English tenses - How to fill in the verbs
... Put in not after the auxiliary. (Simple Present don't or doesn't; Simple Past didn't) Now fill in the verbform into the gap. doesn't play (Do not put an -s on the full verb, the s is in doesn't. The adverb of frequency always goes before the full verb play.) Peter doesn't always play football. Examp ...
... Put in not after the auxiliary. (Simple Present don't or doesn't; Simple Past didn't) Now fill in the verbform into the gap. doesn't play (Do not put an -s on the full verb, the s is in doesn't. The adverb of frequency always goes before the full verb play.) Peter doesn't always play football. Examp ...
An algebraic approach to French sentence structure
... These two occurrences of qui have distinct translations into German (wer/wes) or into pedantic English (who/whom). ...
... These two occurrences of qui have distinct translations into German (wer/wes) or into pedantic English (who/whom). ...
DGP 6th Five-Day Plan Sent. 4
... 2. Label the parts of speech in the sentence above by using the abbreviations in the word bank below. Day 1 Word Bank: n - noun (2) pos pro – possessive pronoun (1) av – action verb (1) – pres (present), past (past), f (future) adj – adjective (1) hv – helping verb (1) art – article (1) ...
... 2. Label the parts of speech in the sentence above by using the abbreviations in the word bank below. Day 1 Word Bank: n - noun (2) pos pro – possessive pronoun (1) av – action verb (1) – pres (present), past (past), f (future) adj – adjective (1) hv – helping verb (1) art – article (1) ...
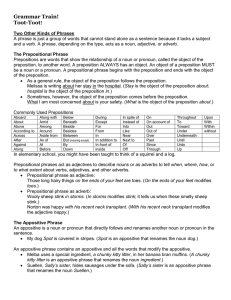
A BOTTOM UP WAY OF ANALYZING A SENTENCE
... prepositional phrases. Recognize that there is some “layering” here. Noun phrases, for example, can stand alone – or as parts of prepositional phrases. Adjective phrases can fold into noun phrases. It is possible to have a prepositional phrase with a noun phrase that contains an adjective phrase! WH ...
... prepositional phrases. Recognize that there is some “layering” here. Noun phrases, for example, can stand alone – or as parts of prepositional phrases. Adjective phrases can fold into noun phrases. It is possible to have a prepositional phrase with a noun phrase that contains an adjective phrase! WH ...
File
... Punctuation pointer: Most of the time appositive phrases are separated from the sentence by commas – but sometimes they are not. Set an appositive phrase off by commas if it is not essential to the meaning of the sentence. If you could leave the phrase out, and the reader would clearly understand t ...
... Punctuation pointer: Most of the time appositive phrases are separated from the sentence by commas – but sometimes they are not. Set an appositive phrase off by commas if it is not essential to the meaning of the sentence. If you could leave the phrase out, and the reader would clearly understand t ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Grammar
... Prescriptive rules exist only to express a preference for one structure or usage or linguistic item over another. A prescriptive grammar will not contain rules that tell you to put articles before nouns, rather than after, because no native speakers of English put articles after nouns. Prescriptive ...
... Prescriptive rules exist only to express a preference for one structure or usage or linguistic item over another. A prescriptive grammar will not contain rules that tell you to put articles before nouns, rather than after, because no native speakers of English put articles after nouns. Prescriptive ...
Identifying Declarative, Interrogative, Imperative, and Exclamatory
... (3) a comma, but ONLY when the simple sentences are being treated as items in a series: The dog barked, the cat yowled, and the rabbit chewed. 3.A complex sentence consists of a combination of an independent clause and a dependent clause. An example with a relative clause as the dependent clause: Th ...
... (3) a comma, but ONLY when the simple sentences are being treated as items in a series: The dog barked, the cat yowled, and the rabbit chewed. 3.A complex sentence consists of a combination of an independent clause and a dependent clause. An example with a relative clause as the dependent clause: Th ...
Elements of Sentences - English Composition 108
... Elements of Sentences are two : Subjects (nouns, pronouns ,names the topic of the sentence) and Predicates ( includes a verb(s) says what the subject is or does) ...
... Elements of Sentences are two : Subjects (nouns, pronouns ,names the topic of the sentence) and Predicates ( includes a verb(s) says what the subject is or does) ...
The Noun: A Comparative Analysis between the Arabic and the
... On the other hand, the word ‘`Al’’ is called definite article (i.e. )المعرفة, i.e. Al- ال, is the definite article in the Arabic language: whose function is to render the noun which it is prefixed definite. For example, the word (‘ )الجديقةgarden ‘can be made definite by prefixing it with al- ...
... On the other hand, the word ‘`Al’’ is called definite article (i.e. )المعرفة, i.e. Al- ال, is the definite article in the Arabic language: whose function is to render the noun which it is prefixed definite. For example, the word (‘ )الجديقةgarden ‘can be made definite by prefixing it with al- ...
An algebraic approach to French sentence structure
... These two occurrences of qui have distinct translations into German (wer/wes) or into pedantic English (who/whom). INSERT SECTION 8 HERE 9. Some final words. ...
... These two occurrences of qui have distinct translations into German (wer/wes) or into pedantic English (who/whom). INSERT SECTION 8 HERE 9. Some final words. ...
Linking Words
... Enough and too 'enough' goes AFTER ADJECTIVES & ADVERBS but BEFORE NOUNS. E.g.. You won't pass the exam if you don't work hard enough. OR He didn't get the job because he didn't have enough experience. 'ENOUGH' can also be used alone. E.g.. I'll lend you some money if you haven't got enough. 'TOO' ...
... Enough and too 'enough' goes AFTER ADJECTIVES & ADVERBS but BEFORE NOUNS. E.g.. You won't pass the exam if you don't work hard enough. OR He didn't get the job because he didn't have enough experience. 'ENOUGH' can also be used alone. E.g.. I'll lend you some money if you haven't got enough. 'TOO' ...
Relative Clauses - The Tlingit Language
... exceptions in published texts. I suspect the difference in stem variation between relatives and non-relatives is prosodic and intonational rather than morphophonological, and hence it may be more lexible than what Leer describes. I indicate stem variation in glosses but will otherwise ignore it. Tl ...
... exceptions in published texts. I suspect the difference in stem variation between relatives and non-relatives is prosodic and intonational rather than morphophonological, and hence it may be more lexible than what Leer describes. I indicate stem variation in glosses but will otherwise ignore it. Tl ...
Prepositions and particles in English
... words assigning case to the NPs they take as complements. However, not only is the class of prepositions an open‐class gradually including new members through a process of grammaticalization of some expressions, but it stands in a continuum with several other word cl ...
... words assigning case to the NPs they take as complements. However, not only is the class of prepositions an open‐class gradually including new members through a process of grammaticalization of some expressions, but it stands in a continuum with several other word cl ...
German Reference Grammar
... With few exceptions, all nouns in the dative plural end in -n. If no -n is present in the normal plural form, one must be added. The addition of the -n causes no changes in the rest of the noun. Looking at the group of six nouns in §5, we see that Flaschen and Kanadierinnen already end in -n. Theref ...
... With few exceptions, all nouns in the dative plural end in -n. If no -n is present in the normal plural form, one must be added. The addition of the -n causes no changes in the rest of the noun. Looking at the group of six nouns in §5, we see that Flaschen and Kanadierinnen already end in -n. Theref ...
A Light Rule-based Approach to English Subject
... and each has a specific syntactic or even semantic role, which is shown in Table 2. The detailed roles of these POS tags will give basic criterion to locate subject and its predicate in a sentence. As for lexicons, it is used to determine if a verb is in root form or not. To judge whether a verb has ...
... and each has a specific syntactic or even semantic role, which is shown in Table 2. The detailed roles of these POS tags will give basic criterion to locate subject and its predicate in a sentence. As for lexicons, it is used to determine if a verb is in root form or not. To judge whether a verb has ...
a brief description of english primary auxiliary verbs
... In linguistic, an auxiliary verb ( also called helping verb ) is a verb functioning to give further semantic or syntactic information about the main verb (non-auxiliary verb) following it. In English, every clause consists of a main verb and optionally one or more auxiliary verbs. For examples, have ...
... In linguistic, an auxiliary verb ( also called helping verb ) is a verb functioning to give further semantic or syntactic information about the main verb (non-auxiliary verb) following it. In English, every clause consists of a main verb and optionally one or more auxiliary verbs. For examples, have ...
Lesson 22 Day 3
... soft yawn walk What letters stand for the /ô/ sound in these words? ough, o, aw, al These letter combinations are not always pronounced /ô/. There is no good rule to know when words spelled this way are pronounced with the /ô/ sound. You will have to memorize the spelling of the words. ...
... soft yawn walk What letters stand for the /ô/ sound in these words? ough, o, aw, al These letter combinations are not always pronounced /ô/. There is no good rule to know when words spelled this way are pronounced with the /ô/ sound. You will have to memorize the spelling of the words. ...
You and I will meet later. Object Pronouns An object pronoun
... A reflexive pronoun refers to a noun or another pronoun and indicates that the same person or thing is involved. Reflexive pronouns are formed by adding –self or –selves to certain personal and possessive pronouns ...
... A reflexive pronoun refers to a noun or another pronoun and indicates that the same person or thing is involved. Reflexive pronouns are formed by adding –self or –selves to certain personal and possessive pronouns ...
AUTOMATIC PARSING OF PORTUGUESE Eckhard Bick
... When comparing different syntactic descriptions, information content and constituent structure are only two of all the possible judgement perspectives, and both are motivated by certain theoretical backgrounds, like functional or generative grammar. It may be more revealing, however, to take into ac ...
... When comparing different syntactic descriptions, information content and constituent structure are only two of all the possible judgement perspectives, and both are motivated by certain theoretical backgrounds, like functional or generative grammar. It may be more revealing, however, to take into ac ...
devising a method for the identification of english back
... the resulting words are presented in general dictionaries as stylistically neutral, they tend to be used in a limited number of contexts, especially words associated with professional areas like, business, economics, industry or education, etc. Such words can be considered either formal (accreditate ...
... the resulting words are presented in general dictionaries as stylistically neutral, they tend to be used in a limited number of contexts, especially words associated with professional areas like, business, economics, industry or education, etc. Such words can be considered either formal (accreditate ...
I - Гаврикова Юлия Александровна
... accept conventions and limitations that aren't necessarily called for. In English, for example, we don't have words like fwost or zpink or abtholve because we never normally combine those letters to make those sounds, though there's no reason why we couldn't if we wanted to. We just don't. Chinese t ...
... accept conventions and limitations that aren't necessarily called for. In English, for example, we don't have words like fwost or zpink or abtholve because we never normally combine those letters to make those sounds, though there's no reason why we couldn't if we wanted to. We just don't. Chinese t ...
File - ToliverEnglish
... trip and then to put half of them back (4) in the closet. Of course, travelers should give particularly careful thought to walking shoes, (5) the most important item of apparel on any sightseeing trip. Experienced travelers pack only two or three changes of casual clothing, even if they plan (6) to ...
... trip and then to put half of them back (4) in the closet. Of course, travelers should give particularly careful thought to walking shoes, (5) the most important item of apparel on any sightseeing trip. Experienced travelers pack only two or three changes of casual clothing, even if they plan (6) to ...
LANGUAGE AS MATHEMATICS
... Arabic statement "Al-aa-ela Ta-kol", i.e. "The family is eating", follows. Yet since the subject plus the verb is mathematically equal to the verb plus the subject, it follows that the equation the verb plus the subject should be a true equation of Arabic, exactly as the equation the subject plus th ...
... Arabic statement "Al-aa-ela Ta-kol", i.e. "The family is eating", follows. Yet since the subject plus the verb is mathematically equal to the verb plus the subject, it follows that the equation the verb plus the subject should be a true equation of Arabic, exactly as the equation the subject plus th ...
Государственный экзамен ООЗО 2015 Теория первого
... courts. Emily—her mother—had never been able to resist distinction. That had been the beginning of Monty—he had worn such perfect waistcoats and gardenias, and had known so much about all that was fast—impossible not to be impressed by him. Ah, well! She did not regret him now. Without him she would ...
... courts. Emily—her mother—had never been able to resist distinction. That had been the beginning of Monty—he had worn such perfect waistcoats and gardenias, and had known so much about all that was fast—impossible not to be impressed by him. Ah, well! She did not regret him now. Without him she would ...
A Brief Syntactic Typology of Philippine Languages
... are determined by both semantic and morphosyntactic considerations. Since we claim that all languages under consideration are probably ergative, we do not distinguish an Accusative case form. We also assume that there are two semantic macroroles needing specification in linguistic description, i.e., ...
... are determined by both semantic and morphosyntactic considerations. Since we claim that all languages under consideration are probably ergative, we do not distinguish an Accusative case form. We also assume that there are two semantic macroroles needing specification in linguistic description, i.e., ...