discussing their understanding of texts and explaining the meaning of words in context Asking qu ...
Philosophy 103 Linguistics 103 Introductory Logic
... The INTENSION (with an S) of a term (or idea or concept) is the definition of the term. It is the rule according to which something either is or is not part of the extension of the term. The INTENSION of ‘human being’ is something like: “bipedal mammal of the genus homo, species sapiens, capable of ...
... The INTENSION (with an S) of a term (or idea or concept) is the definition of the term. It is the rule according to which something either is or is not part of the extension of the term. The INTENSION of ‘human being’ is something like: “bipedal mammal of the genus homo, species sapiens, capable of ...
Day 10.1. Morphology = study of word structure Syntax = study of
... There are several sub-classes of verbs which differ primarily in terms of what can and must appear to the right of the verb, classes such as transitive, intransitive, ditransitive, sentential, and linking (or copulative) verbs. We'll talk about these later on. In addition, some of them are discussed ...
... There are several sub-classes of verbs which differ primarily in terms of what can and must appear to the right of the verb, classes such as transitive, intransitive, ditransitive, sentential, and linking (or copulative) verbs. We'll talk about these later on. In addition, some of them are discussed ...
Modification - (`Dick`) Hudson
... You could continue by using this pair to modify yet another noun, and so on until you all run out of imagination or stamina: car owner insurance, car owner insurance premium, ... Needless to say, many other variants of the game are possible: you could add modifiers to the dependent (premium – insura ...
... You could continue by using this pair to modify yet another noun, and so on until you all run out of imagination or stamina: car owner insurance, car owner insurance premium, ... Needless to say, many other variants of the game are possible: you could add modifiers to the dependent (premium – insura ...
Phonology
... affixes (tense, adjective & adverb) Syntactical information – how does it function in a sentence (blessed – verb or adjective / does verb take an object) Semantic information – can define or provide synonyms, know related words Pragmatic information - real world use, register ...
... affixes (tense, adjective & adverb) Syntactical information – how does it function in a sentence (blessed – verb or adjective / does verb take an object) Semantic information – can define or provide synonyms, know related words Pragmatic information - real world use, register ...