abstract
... aspect for L1 and L2 learners. In Russian, all verbs are either perfective or imperfective, and the use and meaning of aspect is a topic of long-standing debate (cf. Janda 2004 and Janda et al. 2013). It is unclear how children acquire this grammatical distinction in L1 (Stoll 2001), and it is clear ...
... aspect for L1 and L2 learners. In Russian, all verbs are either perfective or imperfective, and the use and meaning of aspect is a topic of long-standing debate (cf. Janda 2004 and Janda et al. 2013). It is unclear how children acquire this grammatical distinction in L1 (Stoll 2001), and it is clear ...
Document
... • Wednesday - wrap up semantics • + some comments on language preservation • also: in-class USRIs • Friday - review session (for whoever wants one) • We will attempt to grade the semantics homeworks between Wednesday and Friday. ...
... • Wednesday - wrap up semantics • + some comments on language preservation • also: in-class USRIs • Friday - review session (for whoever wants one) • We will attempt to grade the semantics homeworks between Wednesday and Friday. ...
to the definitions in Word format
... The form of a noun or pronoun that is employed in speaking or writing when referring to only one The essential basics of a story, narrative, or poem The subject of a sentence or clause is the part of the sentence or clause about which something is .. A group of letters added to the end of a word to ...
... The form of a noun or pronoun that is employed in speaking or writing when referring to only one The essential basics of a story, narrative, or poem The subject of a sentence or clause is the part of the sentence or clause about which something is .. A group of letters added to the end of a word to ...
Present Tenses
... 1.General truths and facts (to state truths and describe things which we FEEL are facts/permanent situations, things which are generally true) The British drink a lot of tea. A broken arm in adults doesn’t heal as fast as in kids. Birds fly south in the winter 2.Repeated events/actions (to describe ...
... 1.General truths and facts (to state truths and describe things which we FEEL are facts/permanent situations, things which are generally true) The British drink a lot of tea. A broken arm in adults doesn’t heal as fast as in kids. Birds fly south in the winter 2.Repeated events/actions (to describe ...
Subject Verb Agreement reminders
... Everybody who went on the France trip was staying a week longer to travel in Italy. *A few indefinite pronouns (all, any, none, some) may be singular or plural depending on the noun or pronoun they refer to. Some of our luggage was stolen. None of his complaints are valid. Some of the rocks are jagg ...
... Everybody who went on the France trip was staying a week longer to travel in Italy. *A few indefinite pronouns (all, any, none, some) may be singular or plural depending on the noun or pronoun they refer to. Some of our luggage was stolen. None of his complaints are valid. Some of the rocks are jagg ...
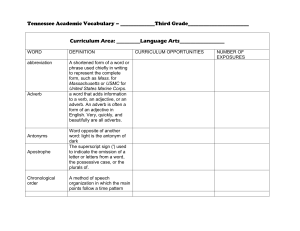
Year 5 Glossary
... places, or thing (i.e. its own name). It common, countable: a book, books, includes days of the week and months of the year, but not seasons. two chocolates, one day, fewer ideas Proper nouns start with a capital ...
... places, or thing (i.e. its own name). It common, countable: a book, books, includes days of the week and months of the year, but not seasons. two chocolates, one day, fewer ideas Proper nouns start with a capital ...
THE PHRASE
... decide, suggest when followed by that): His professor suggested (that) he take up writing classes; The board insisted that she resign immediately; The judge asked he be given a life sentence. The use of the mandative subjunctive is more common in American English. However, it has made a considerable ...
... decide, suggest when followed by that): His professor suggested (that) he take up writing classes; The board insisted that she resign immediately; The judge asked he be given a life sentence. The use of the mandative subjunctive is more common in American English. However, it has made a considerable ...
THE PHRASE
... decide, suggest when followed by that): His professor suggested (that) he take up writing classes; The board insisted that she resign immediately; The judge asked he be given a life sentence. The use of the mandative subjunctive is more common in American English. However, it has made a considerable ...
... decide, suggest when followed by that): His professor suggested (that) he take up writing classes; The board insisted that she resign immediately; The judge asked he be given a life sentence. The use of the mandative subjunctive is more common in American English. However, it has made a considerable ...
Confused Words
... Their, There, or They’re? There: Can be used either as an expletive at the beginning of a sentence or as an adverb. • There are many obstacles to a good harvest. • The fields over there will be ...
... Their, There, or They’re? There: Can be used either as an expletive at the beginning of a sentence or as an adverb. • There are many obstacles to a good harvest. • The fields over there will be ...
Genre of Literature
... Do now: Break down morphology this word /immobilization/ How many morphemes ? The word’s meaning? When morphemes are added to the end of a word it changes the parts of speech (word class) but it does not change the meaning. When they are added to the beginning of a word, the meaning changes but the ...
... Do now: Break down morphology this word /immobilization/ How many morphemes ? The word’s meaning? When morphemes are added to the end of a word it changes the parts of speech (word class) but it does not change the meaning. When they are added to the beginning of a word, the meaning changes but the ...
Subject and Verb Agreement
... 2. My friend (gives/give) me his potato chips at lunch. 3. She always (sings/sing) that song. 4. He (takes/take) pride in his work. 5. Gregory (fishes/fish) for bass in the lake. 6. We (is/are) tired and hungry. 7. The watermelons (was/were) sitting in the truck bed. 8. They (has/have) a blue house. ...
... 2. My friend (gives/give) me his potato chips at lunch. 3. She always (sings/sing) that song. 4. He (takes/take) pride in his work. 5. Gregory (fishes/fish) for bass in the lake. 6. We (is/are) tired and hungry. 7. The watermelons (was/were) sitting in the truck bed. 8. They (has/have) a blue house. ...
Parts of Speech
... A preposition is a word that shows the relationship of a noun or a pronoun to another word in a sentence. E.g. The mother of the kittens lives here. (Of shows the relationship of the mother to the kittens.) I will see you after lunch. (After expresses the time relationship between lunch and whe ...
... A preposition is a word that shows the relationship of a noun or a pronoun to another word in a sentence. E.g. The mother of the kittens lives here. (Of shows the relationship of the mother to the kittens.) I will see you after lunch. (After expresses the time relationship between lunch and whe ...
Y2 Curriculum and SATs Information
... or place (here, there, everywhere) Can come before or after the verb The spider wriggled wildly/ The mildly agitated spider The wizard grinned often/ The frequently moody babysitter.../ The bride was truly beautiful Games – Charades- How did you... Eat? (greedily, slowly, at speed, with enthusia ...
... or place (here, there, everywhere) Can come before or after the verb The spider wriggled wildly/ The mildly agitated spider The wizard grinned often/ The frequently moody babysitter.../ The bride was truly beautiful Games – Charades- How did you... Eat? (greedily, slowly, at speed, with enthusia ...
Reflexive Pronouns in RECIPROCAL actions
... – to take away quitar quitarse to take off – to lose perder perderse to get lost – to sleep dormir dormirse to fall asleep – to be located quedar quedarse to stay/remain – to return volver volverse to become Other verbs are always reflexive : – to realize darse cuenta de – to ...
... – to take away quitar quitarse to take off – to lose perder perderse to get lost – to sleep dormir dormirse to fall asleep – to be located quedar quedarse to stay/remain – to return volver volverse to become Other verbs are always reflexive : – to realize darse cuenta de – to ...
Sentence Fragments - San Jose State University
... Example: He, being[participle] part of the middle class, could not imagine how difficult it is to survive[infinitive] on minimum-wage earnings[gerund]. ◦ Predicates that are contained within dependent clauses cannot be used as the main verb in a sentence. Subordinating conjunctions (e.g if, since, b ...
... Example: He, being[participle] part of the middle class, could not imagine how difficult it is to survive[infinitive] on minimum-wage earnings[gerund]. ◦ Predicates that are contained within dependent clauses cannot be used as the main verb in a sentence. Subordinating conjunctions (e.g if, since, b ...
Glossary - Hatfield Academy
... Used with nouns they limit the reference of the noun in some way. There are a number of different types: Articles: a, an, the Demonstratives: this, that, these, those Possessives: my, your, his, her, its, our, their Quantifiers: some, any, no, many, much, few, little, both, all, either, neither, eac ...
... Used with nouns they limit the reference of the noun in some way. There are a number of different types: Articles: a, an, the Demonstratives: this, that, these, those Possessives: my, your, his, her, its, our, their Quantifiers: some, any, no, many, much, few, little, both, all, either, neither, eac ...
II final guia de estudio 2011
... o The verbs ser and estar are irregular in the preterite. Notice that the preterite forms of ser are identical to those of ir. Verbs with reflexive pronouns and direct obejects: (p.142) o You can use a reflexive pronoun with a direct object. The direct object is often a part of the body or something ...
... o The verbs ser and estar are irregular in the preterite. Notice that the preterite forms of ser are identical to those of ir. Verbs with reflexive pronouns and direct obejects: (p.142) o You can use a reflexive pronoun with a direct object. The direct object is often a part of the body or something ...
Exercise 1 - HCC Learning Web
... A verb phrase (VP) comes after the subject NP in a sentence. The VP can include one or more words, but it must contain a verb that tells time (past or present) and tense ( simple present, present continuous, simple past, present perfect, for example) or mood (modals). Most verbs show an action. Alth ...
... A verb phrase (VP) comes after the subject NP in a sentence. The VP can include one or more words, but it must contain a verb that tells time (past or present) and tense ( simple present, present continuous, simple past, present perfect, for example) or mood (modals). Most verbs show an action. Alth ...
LING 220 LECTURE #12 SYNTAX: THE ANALYSIS OF SENTENCE
... etc. The lexical category around which the phrase is built: HEAD of the phrase. It is not possible to have a VP without a V, a NP without a N, etc. However, it is possible to have a phrase in which only the HEAD position is filled: ...
... etc. The lexical category around which the phrase is built: HEAD of the phrase. It is not possible to have a VP without a V, a NP without a N, etc. However, it is possible to have a phrase in which only the HEAD position is filled: ...
Clauses Intro 11th
... clause for more information (*MUST have a S/V after it!) After, since, before, while, because, although, so that, if, when, whenever, as, even though, until, unless, etc. Examples: Because she was hungry. ...
... clause for more information (*MUST have a S/V after it!) After, since, before, while, because, although, so that, if, when, whenever, as, even though, until, unless, etc. Examples: Because she was hungry. ...
`Ground` Form Revisited - Stony Brook University
... Current analyses of the Arabic verb treat the ground form as basic, and there is frequently no distinction between the meaning associated with a consonantal root and the meaning assigned to the ground form verb in which that root appears (Holes, 2004; Watson, 2002). This causes problems when members ...
... Current analyses of the Arabic verb treat the ground form as basic, and there is frequently no distinction between the meaning associated with a consonantal root and the meaning assigned to the ground form verb in which that root appears (Holes, 2004; Watson, 2002). This causes problems when members ...