Types of Phrases Notes
... 3. Adverbs clause: A dependent clause introduced by subordinating conjunction can act the same way as a one word adverb. Put a comma after the dependent clause if it precedes the main clause; do not use a comma if the dependent clause comes after the main clause. Adverb (or subordinate) clauses are ...
... 3. Adverbs clause: A dependent clause introduced by subordinating conjunction can act the same way as a one word adverb. Put a comma after the dependent clause if it precedes the main clause; do not use a comma if the dependent clause comes after the main clause. Adverb (or subordinate) clauses are ...
Pie Corbett`s Talk for Writing teaching guide for progression in
... Short sentences to move events on quickly e.g. It was midnight. It’s great fun. Start with a simile e.g. As curved as a ball, the moon shone brightly ...
... Short sentences to move events on quickly e.g. It was midnight. It’s great fun. Start with a simile e.g. As curved as a ball, the moon shone brightly ...
Adverbs - Monmouth University
... This form compares a greater or lesser degree of whatever quality is named. The structure of a comparative is usually formed with the positive form of the adverb, plus the suffix –er, or (especially in the case of longer words) the modifiers “more” (or “less”) before the adverb. For example: sooner, ...
... This form compares a greater or lesser degree of whatever quality is named. The structure of a comparative is usually formed with the positive form of the adverb, plus the suffix –er, or (especially in the case of longer words) the modifiers “more” (or “less”) before the adverb. For example: sooner, ...
I was sure I was correct. Shannon is surely ready for her final exam
... This form compares a greater or lesser degree of whatever quality is named. The structure of a comparative is usually formed with the positive form of the adverb, plus the suffix –er, or (especially in the case of longer words) the modifiers “more” (or “less”) before the adverb. For example: sooner, ...
... This form compares a greater or lesser degree of whatever quality is named. The structure of a comparative is usually formed with the positive form of the adverb, plus the suffix –er, or (especially in the case of longer words) the modifiers “more” (or “less”) before the adverb. For example: sooner, ...
Standard(s) - WordPress.com
... practice with examples of - I want + infinitive, I would like + infinitive. They will practice asking and responding in pairs: What do you want (to do) now? What would you like to do today? W, H, E, R, T, O Concurrently, Heritage speaking students will practice and enhance their literacy skills in L ...
... practice with examples of - I want + infinitive, I would like + infinitive. They will practice asking and responding in pairs: What do you want (to do) now? What would you like to do today? W, H, E, R, T, O Concurrently, Heritage speaking students will practice and enhance their literacy skills in L ...
Bleached taboo-term predicates in American Sign Language
... In the present paper, the terms studied involve religion and sex. While the predicates here, with one exception, are historically based on taboo-terms, they have lost the emotional charge typically associated with taboo terms to such an extent that many signers use them now without intending any sen ...
... In the present paper, the terms studied involve religion and sex. While the predicates here, with one exception, are historically based on taboo-terms, they have lost the emotional charge typically associated with taboo terms to such an extent that many signers use them now without intending any sen ...
Pronouns - Alexis Kitchens
... • You will find "who," "whom," and occasionally "which" used to refer to people, and "which" and "what" used to refer to things and to animals. • "Who" acts as the subject of a verb, while "whom" acts as the object of a verb, preposition, or a verbal. • Which wants to see the dentist first? • ("Whic ...
... • You will find "who," "whom," and occasionally "which" used to refer to people, and "which" and "what" used to refer to things and to animals. • "Who" acts as the subject of a verb, while "whom" acts as the object of a verb, preposition, or a verbal. • Which wants to see the dentist first? • ("Whic ...
Las clases avanzadas de Español
... ONLY IF the action has not yet happened. Finally, look out for words like aunque, donde, cuando, quien that MIGHT require the subjunctive or the indicative. ...
... ONLY IF the action has not yet happened. Finally, look out for words like aunque, donde, cuando, quien that MIGHT require the subjunctive or the indicative. ...
Slide 62 Daily Oral Language
... 2. “When did you buy it?” she ask them. 3. Jane asked, “When will we are able to go sailing?” 4. Her father thinked, that he should ...
... 2. “When did you buy it?” she ask them. 3. Jane asked, “When will we are able to go sailing?” 4. Her father thinked, that he should ...
Syntactic and semantic constraints on the formation and
... assuming that the roots from which they are constructed are so-called ‘manner’ roots – roots which act as predicates of the events that the verbs describe. In this regard, the verbs in (6a) do not differ essentially from those in (6b). Those verbs too are built from roots that express properties of ...
... assuming that the roots from which they are constructed are so-called ‘manner’ roots – roots which act as predicates of the events that the verbs describe. In this regard, the verbs in (6a) do not differ essentially from those in (6b). Those verbs too are built from roots that express properties of ...
Verbals powerpoint
... An Infinitive Phrase is a group of words consisting of an infinitive and followed most often by modifiers, direct objects, and/or prepositional phrases. We intended to leave early. The infinitive phrase functions as the direct object of the verb intended. to leave (infinitive) early (adverb) I have ...
... An Infinitive Phrase is a group of words consisting of an infinitive and followed most often by modifiers, direct objects, and/or prepositional phrases. We intended to leave early. The infinitive phrase functions as the direct object of the verb intended. to leave (infinitive) early (adverb) I have ...
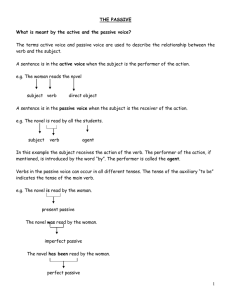
THE PASSIVE
... What is meant by the active and the passive voice? The terms active voice and passive voice are used to describe the relationship between the verb and the subject. A sentence is in the active voice when the subject is the performer of the action. e.g. The woman reads the novel ...
... What is meant by the active and the passive voice? The terms active voice and passive voice are used to describe the relationship between the verb and the subject. A sentence is in the active voice when the subject is the performer of the action. e.g. The woman reads the novel ...
Single Morpheme Tendencies in Spanish English Codeswitching
... therefore insertions permitted in the MLF Model. Nouns by far outnumber all other lexical categories among insertions. Other researchers, including Gardner-Chloros (1995: 74), Poplack, Wheeler, and Westwood (1990: 193), Köppe and Meisel (1995: 281-282), and Myers-Scotton (1993b: 15), have found tha ...
... therefore insertions permitted in the MLF Model. Nouns by far outnumber all other lexical categories among insertions. Other researchers, including Gardner-Chloros (1995: 74), Poplack, Wheeler, and Westwood (1990: 193), Köppe and Meisel (1995: 281-282), and Myers-Scotton (1993b: 15), have found tha ...
from latin to english: functional shift and malpropism
... Many Latin adverbs reappear as English nouns. Latin alibi means 'elsewhere', but is used in English of 'a plea that one was in another place at the time when a crime was committed'. Tandem, 'at length' in Latin, appears in eithteenth-century English in the sense 'a twowheeled vehicle drawn by two ho ...
... Many Latin adverbs reappear as English nouns. Latin alibi means 'elsewhere', but is used in English of 'a plea that one was in another place at the time when a crime was committed'. Tandem, 'at length' in Latin, appears in eithteenth-century English in the sense 'a twowheeled vehicle drawn by two ho ...
Source: History_of_Spanish_Language_Irregularities
... everywhere else had evolved to con. So speakers added the preposition con to the beginning of these forms, producing conmego, contego, consego, which quickly shifted to conmigo, contigo, consigo because the pronouns mí, ti, si (not me, te, se) followed all other prepositions. QUESTION: Why do some v ...
... everywhere else had evolved to con. So speakers added the preposition con to the beginning of these forms, producing conmego, contego, consego, which quickly shifted to conmigo, contigo, consigo because the pronouns mí, ti, si (not me, te, se) followed all other prepositions. QUESTION: Why do some v ...
Gerund
... An Infinitive Phrase is a group of words consisting of an infinitive and followed most often by modifiers, direct objects, and/or prepositional phrases. We intended to leave early. The infinitive phrase functions as the direct object of the verb intended. to leave (infinitive) early (adverb) I have ...
... An Infinitive Phrase is a group of words consisting of an infinitive and followed most often by modifiers, direct objects, and/or prepositional phrases. We intended to leave early. The infinitive phrase functions as the direct object of the verb intended. to leave (infinitive) early (adverb) I have ...
Complement Structures Equi and Raising
... CONTENT is token identical to the CONTENT of the XP[+PRD] The unexpressed subject of the XP[+PRD] complement is structure shared with the postcopular NP complement CONTENT is not determined by subject, but by the postcopular NP and the XP element CONTENT is complete even before adding Subject NPth ...
... CONTENT is token identical to the CONTENT of the XP[+PRD] The unexpressed subject of the XP[+PRD] complement is structure shared with the postcopular NP complement CONTENT is not determined by subject, but by the postcopular NP and the XP element CONTENT is complete even before adding Subject NPth ...
Interrogating possessive have: a case study
... got is mentioned as a possessive construction, with a note that it is “more often used instead of the present tense of have when talking about possession” (Hands & Berry 2011: 151). In the late American generative linguist James D. McCawley’s famous handbook titled The Major Syntactic Phenomena of E ...
... got is mentioned as a possessive construction, with a note that it is “more often used instead of the present tense of have when talking about possession” (Hands & Berry 2011: 151). In the late American generative linguist James D. McCawley’s famous handbook titled The Major Syntactic Phenomena of E ...
It`s the book. (this sentence is incomplete) Defining relative clauses
... It takes the place of his, her, their or a noun in possessive case ‘s. Andy Warhol was a pop artist whose paintings are famous worldwide.(His paintings are ...
... It takes the place of his, her, their or a noun in possessive case ‘s. Andy Warhol was a pop artist whose paintings are famous worldwide.(His paintings are ...
Study Sheet: Dossier #1 (Episode #1) - Request a Spot account
... venir = viendr, avoir = aur, pouvoir = pourr, vouloir = voudr, devoir = devr. Refer to your irregular verb sheet for others. You will always get a better response from Francophone speakers if you use the conditional to make requests. It also serves as an indicator of your level of proficiency in the ...
... venir = viendr, avoir = aur, pouvoir = pourr, vouloir = voudr, devoir = devr. Refer to your irregular verb sheet for others. You will always get a better response from Francophone speakers if you use the conditional to make requests. It also serves as an indicator of your level of proficiency in the ...
spanish iii review guide for final exam
... certain, factual, real – i.e., actions and events that belong to the realm of her experience of the world (note that “experience” includes things one “knows” indirectly through books, TV, other people, etc.). She uses the subjunctive to talk about actions and events that she regards as being in some ...
... certain, factual, real – i.e., actions and events that belong to the realm of her experience of the world (note that “experience” includes things one “knows” indirectly through books, TV, other people, etc.). She uses the subjunctive to talk about actions and events that she regards as being in some ...
Pronoun Concord
... It is Kay who is in command. It is they who are complaining. But 3rd person concord prevails in informal English where the objective case pronoun me is used: It's me who's to blame. Similarly, 3rd person singular may be used in informal English in these constructions when the pronoun you has singula ...
... It is Kay who is in command. It is they who are complaining. But 3rd person concord prevails in informal English where the objective case pronoun me is used: It's me who's to blame. Similarly, 3rd person singular may be used in informal English in these constructions when the pronoun you has singula ...
Compound Subjects, Predicates, and Sentences
... Here. V and but or Sam and Pam are best friends. ...
... Here. V and but or Sam and Pam are best friends. ...