AQA ECON3 – June 2013 – Q7 – Model Answer
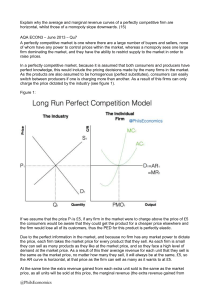
... If we assume that the price P1 is £5, if any firm in the market were to charge above the price of £5 the consumers would be aware that they could get the product for a cheaper price elsewhere and the firm would lose all of its customers, thus the PED for this product is perfectly elastic. Due to the ...
... If we assume that the price P1 is £5, if any firm in the market were to charge above the price of £5 the consumers would be aware that they could get the product for a cheaper price elsewhere and the firm would lose all of its customers, thus the PED for this product is perfectly elastic. Due to the ...
Lecture 01
... – An industry with only a few large sellers. – Entry by new competitors is hard because large capital investment is needed. – The actions of one firm can significantly affect the sales of every other firm in the industry. – The prices of comparable products are usually similar. – As the trend toward ...
... – An industry with only a few large sellers. – Entry by new competitors is hard because large capital investment is needed. – The actions of one firm can significantly affect the sales of every other firm in the industry. – The prices of comparable products are usually similar. – As the trend toward ...
5. Unit 4- Market structures
... Governments also protect consumers from being sold poor quality or even harmful goods through consumer protection laws. These protect consumers from exploitation and harmful business activities, e.g. it is an offence to sell goods or services which are unsafe or in an unsatisfactory condition or to ...
... Governments also protect consumers from being sold poor quality or even harmful goods through consumer protection laws. These protect consumers from exploitation and harmful business activities, e.g. it is an offence to sell goods or services which are unsafe or in an unsatisfactory condition or to ...
Eco 284
... Complete the following questions. Label all graphs completely. 10 points each. 1. Using a general example, prove the profit maximizing decision rule for determining the output level. Note: a mathematical (calculus) proof is neither necessary nor sufficient - you must include economic definitions for ...
... Complete the following questions. Label all graphs completely. 10 points each. 1. Using a general example, prove the profit maximizing decision rule for determining the output level. Note: a mathematical (calculus) proof is neither necessary nor sufficient - you must include economic definitions for ...
Review of Supply and Demand
... In addition to the price of a good, factors that may affect the supply for a good are: P Prices of other goods that firms could produce ...
... In addition to the price of a good, factors that may affect the supply for a good are: P Prices of other goods that firms could produce ...
4. Market Profile Instructions
... • Explain the process of market segmentation as one of identifying the “dimensions” of a market (e.g. demographic dimensions, geographic dimensions, and behavioural dimensions) that are most likely to be influenced by the product and marketing effort • Students could… • Put a monetary dimension to t ...
... • Explain the process of market segmentation as one of identifying the “dimensions” of a market (e.g. demographic dimensions, geographic dimensions, and behavioural dimensions) that are most likely to be influenced by the product and marketing effort • Students could… • Put a monetary dimension to t ...
The market
... We have become more specialised and as a result have become more interdependent with other people. By specialling we need to exchange goods and services and there must be some formal way of making these exchanges. Diversity of markets -size and extent Markets can be small, relatively large and huge ...
... We have become more specialised and as a result have become more interdependent with other people. By specialling we need to exchange goods and services and there must be some formal way of making these exchanges. Diversity of markets -size and extent Markets can be small, relatively large and huge ...
UNIT C The Business of Fashion
... •What is the most efficient method of transportation? •Storing products** ...
... •What is the most efficient method of transportation? •Storing products** ...
Target Market
... potential customer who has an unfulfilled desire and is FINANCIALLY ABLE AND WILLING to satisfy that desire. Businesses strive to meet the needs and wants of their customers. ...
... potential customer who has an unfulfilled desire and is FINANCIALLY ABLE AND WILLING to satisfy that desire. Businesses strive to meet the needs and wants of their customers. ...
Why a circular flow?
... Product markets • Operate as the points of exchange between consumers who use money incomes to buy these goods and services produced by businesses. • Money income itself does not have value, since money must be used in exchange for the goods and services that satisfy our wants. ...
... Product markets • Operate as the points of exchange between consumers who use money incomes to buy these goods and services produced by businesses. • Money income itself does not have value, since money must be used in exchange for the goods and services that satisfy our wants. ...
Understanding Marketing
... enough of the organization’s products. The organization must, therefore, undertake an aggressive selling and promotion effort ...
... enough of the organization’s products. The organization must, therefore, undertake an aggressive selling and promotion effort ...
Microeconomic Concepts Describe how households, businesses
... Oligopoly – a market structure in which a few, relatively large firms account for all or most of the production or sale of a good or service in a market, barriers to new producers are high. Examples are cars, airlines, and movie studios. Monopolistic competition – a market structure where slightly d ...
... Oligopoly – a market structure in which a few, relatively large firms account for all or most of the production or sale of a good or service in a market, barriers to new producers are high. Examples are cars, airlines, and movie studios. Monopolistic competition – a market structure where slightly d ...
EOCT Study Guide
... Oligopoly – a market structure in which a few, relatively large firms account for all or most of the production or sale of a good or service in a market, barriers to new producers are high. Examples are cars, airlines, and movie studios. Monopolistic competition – a market structure where slightly d ...
... Oligopoly – a market structure in which a few, relatively large firms account for all or most of the production or sale of a good or service in a market, barriers to new producers are high. Examples are cars, airlines, and movie studios. Monopolistic competition – a market structure where slightly d ...























