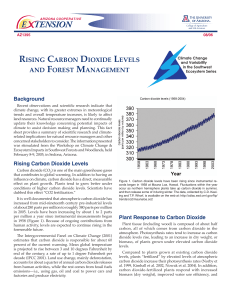
Rising Carbon Dioxide Levels and Forest Management
... keeping carbon sequestered in southwestern forests. Forestry practices such as thinning treatments, intermediate, shelterwood and seed-tree harvest cuts, as opposed to clear-cuts, also leave many mature trees standing. Carbon dioxide continues to be taken up by the remaining trees, which can grow be ...
... keeping carbon sequestered in southwestern forests. Forestry practices such as thinning treatments, intermediate, shelterwood and seed-tree harvest cuts, as opposed to clear-cuts, also leave many mature trees standing. Carbon dioxide continues to be taken up by the remaining trees, which can grow be ...
The Carbon Cycle – Questions on reading web article
... CO2. Burning oil and coal releases carbon into the atmosphere far more rapidly than it is being removed, and this imbalance causes atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations to increase. In addition, by clearing forests, we reduce the ability of photosynthesis to remove CO2 from the atmosphere, also ...
... CO2. Burning oil and coal releases carbon into the atmosphere far more rapidly than it is being removed, and this imbalance causes atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations to increase. In addition, by clearing forests, we reduce the ability of photosynthesis to remove CO2 from the atmosphere, also ...
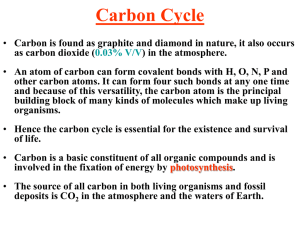
Carbon Cycle
... • The Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is an amendment to the international treaty on climate change, assigning mandatory emission limitations for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions to the signatory nations. • The objective of the protocol is the "st ...
... • The Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is an amendment to the international treaty on climate change, assigning mandatory emission limitations for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions to the signatory nations. • The objective of the protocol is the "st ...
1 Carbon management and scenario planning at landscape scale
... step when quantifying regional and global C budgets (Paustian et al., 1997). The modelling of SOC content is a way of indirectly assessing C sequestration to complement direct measurements. Modelling may also help in the identification of areas with a large potential for increased SOC sequestration ...
... step when quantifying regional and global C budgets (Paustian et al., 1997). The modelling of SOC content is a way of indirectly assessing C sequestration to complement direct measurements. Modelling may also help in the identification of areas with a large potential for increased SOC sequestration ...
A Pilot Project in the Thermal Power Plant of NALCO, India (Pradhan).
... Agriculture Organization of United Nations, http://www.fao.org/forestry/17111/en/ 2. Carbon to Amount CO2 1 mole of carbon give 1 mol of CO2 Molcular wt of C = 12 & CO2 is 44 So Molar ratio = 44/12 = 3.6 ( 1 kg of carbon is equivalent to 3.6 kg of CO2) 3. Sequestration of CO2 48kg biomass / 2 = 24 k ...
... Agriculture Organization of United Nations, http://www.fao.org/forestry/17111/en/ 2. Carbon to Amount CO2 1 mole of carbon give 1 mol of CO2 Molcular wt of C = 12 & CO2 is 44 So Molar ratio = 44/12 = 3.6 ( 1 kg of carbon is equivalent to 3.6 kg of CO2) 3. Sequestration of CO2 48kg biomass / 2 = 24 k ...
http://www.tigurl.org/images/tiged/docs/activities/565.pdf
... and oceans uses carbon dioxide dissolved in water. Phytoplankton is one of these important plants as they produce up to 50% of the atmospheric oxygen through photosynthesis. Other important sinks are the worlds oceans. The world’s oceans are absorbing an unprecedented amount of carbon dioxide (CO2), ...
... and oceans uses carbon dioxide dissolved in water. Phytoplankton is one of these important plants as they produce up to 50% of the atmospheric oxygen through photosynthesis. Other important sinks are the worlds oceans. The world’s oceans are absorbing an unprecedented amount of carbon dioxide (CO2), ...
Long-term grazing exclusion did not provide adequate soil carbon
... and vegetation has been widely emphasized. Evidence is now emerging that a significant proportion of the carbon is stored in soils as opposed to vegetation. Soils store the largest amount of terrestrial carbon as plant residues and litters. Consequently, there is increasing need to link soil carbon ...
... and vegetation has been widely emphasized. Evidence is now emerging that a significant proportion of the carbon is stored in soils as opposed to vegetation. Soils store the largest amount of terrestrial carbon as plant residues and litters. Consequently, there is increasing need to link soil carbon ...
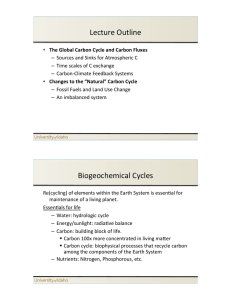
Lecture`Outline` Biogeochemical`Cycles`
... plant biomass using sunlight. Carbon flux from atmosphere to organic carbon in vegetation. Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight = Sugar+ Oxygen Respiration: Release of carbon from plant biomass into atmospheric carbon dioxide (opposite of photosynthesis, accelerated by enzymes) ...
... plant biomass using sunlight. Carbon flux from atmosphere to organic carbon in vegetation. Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight = Sugar+ Oxygen Respiration: Release of carbon from plant biomass into atmospheric carbon dioxide (opposite of photosynthesis, accelerated by enzymes) ...
potential carbon sequestration projects in the philippines 126
... forests contributed 3.7 billion tonnes of C to the atmosphere of which 70 per cent (2.6 billion tonnes) were released this century (Lasco and Pulhin 2000). However, present land-use cover also absorbs carbon through regenerating forests and planted trees. The vast areas of degraded land in the Phili ...
... forests contributed 3.7 billion tonnes of C to the atmosphere of which 70 per cent (2.6 billion tonnes) were released this century (Lasco and Pulhin 2000). However, present land-use cover also absorbs carbon through regenerating forests and planted trees. The vast areas of degraded land in the Phili ...
Document
... included in this mini-unit are centered on one aspect of carbon sequestration -- forests/trees as carbon sinks, though teachers can feel free to expand this discussion by including other natural carbon sinks (e.g. soil), as well as those produced by human ingenuity (see Activity 11 in the Carbon TE ...
... included in this mini-unit are centered on one aspect of carbon sequestration -- forests/trees as carbon sinks, though teachers can feel free to expand this discussion by including other natural carbon sinks (e.g. soil), as well as those produced by human ingenuity (see Activity 11 in the Carbon TE ...
Long-term grazing exclusion did not provide adequate soil carbon
... and vegetation has been widely emphasized. Evidence is now emerging that a significant proportion of the carbon is stored in soils as opposed to vegetation. Soils store the largest amount of terrestrial carbon as plant residues and litters. Consequently, there is increasing need to link soil carbon ...
... and vegetation has been widely emphasized. Evidence is now emerging that a significant proportion of the carbon is stored in soils as opposed to vegetation. Soils store the largest amount of terrestrial carbon as plant residues and litters. Consequently, there is increasing need to link soil carbon ...
Introduction
... organic carbon stocks and stock changes. These methods are characterized by flexibility, ranging from the Tier 1 default method prescribed by IPCC with fixed default values, to methods that incorporate local information to estimate carbon stock changes at Tier 2 level, and to more advanced modelling ...
... organic carbon stocks and stock changes. These methods are characterized by flexibility, ranging from the Tier 1 default method prescribed by IPCC with fixed default values, to methods that incorporate local information to estimate carbon stock changes at Tier 2 level, and to more advanced modelling ...
Wetlands and carbon - Waquoit Bay National Estuarine Research
... releases. Carbon sinks can serve to partially offset greenhouse gas emissions. Forests and oceans are both large carbon sinks. Carbon source: A reservoir or component of the carbon cycle that releases more carbon than it absorbs. For example, emissions through the burning of fossil fuels are a sourc ...
... releases. Carbon sinks can serve to partially offset greenhouse gas emissions. Forests and oceans are both large carbon sinks. Carbon source: A reservoir or component of the carbon cycle that releases more carbon than it absorbs. For example, emissions through the burning of fossil fuels are a sourc ...
GLOBAL SYMPOSIUM ON SOIL ORGANIC CARBON, Rome, Italy
... soil carbon storage needed in every terrestrial habitat and ecosystem, but increases in soil carbon storage lifetime will also be essential. We calculate here how long it takes to reduce atmospheric CO2 to safe preindustrial levels and show the results graphically as a function of the global increas ...
... soil carbon storage needed in every terrestrial habitat and ecosystem, but increases in soil carbon storage lifetime will also be essential. We calculate here how long it takes to reduce atmospheric CO2 to safe preindustrial levels and show the results graphically as a function of the global increas ...
Sequestration of Carbon Along Our Coasts: Important Sinks
... Wetlands have been valued to be worth over $2,800 per hectare on average globally. More specifically, mangrove forests provide at least US $1.6 billion each year in ecosystem services and support coastal livelihoods worldwide. It is estimated that almost 80% of global fish catches are directly or in ...
... Wetlands have been valued to be worth over $2,800 per hectare on average globally. More specifically, mangrove forests provide at least US $1.6 billion each year in ecosystem services and support coastal livelihoods worldwide. It is estimated that almost 80% of global fish catches are directly or in ...
What satellites tell us about the global carbon budget
... Tipping Points in the Carbon-Climate System If the natural sinks on land and ocean are beginning to decline: 1.more of the carbon emitted stays in the atmosphere, 2.the rate of climatic disruption increases, 3.it is more difficult to manage the carbon cycle, 4.the carbon cycle is not behaving as th ...
... Tipping Points in the Carbon-Climate System If the natural sinks on land and ocean are beginning to decline: 1.more of the carbon emitted stays in the atmosphere, 2.the rate of climatic disruption increases, 3.it is more difficult to manage the carbon cycle, 4.the carbon cycle is not behaving as th ...
What Trees Can Do to Reduce Atmospheric C02
... have occurred over the last 200 years. Collectively, these gases are referred to as ‘greenhouse gases’ (GHG), because they absorb longwave radiation emitted from the Earth and this leads to the heating of the atmosphere. From gases trapped in bubbles in ice cores, it is known that the concentration ...
... have occurred over the last 200 years. Collectively, these gases are referred to as ‘greenhouse gases’ (GHG), because they absorb longwave radiation emitted from the Earth and this leads to the heating of the atmosphere. From gases trapped in bubbles in ice cores, it is known that the concentration ...
Expert Scientific Statement: The Potential of Irish Grassland Soils to
... Secondly, there is now a growing body of international published research from Europe, New Zealand, China and the USA (Feng, 2012; Feng et al., 2013) showing that many grassland soils are not carbon saturated, and therefore have the potential to sequester additional carbon from the atmosphere for m ...
... Secondly, there is now a growing body of international published research from Europe, New Zealand, China and the USA (Feng, 2012; Feng et al., 2013) showing that many grassland soils are not carbon saturated, and therefore have the potential to sequester additional carbon from the atmosphere for m ...
Carbon Dioxide: Present Scenario, Future Trends and Techniques
... Biochar is a black carbon material produced from the decomposition of plant-derived organic matter (biomass) in a low or zero oxygen environment (i.e. pyrolysis or gasification) to release energy rich gases which are then used for producing liquid fuels or directly for power generation [11]. Plants ...
... Biochar is a black carbon material produced from the decomposition of plant-derived organic matter (biomass) in a low or zero oxygen environment (i.e. pyrolysis or gasification) to release energy rich gases which are then used for producing liquid fuels or directly for power generation [11]. Plants ...
PDF
... conditions existing across the state (Slide 14). The results from the assessment were compiled into a database that can be queried by local managers by county and soil type, to display estimated changes in soil carbon for a variety of different management alternatives (Slide 15). The data were also ...
... conditions existing across the state (Slide 14). The results from the assessment were compiled into a database that can be queried by local managers by county and soil type, to display estimated changes in soil carbon for a variety of different management alternatives (Slide 15). The data were also ...
Important Concepts for chemical cycling
... • An “endangered” species is one that is in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant portion of its range. A “threatened” species is one that is likely to become endangered in the foreseeable future. ...
... • An “endangered” species is one that is in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant portion of its range. A “threatened” species is one that is likely to become endangered in the foreseeable future. ...
Giving Definition to Indefinite Contracts for the Trading, Storage and
... Carbon dioxide is a versatile material, being used in many processes and applications - each of which takes advantage of one or more these characteristics: reactivity, inertness and/ or coldness. Carbon dioxide is commonly used as a raw material for production of various chemicals; as a working mate ...
... Carbon dioxide is a versatile material, being used in many processes and applications - each of which takes advantage of one or more these characteristics: reactivity, inertness and/ or coldness. Carbon dioxide is commonly used as a raw material for production of various chemicals; as a working mate ...
What_are_scientists_trying_to_find_out
... Globally, wetlands store an estimated 300 to 700 billion tons of carbon. “The existing storage of carbon in wetlands approaches the amount of carbon you have in the atmosphere,” says Jon Kusler, associate director of the Association of State Wetland Managers. Scott Bridgham at the University of Oreg ...
... Globally, wetlands store an estimated 300 to 700 billion tons of carbon. “The existing storage of carbon in wetlands approaches the amount of carbon you have in the atmosphere,” says Jon Kusler, associate director of the Association of State Wetland Managers. Scott Bridgham at the University of Oreg ...
MSWord
... decomposition and (2) nutrient release. The overall effect of this is the transfer of CO2 and nutrients between surface waters and the deep ocean. Terrestrial sinks are also where a lot of carbon is stored, taken out from the atmosphere, until chemical processes can remove it again. One of the great ...
... decomposition and (2) nutrient release. The overall effect of this is the transfer of CO2 and nutrients between surface waters and the deep ocean. Terrestrial sinks are also where a lot of carbon is stored, taken out from the atmosphere, until chemical processes can remove it again. One of the great ...
the 4 per mil concept - Agriculture and agricultural soils facing
... Carbon sequestration in soils • The adoption of best agronomic practices allows a significant carbon sequestration rate, reaching locally up to 4 per mil (4‰) of the soil organic carbon stock for some of the documented examples. • Over a meaningful depth for carbon sequestration, i.e. 0-40 cm, the ...
... Carbon sequestration in soils • The adoption of best agronomic practices allows a significant carbon sequestration rate, reaching locally up to 4 per mil (4‰) of the soil organic carbon stock for some of the documented examples. • Over a meaningful depth for carbon sequestration, i.e. 0-40 cm, the ...
Carbon sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of capture and long-term storage of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon sequestration describes long-term storage of carbon dioxide or other forms of carbon to either mitigate or defer global warming and avoid dangerous climate change. It has been proposed as a way to slow the atmospheric and marine accumulation of greenhouse gases, which are released by burning fossil fuels.Carbon dioxide is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, or physical processes. Artificial processes have been devised to produce similar effects, including large-scale, artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced CO2 using subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks.