Grammar on mathematical principles
... that the subject, or object, under that verb be the same as the subject, or object, of the verb itself. It is reasonable to expect that the object under they undergo, they deseroe should be the same they (i.e. same as the main subject), or that the subject under they admit, they promise should be th ...
... that the subject, or object, under that verb be the same as the subject, or object, of the verb itself. It is reasonable to expect that the object under they undergo, they deseroe should be the same they (i.e. same as the main subject), or that the subject under they admit, they promise should be th ...
1 An Introduction to Word classes
... This approach has certain merits, since it allows us to determine word classes by replacing words in a sentence with words of "similar" meaning. For instance, in the sentence My son cooks dinner every Sunday, we can replace the verb cooks with other "action" words: ...
... This approach has certain merits, since it allows us to determine word classes by replacing words in a sentence with words of "similar" meaning. For instance, in the sentence My son cooks dinner every Sunday, we can replace the verb cooks with other "action" words: ...
Chapter 6 Verb stems and incorporation
... The previous chapters dealt with various aspects of inflection in Meskwaki: chapter 3 on the inflectional categories and their realization on nouns and pronouns; chapter 4 on the internal organization of one of the verbal inflectional paradigms; and chapter 5 on the syntactic, semantic, and pragmati ...
... The previous chapters dealt with various aspects of inflection in Meskwaki: chapter 3 on the inflectional categories and their realization on nouns and pronouns; chapter 4 on the internal organization of one of the verbal inflectional paradigms; and chapter 5 on the syntactic, semantic, and pragmati ...
Phrase - My Teacher Pages
... The Infinitive Phrase Infinitive Phrase – consists of an infinitive and any modifiers or complements the infinitive has.(including prepositional phrases) The entire phrase may be used as a noun, adjective, or ...
... The Infinitive Phrase Infinitive Phrase – consists of an infinitive and any modifiers or complements the infinitive has.(including prepositional phrases) The entire phrase may be used as a noun, adjective, or ...
Using German Synonyms - Assets
... In all languages most words, especially the most frequent ones, cover a wide range of possible related senses (this is known as polysemy), and it is very rare for apparently equivalent words in different languages to cover exactly the same range. German kochen, for example, can be used to refer to ` ...
... In all languages most words, especially the most frequent ones, cover a wide range of possible related senses (this is known as polysemy), and it is very rare for apparently equivalent words in different languages to cover exactly the same range. German kochen, for example, can be used to refer to ` ...
The verb krijgen `to get` as an undative verb
... like de storm ‘the tempest’: De storm brak het raam ‘The storm broke the window’. ...
... like de storm ‘the tempest’: De storm brak het raam ‘The storm broke the window’. ...
Phrases and Clauses
... These clauses simply do not form complete thoughts or sentences by themselves. Those subordinate conjunctions--since, when, and because, cause the listener to expect the speaker to add some extra material. The thought is incomplete. If you walked up to a friend in the dorms and said, "since she laug ...
... These clauses simply do not form complete thoughts or sentences by themselves. Those subordinate conjunctions--since, when, and because, cause the listener to expect the speaker to add some extra material. The thought is incomplete. If you walked up to a friend in the dorms and said, "since she laug ...
The Regular, Irregular, and Pronominal Commands
... Part II: Using Verbs Correctly with Questions, Commands, and Such Use the tu command when speaking to one person with whom you’re familiar. You use the vous command when speaking to one person with whom you aren’t familiar, a superior (like your boss or your professor), or someone older than you; an ...
... Part II: Using Verbs Correctly with Questions, Commands, and Such Use the tu command when speaking to one person with whom you’re familiar. You use the vous command when speaking to one person with whom you aren’t familiar, a superior (like your boss or your professor), or someone older than you; an ...
Sentence Patterns
... Pattern #5: Open with a prepositional phrase. 1. A prepositional phrase contains a preposition and a noun/pronoun known as an object. These phrases modify nouns and verbs. 2. Prepositions connect their objects to other words in a sentence. 3. Prepositions describe direction (from, over), position (u ...
... Pattern #5: Open with a prepositional phrase. 1. A prepositional phrase contains a preposition and a noun/pronoun known as an object. These phrases modify nouns and verbs. 2. Prepositions connect their objects to other words in a sentence. 3. Prepositions describe direction (from, over), position (u ...
Chapter 6 Syntax: Words in Combination
... words into phrases and sentences. As with other aspects of language, syntactic structures are principled and systematic, with the potential for detailed analysis and description. Words that occur in phrases and sentences can be shown not only to have semantic, or meaningful, relationships to each ot ...
... words into phrases and sentences. As with other aspects of language, syntactic structures are principled and systematic, with the potential for detailed analysis and description. Words that occur in phrases and sentences can be shown not only to have semantic, or meaningful, relationships to each ot ...
clean - LAGB Education Committee
... agent. If a verb describes an action, the person or thing that carries out the action is the agent. The agent is the 'do-er' of the action. For instance, in Mary caught the ball, Mary (the person, not the word) is the agent, and similarly, the ball is called the 'patient'. This analysis and termino ...
... agent. If a verb describes an action, the person or thing that carries out the action is the agent. The agent is the 'do-er' of the action. For instance, in Mary caught the ball, Mary (the person, not the word) is the agent, and similarly, the ball is called the 'patient'. This analysis and termino ...
what is a complete sentence?
... 3. Elements joined by correlative conjunctions, such as "either . . . or" and not "only . . .but also," should be parallel. 4. Two elements that are compared or contrasted should be expressed in parallel structures. ...
... 3. Elements joined by correlative conjunctions, such as "either . . . or" and not "only . . .but also," should be parallel. 4. Two elements that are compared or contrasted should be expressed in parallel structures. ...
The Present Perfect
... The Present Perfect • Certain verbs that have a double vowel in the infinitive form (except those with the ...
... The Present Perfect • Certain verbs that have a double vowel in the infinitive form (except those with the ...
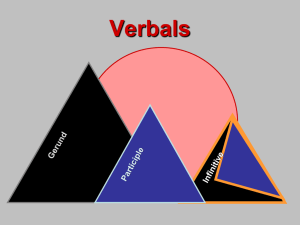
Verbals - Taylor County Schools
... • I missed the road to take to the beach. • The place to see moose is Canada. • I need a place to keep my book bag. Adjective infinitive phrases will come directly after a noun and modify it by answering “which?” or “what kind?.” ...
... • I missed the road to take to the beach. • The place to see moose is Canada. • I need a place to keep my book bag. Adjective infinitive phrases will come directly after a noun and modify it by answering “which?” or “what kind?.” ...
5 The acquisition of Dutch
... since t h e first Arabic grammars (around 790 AC), two types of sentences have been distinguished - nominal and verbal sentences. T h e former lack a finite verb. In fact, they are predicative constructions in which t h e copula, if in present tense and not negated, is regularly o m i t t e d . In o ...
... since t h e first Arabic grammars (around 790 AC), two types of sentences have been distinguished - nominal and verbal sentences. T h e former lack a finite verb. In fact, they are predicative constructions in which t h e copula, if in present tense and not negated, is regularly o m i t t e d . In o ...
Grammar Notebook - Laurel County Schools
... *APPLICATION 1—Copy the sentences into your notebook. Then, underline the participle/Participle phrases in each. ...
... *APPLICATION 1—Copy the sentences into your notebook. Then, underline the participle/Participle phrases in each. ...
p. 214 The Present Perfect Tense
... The Present Perfect • Certain verbs that have a double vowel in the infinitive form (except those with the ...
... The Present Perfect • Certain verbs that have a double vowel in the infinitive form (except those with the ...
The Present Perfect
... The Present Perfect • Certain verbs that have a double vowel in the infinitive form (except those with the ...
... The Present Perfect • Certain verbs that have a double vowel in the infinitive form (except those with the ...
Use of `do` as a full verb
... deck.” “She will be arriving this afternoon.” Occasionally, though, the verb will stand by itself, alone, in a sentence. This is especially true in simple, brief answers to questions. “Who's going to the movies with me?” “I am.” “Who's responsible for this mess in the engine room?” “She is.” In sent ...
... deck.” “She will be arriving this afternoon.” Occasionally, though, the verb will stand by itself, alone, in a sentence. This is especially true in simple, brief answers to questions. “Who's going to the movies with me?” “I am.” “Who's responsible for this mess in the engine room?” “She is.” In sent ...
A participle is a verb form used as an adjective to modify nouns and
... A participial phrase should refer clearly to a noun or pronoun in the sentence. We have to be careful when combining sentences such as these: I curled my toes and squinted. The doctor prepared to puncture my arm with a needle. Notice what happens if we drop "I" and change the first sentence to a par ...
... A participial phrase should refer clearly to a noun or pronoun in the sentence. We have to be careful when combining sentences such as these: I curled my toes and squinted. The doctor prepared to puncture my arm with a needle. Notice what happens if we drop "I" and change the first sentence to a par ...
Motion events can be segmented into several components
... of this, manner is frequently encoded even when it is not important in the context. In V-languages, manner expression is entirely optional, as we saw in (2). Path-only constructions are less complex than path + manner constructions, as the former only need a path verb whereas the latter need an adde ...
... of this, manner is frequently encoded even when it is not important in the context. In V-languages, manner expression is entirely optional, as we saw in (2). Path-only constructions are less complex than path + manner constructions, as the former only need a path verb whereas the latter need an adde ...
Holt Handbook Chapter 5
... NOTE: a group of words that has both a verb and its subject is called a clause. ...
... NOTE: a group of words that has both a verb and its subject is called a clause. ...
Gustar - Images
... am whom is being pleased; Montar a Caballo is the real Subject - it is what is pleasing me. Gusta is the active verb and is singular because horseback riding is a concept or an action - at any rate, Montar is an infinitive and infinitives are ALWAYS SINGULAR. Gustar requires an indirect object prono ...
... am whom is being pleased; Montar a Caballo is the real Subject - it is what is pleasing me. Gusta is the active verb and is singular because horseback riding is a concept or an action - at any rate, Montar is an infinitive and infinitives are ALWAYS SINGULAR. Gustar requires an indirect object prono ...
Lexical semantics

Lexical semantics (also known as lexicosemantics), is a subfield of linguistic semantics. The units of analysis in lexical semantics are lexical units which include not only words but also sub-words or sub-units such as affixes and even compound words and phrases. Lexical units make up the catalogue of words in a language, the lexicon. Lexical semantics looks at how the meaning of the lexical units correlates with the structure of the language or syntax. This is referred to as syntax-semantic interface.The study of lexical semantics looks at: the classification and decomposition of lexical items the differences and similarities in lexical semantic structure cross-linguistically the relationship of lexical meaning to sentence meaning and syntax.Lexical units, also referred to as syntactic atoms, can stand alone such as in the case of root words or parts of compound words or they necessarily attach to other units such as prefixes and suffixes do. The former are called free morphemes and the latter bound morphemes. They fall into a narrow range of meanings (semantic fields) and can combine with each other to generate new meanings.