a brief comparative study on main word
... may develop the main means of enriching the vocabulary in Romanian and in English, pointing out similarities and differences. The most productive means are derivation, compounding and conversion. Derivation is the process of obtaining new words in a language by means of adding prefixes (prefixation) ...
... may develop the main means of enriching the vocabulary in Romanian and in English, pointing out similarities and differences. The most productive means are derivation, compounding and conversion. Derivation is the process of obtaining new words in a language by means of adding prefixes (prefixation) ...
Verbs I - University of Newcastle
... Future Perfect: I am afraid that I will have left for Callaghan by the time you arrive at my apartment. (Here, the speaker is looking ahead to a time when his or her friend is just arriving at the apartment in question but the speaker will already have left. That is, the speaker is projecting himsel ...
... Future Perfect: I am afraid that I will have left for Callaghan by the time you arrive at my apartment. (Here, the speaker is looking ahead to a time when his or her friend is just arriving at the apartment in question but the speaker will already have left. That is, the speaker is projecting himsel ...
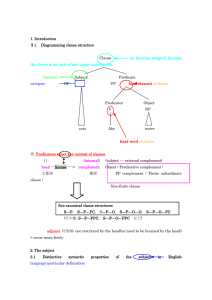
Notes on the sheet entitled “Some Additional Review” 1. Morphology
... So hydr- and salin- carry consistent meaning but can’t stand alone. You might say, for example, that they’re some sort of “defective” words in English; they have real-word meaning but must be attached to some other affix. As a matter of fact, linguists call these forms “bound roots.” They have clear ...
... So hydr- and salin- carry consistent meaning but can’t stand alone. You might say, for example, that they’re some sort of “defective” words in English; they have real-word meaning but must be attached to some other affix. As a matter of fact, linguists call these forms “bound roots.” They have clear ...
appositive - WordPress.com
... In the examples below, participial adjectives are in italics, and following each example a brief explanation of the participial adjective is in parentheses. To better understand how to use participial adjectives, think about regular adjectives you could use to replace each participial adjective ...
... In the examples below, participial adjectives are in italics, and following each example a brief explanation of the participial adjective is in parentheses. To better understand how to use participial adjectives, think about regular adjectives you could use to replace each participial adjective ...
Document
... ・O: a participant in the situation. ・PC: a property that is ascribed to the referent of the subject NP. Syntactic differences between PC and O (a) PC can have the form of AdjP (as well as NP). [21] (b) PC can have the form of a bare role NP. [22] (c) PC does not correspond to the subject of a passiv ...
... ・O: a participant in the situation. ・PC: a property that is ascribed to the referent of the subject NP. Syntactic differences between PC and O (a) PC can have the form of AdjP (as well as NP). [21] (b) PC can have the form of a bare role NP. [22] (c) PC does not correspond to the subject of a passiv ...
Syntax
... But linguists require more objective ways of determining syntactic categories. There are two tests one can use: ...
... But linguists require more objective ways of determining syntactic categories. There are two tests one can use: ...
Nominal Complements: Subjective and Objective Complements
... As the examples below show, the subjective complement may be a noun or an adjective, though for verbs with the sense ‘turn into, metamorphose into’, only a noun would be pragmatically appropriate. There are several variants with verbs and subjective complements. The simplest form is VERB+COMPLEMENT. ...
... As the examples below show, the subjective complement may be a noun or an adjective, though for verbs with the sense ‘turn into, metamorphose into’, only a noun would be pragmatically appropriate. There are several variants with verbs and subjective complements. The simplest form is VERB+COMPLEMENT. ...
GCSE French Grammar Notes
... In English, the infinitive of a verb start with to + the verb: to eat. It’s also called a full verb. In French, l’infinitif is a single word with one of the following endings: -ER manger (to eat) -IR finir (to finish) -RE rendre (to give back) ...
... In English, the infinitive of a verb start with to + the verb: to eat. It’s also called a full verb. In French, l’infinitif is a single word with one of the following endings: -ER manger (to eat) -IR finir (to finish) -RE rendre (to give back) ...
ch13
... Tag tj occurs in one of the three previous positions Tag tj occurs two positions earlier and tag tk occurs in the following position ...
... Tag tj occurs in one of the three previous positions Tag tj occurs two positions earlier and tag tk occurs in the following position ...
Passive Voice
... Passive voice sentences are often used in process writing because they focus on the result of the process not on the person who does it. ...
... Passive voice sentences are often used in process writing because they focus on the result of the process not on the person who does it. ...
The Verb System Used in the Milashevich Method
... implies a habitual action, which is imperfective. The horizontal arrows are labelled 'every day' referring to a repeated action, thus also rendering it imperfective. The vertical arrows carry the label ‘already’, which implies a completed action, and thus they carry a perfective connotation. ...
... implies a habitual action, which is imperfective. The horizontal arrows are labelled 'every day' referring to a repeated action, thus also rendering it imperfective. The vertical arrows carry the label ‘already’, which implies a completed action, and thus they carry a perfective connotation. ...
Ancient Greek for Everyone
... • Greek distinguishes three grammatical genders: • Masculine, Feminine, Neuter • English mostly distinguishes these three genders only in pronouns: he, she, it. • For Greek nouns, by contrast, the gender is as much a part of the noun as its spelling and you must know a noun’s gender to comprehend Gr ...
... • Greek distinguishes three grammatical genders: • Masculine, Feminine, Neuter • English mostly distinguishes these three genders only in pronouns: he, she, it. • For Greek nouns, by contrast, the gender is as much a part of the noun as its spelling and you must know a noun’s gender to comprehend Gr ...
Kindergarten & First Grade Writing Folder
... Auxiliary verb (helping verb) employed by the main verb to show tense, mood or voice. These are: Modals which include can/could, may/might, shall/should, will/would and others. Other auxiliary verbs include do/does/did/done, be/am//is/are/been, was/were, have/has/had when combined with other verbs. ...
... Auxiliary verb (helping verb) employed by the main verb to show tense, mood or voice. These are: Modals which include can/could, may/might, shall/should, will/would and others. Other auxiliary verbs include do/does/did/done, be/am//is/are/been, was/were, have/has/had when combined with other verbs. ...
No nouns, no verbs? A rejoinder to Panagiotidis David Barner1 and
... (3) the types of syntactic rules that have been proposed to explain innovation do not result in clear syntactic violations; (4) many generated strings seem nonetheless unacceptable; (5) the details of meta-linguistic processes like analogy are not sufficiently specified to generate clear prediction ...
... (3) the types of syntactic rules that have been proposed to explain innovation do not result in clear syntactic violations; (4) many generated strings seem nonetheless unacceptable; (5) the details of meta-linguistic processes like analogy are not sufficiently specified to generate clear prediction ...
Possessive pronouns as determiners in Japanese-to
... This section describes the overall process of translation in ALT-J/E, and in particular how the possessive pronouns in noun phrases from groups (I) and (II) are translated. The overall process of translation can be divided into seven parts. First, ALT-J/E splits the Japanese text into morphemes. Sec ...
... This section describes the overall process of translation in ALT-J/E, and in particular how the possessive pronouns in noun phrases from groups (I) and (II) are translated. The overall process of translation can be divided into seven parts. First, ALT-J/E splits the Japanese text into morphemes. Sec ...
Slide 62 Daily Oral Language
... Dependent Clause Review A dependent clause is a sentence part that has both a subject and a verb and does not make sense by itself. For each sentence below write the dependent clause. 1. Before the ship pulls out, the captain must check the compass and the map. 2. Caught up in the festival excitemen ...
... Dependent Clause Review A dependent clause is a sentence part that has both a subject and a verb and does not make sense by itself. For each sentence below write the dependent clause. 1. Before the ship pulls out, the captain must check the compass and the map. 2. Caught up in the festival excitemen ...
1 e semaine de novembre
... venir et partir : Je pars en Europe pour six mois. With other verbs, you can use both depending if you want to emphasize the duration (using PENDANT) or the realization of the action (with POUR). ...
... venir et partir : Je pars en Europe pour six mois. With other verbs, you can use both depending if you want to emphasize the duration (using PENDANT) or the realization of the action (with POUR). ...
The structure of the English Sentence
... Never (before), No sooner... than, Not only ... but also, Nowhere, Seldom, Rarely, Scarcely (ever)... when. Little did I know about that problem. With Only after, Only if, Only when, Only by, Not since and Not till/until the inversion occurs in the main clause. Only if you see him will you understan ...
... Never (before), No sooner... than, Not only ... but also, Nowhere, Seldom, Rarely, Scarcely (ever)... when. Little did I know about that problem. With Only after, Only if, Only when, Only by, Not since and Not till/until the inversion occurs in the main clause. Only if you see him will you understan ...
Semantic change in the grammaticalization of classifiers in
... (1) the lexical meaning before a lexeme enters into the grammatical form, “NUM+NP/CL” (2) the classifier meaning in the grammatical form “NUM+CL+NP” categorical change: verbal/nominalclassifier meaning ...
... (1) the lexical meaning before a lexeme enters into the grammatical form, “NUM+NP/CL” (2) the classifier meaning in the grammatical form “NUM+CL+NP” categorical change: verbal/nominalclassifier meaning ...
Word order in English – Common Errors
... When there are more than one verb, we usually put an adverb after the first verb. Let's see the following examples: 1. I can never forget her. ( can = the first verb, forget = the second verb ) 2. She has always loved him. ( has = the first verb, loved = the second verb.) 3. This house has probably ...
... When there are more than one verb, we usually put an adverb after the first verb. Let's see the following examples: 1. I can never forget her. ( can = the first verb, forget = the second verb ) 2. She has always loved him. ( has = the first verb, loved = the second verb.) 3. This house has probably ...
Grammar20142015
... subordinator such as because, since, after, although, or when (and many others) or a relative pronoun such as that, who, or ...
... subordinator such as because, since, after, although, or when (and many others) or a relative pronoun such as that, who, or ...
teaching hebrew noun patterns through general
... Table 3 presents each pattern in its typical place, that is to say, it presents each pattern in its dominant semantic function (according to my perception and my findings), but it does not support an argument that every pattern has only one function, since this is untrue. The method of exposition ad ...
... Table 3 presents each pattern in its typical place, that is to say, it presents each pattern in its dominant semantic function (according to my perception and my findings), but it does not support an argument that every pattern has only one function, since this is untrue. The method of exposition ad ...
Journal of the Linguistic Society of Papua New Guinea
... feet of a duck in another pattern; it is the ‘picture’ that each Mind’s Eye sees which makes parts of the whole to be what they are in each person’s understanding. ...
... feet of a duck in another pattern; it is the ‘picture’ that each Mind’s Eye sees which makes parts of the whole to be what they are in each person’s understanding. ...
scientific writing #2
... Dependent clauses begin with introductory words such as: because, since, as, although, when Infinitive phrases are verb phrases that begin with the word “to” These help show the relative importance of details ...
... Dependent clauses begin with introductory words such as: because, since, as, although, when Infinitive phrases are verb phrases that begin with the word “to” These help show the relative importance of details ...