ASPECTS OF THE SEMANTICS OF THE AKAN
... It is these considerations and others which constitute the object of this paper. It focuses primarily on the semanticity of the Akan phrasal verb and especially how it responds to the questions of idiomaticity and transparency or relativity. It examines the issue of sense relations as far as the ph ...
... It is these considerations and others which constitute the object of this paper. It focuses primarily on the semanticity of the Akan phrasal verb and especially how it responds to the questions of idiomaticity and transparency or relativity. It examines the issue of sense relations as far as the ph ...
What we will learn
... Joanna Rios & Jose Fernandez Torres. McGraw-Hill's Complete Medical Spanish, Second Edition, McGraw Hill, 2010. ($17) -- 1st edition may also be used Available at the following websites: http://search.barnesandnoble.com/ http://www.amazon.com ...
... Joanna Rios & Jose Fernandez Torres. McGraw-Hill's Complete Medical Spanish, Second Edition, McGraw Hill, 2010. ($17) -- 1st edition may also be used Available at the following websites: http://search.barnesandnoble.com/ http://www.amazon.com ...
Prepositional Phrases
... **See handout for common prepositions and compound preps. Practice pg. 363 ex. 1 ...
... **See handout for common prepositions and compound preps. Practice pg. 363 ex. 1 ...
DIRECT OBJECT!
... How many points did Kevin score? Whom did the team choose as captain? Which does do you prefer? Whom did you see there? Whose phone did you borrow? How many books did Tim read? What will you do about your missing keys? ...
... How many points did Kevin score? Whom did the team choose as captain? Which does do you prefer? Whom did you see there? Whose phone did you borrow? How many books did Tim read? What will you do about your missing keys? ...
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
... Periodic Sentence - clauses arranged in order of climax, with the concluding information or thought being withheld until the end (Willow switch dangling in mid-grip, the grimace-faced teacher stormed into the room.”) Phrase – a group of words acting as a single part of speech, without its own subjec ...
... Periodic Sentence - clauses arranged in order of climax, with the concluding information or thought being withheld until the end (Willow switch dangling in mid-grip, the grimace-faced teacher stormed into the room.”) Phrase – a group of words acting as a single part of speech, without its own subjec ...
paragraph
... by comparison, in a like manner, as, with, as though, both, like, just as Contrast: but, by contrast, in contrast, despite, however, instead, nevertheless, on (to) the contrary, in spite of, still, yet, unlike, even so, rather than, otherwise ...
... by comparison, in a like manner, as, with, as though, both, like, just as Contrast: but, by contrast, in contrast, despite, however, instead, nevertheless, on (to) the contrary, in spite of, still, yet, unlike, even so, rather than, otherwise ...
(Texto 306) 27/11/2007: Curso de gramática da
... You can use a relative pronoun is used to link one phrase or clause to another phrase or clause. The relative pronouns are "who," "whom," "that," and "which." The compounds "whoever," "whomever," and "whichever" are also relative pronouns. You can use the relative pronouns "who" and "whoever" to ref ...
... You can use a relative pronoun is used to link one phrase or clause to another phrase or clause. The relative pronouns are "who," "whom," "that," and "which." The compounds "whoever," "whomever," and "whichever" are also relative pronouns. You can use the relative pronouns "who" and "whoever" to ref ...
Document
... Most sentences need words beyond a subject and a verb to complete their meaning. Direct objects and indirect objects complete ideas and make sentences more specific. A direct object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb and answers the question Whom? or What? They recited the ...
... Most sentences need words beyond a subject and a verb to complete their meaning. Direct objects and indirect objects complete ideas and make sentences more specific. A direct object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb and answers the question Whom? or What? They recited the ...
Parallel: The teacher said that he was a poor student because he
... Punctuation Rule regarding compound prepositions: compound prepositional phrases must be set off from the rest of the sentence using commas! ...
... Punctuation Rule regarding compound prepositions: compound prepositional phrases must be set off from the rest of the sentence using commas! ...
Words and morphemes
... Whereas a root is normally a single morpheme, a stem might contain two or more. For example, a compound noun might function as a stem for the addition of the plural suffix. Morphemes can also (more rarely) be infixes, which are inserted within another form, rather than before or ...
... Whereas a root is normally a single morpheme, a stem might contain two or more. For example, a compound noun might function as a stem for the addition of the plural suffix. Morphemes can also (more rarely) be infixes, which are inserted within another form, rather than before or ...
Head Words and Phrases Heads and their Dependents
... • Often a verb can appear in more than one subclass – Chris couldn’t remember that long shopping list. » NP complement – Chris remembered that they’d left it on the shelf. » Finite clause complement – Chris usually remembers to pick up the list. » Non-finite infinitival clause complement – Chris rem ...
... • Often a verb can appear in more than one subclass – Chris couldn’t remember that long shopping list. » NP complement – Chris remembered that they’d left it on the shelf. » Finite clause complement – Chris usually remembers to pick up the list. » Non-finite infinitival clause complement – Chris rem ...
WORDS FREQUENTLY CONFUSED A / AN
... My cat sits by me when I watch T.V. She is sitting near the window. I sat by Rick. You have sat in the same seat all term. ...
... My cat sits by me when I watch T.V. She is sitting near the window. I sat by Rick. You have sat in the same seat all term. ...
An Updated Typology of Causative Constructions: Form
... choice of one causative construction over another. Dixon’s (2000) claims about prototypical patternings of compact vs. less compact constructions are not well-supported: in order for the claims to be well-supported, the values of Dixon's nine parameters would have to be correlated in individual lang ...
... choice of one causative construction over another. Dixon’s (2000) claims about prototypical patternings of compact vs. less compact constructions are not well-supported: in order for the claims to be well-supported, the values of Dixon's nine parameters would have to be correlated in individual lang ...
3.1 Verbs
... Sentence b: I could have BEEN stung by that bee. Helping Verb Branch - Step 1 Question: Does the main verb end in -ing? Answer: No Solution: Then, the verb is in the passive voice. Helping Verb Branch - Step 2 a. Delete the to be verb. I could have stung by that bee. b. Move the subject (and modifie ...
... Sentence b: I could have BEEN stung by that bee. Helping Verb Branch - Step 1 Question: Does the main verb end in -ing? Answer: No Solution: Then, the verb is in the passive voice. Helping Verb Branch - Step 2 a. Delete the to be verb. I could have stung by that bee. b. Move the subject (and modifie ...
3.1.2 Regular ㄷ verbs
... endings. Whereas a Latin category is identified by possibly dozens of endings, each Korean modifier or ending identifies only itself. So, although it would be possible to invent a specific term for each of the Korean verbs forms, that would not be helpful. It is much clearer to use the ending as the ...
... endings. Whereas a Latin category is identified by possibly dozens of endings, each Korean modifier or ending identifies only itself. So, although it would be possible to invent a specific term for each of the Korean verbs forms, that would not be helpful. It is much clearer to use the ending as the ...
run-on sentence
... • Action verbs are things that the subject does, like run, scream, or jump • Example: The Steelers defeated the Ravens in last night’s game. ...
... • Action verbs are things that the subject does, like run, scream, or jump • Example: The Steelers defeated the Ravens in last night’s game. ...
Studies of particular languages
... study, the use of the reflexive pronoun with the verb. The links between the proclitic me, te, se and the pronominal enclitics moi-meme, lui-meme are examined, and also the differences between 'inherent' reflexive verbs such as s'ivanouir, a. reciprocal verb like s'aimer and a reflexive like se lave ...
... study, the use of the reflexive pronoun with the verb. The links between the proclitic me, te, se and the pronominal enclitics moi-meme, lui-meme are examined, and also the differences between 'inherent' reflexive verbs such as s'ivanouir, a. reciprocal verb like s'aimer and a reflexive like se lave ...
An adverb is a word that qualifies the action of the verb, that is, it
... While this alternation is common in English, it is not common in French where adjectives are rarely used in place of the adverb. Remember that adverbs modify verbs (as well as other adverbs and adjectives) and adjectives modify ...
... While this alternation is common in English, it is not common in French where adjectives are rarely used in place of the adverb. Remember that adverbs modify verbs (as well as other adverbs and adjectives) and adjectives modify ...
Chapter 19: Perfect Passive Verbs
... because when someone asks a question about who is doing something, they often don’t know whether it was a man or a woman. Therefore, it’s pointless to make a distinction in gender. In contrast, those asking questions most often do know whether it was a person or a thing, so the distinction between a ...
... because when someone asks a question about who is doing something, they often don’t know whether it was a man or a woman. Therefore, it’s pointless to make a distinction in gender. In contrast, those asking questions most often do know whether it was a person or a thing, so the distinction between a ...
part of speech tagging
... Simplest method: assume an unknown word could belong to any tag; unknown words are assigned the distribution over POS over the whole lexicon. Some tags are more common than others (for example a new word can be most likely verbs, nouns etc. but not prepositions or articles). Use features of the word ...
... Simplest method: assume an unknown word could belong to any tag; unknown words are assigned the distribution over POS over the whole lexicon. Some tags are more common than others (for example a new word can be most likely verbs, nouns etc. but not prepositions or articles). Use features of the word ...
3 `Derivational verbs` and other multiple
... There is a distinction between singular and plural third person pronouns (in both, men’s and women’s speech) but no such distinction in the verb paradigms. Several prefixes have phonologically determined allophones: if the following morpheme (usually, the stem) starts with a vowel the allomorph endi ...
... There is a distinction between singular and plural third person pronouns (in both, men’s and women’s speech) but no such distinction in the verb paradigms. Several prefixes have phonologically determined allophones: if the following morpheme (usually, the stem) starts with a vowel the allomorph endi ...
Grammar Scheme of Work
... 1. To know that words combine to make sentences and we separate words with spaces 2. To being using the term sentence to identify sentences in text 3. To know that a line of writing is not necessarily the same as a sentence 4. To begin using full stops to demarcate sentences 5. To use a capital lett ...
... 1. To know that words combine to make sentences and we separate words with spaces 2. To being using the term sentence to identify sentences in text 3. To know that a line of writing is not necessarily the same as a sentence 4. To begin using full stops to demarcate sentences 5. To use a capital lett ...
P88-1027 - ACL Anthology Reference Corpus
... Table I. Performance time and parsing efficiency of LSP by part of speech of words defined (adapted from Fox et ul., 1988) In most cases, there is little variation among the parts of speech. The most obvious discrepancy is the slow parsing time for wansifive verbs. We are not yet sure why this is, b ...
... Table I. Performance time and parsing efficiency of LSP by part of speech of words defined (adapted from Fox et ul., 1988) In most cases, there is little variation among the parts of speech. The most obvious discrepancy is the slow parsing time for wansifive verbs. We are not yet sure why this is, b ...
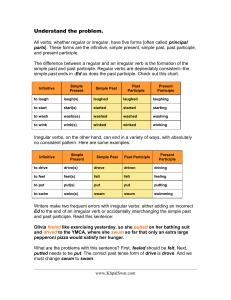
Understand the problem. All verbs, whether regular or irregular
... When you choose an irregular verb for a sentence, however, the simple past and past participle are often different, so you must know the distinction. Here are two examples: Essie drove so cautiously that traffic piled up behind her, causing angry drivers to honk their horns and shout obesities. Dro ...
... When you choose an irregular verb for a sentence, however, the simple past and past participle are often different, so you must know the distinction. Here are two examples: Essie drove so cautiously that traffic piled up behind her, causing angry drivers to honk their horns and shout obesities. Dro ...
Lexical semantics

Lexical semantics (also known as lexicosemantics), is a subfield of linguistic semantics. The units of analysis in lexical semantics are lexical units which include not only words but also sub-words or sub-units such as affixes and even compound words and phrases. Lexical units make up the catalogue of words in a language, the lexicon. Lexical semantics looks at how the meaning of the lexical units correlates with the structure of the language or syntax. This is referred to as syntax-semantic interface.The study of lexical semantics looks at: the classification and decomposition of lexical items the differences and similarities in lexical semantic structure cross-linguistically the relationship of lexical meaning to sentence meaning and syntax.Lexical units, also referred to as syntactic atoms, can stand alone such as in the case of root words or parts of compound words or they necessarily attach to other units such as prefixes and suffixes do. The former are called free morphemes and the latter bound morphemes. They fall into a narrow range of meanings (semantic fields) and can combine with each other to generate new meanings.