Bases of International Marketing
... arise because of dumping (selling a product in a foreign market at a price lower than it is sold for in the domestic market). Other Goals: Development of people; ‘offshore’ plants to supply home markets. Companies usually operate with multiple goals in ...
... arise because of dumping (selling a product in a foreign market at a price lower than it is sold for in the domestic market). Other Goals: Development of people; ‘offshore’ plants to supply home markets. Companies usually operate with multiple goals in ...
INTRODUCTION
... Therefore not everyone can have everything they want. That is what we mean by scarcity. Microeconomics is the study of how individuals and firms can make themselves as well off as possible in a world of scarcity, and the consequences of those individual decisions for markets and the entire ...
... Therefore not everyone can have everything they want. That is what we mean by scarcity. Microeconomics is the study of how individuals and firms can make themselves as well off as possible in a world of scarcity, and the consequences of those individual decisions for markets and the entire ...
price determination
... price, Many producers with the willingness and ability to supply the product at a certain price. Homogeneous Products – The products of the different firms are EXACTLY the same, e.g. fruit. Low-Entry/Exit Barriers – It is relatively easy to enter or exit as a business in a perfectly competitive mark ...
... price, Many producers with the willingness and ability to supply the product at a certain price. Homogeneous Products – The products of the different firms are EXACTLY the same, e.g. fruit. Low-Entry/Exit Barriers – It is relatively easy to enter or exit as a business in a perfectly competitive mark ...
Economics - cloudfront.net
... Lastly, simply explain how new firms have incentive to enter the market after the shift in demand for the product and its effect on marginal revenue and therefore profitability. Part B i. Explain the four conditions that exist for a monopolistic firm and market. ii. Explain and demonstrate why the r ...
... Lastly, simply explain how new firms have incentive to enter the market after the shift in demand for the product and its effect on marginal revenue and therefore profitability. Part B i. Explain the four conditions that exist for a monopolistic firm and market. ii. Explain and demonstrate why the r ...
Information Exchange
... -(1) The information was also individually accessible, albeit against higher costs, and: -(2) It was questionable whether there really were substantial barriers to entry, because non-members managed to compete successfully on the market. Legal and economic approach Nederlandse ...
... -(1) The information was also individually accessible, albeit against higher costs, and: -(2) It was questionable whether there really were substantial barriers to entry, because non-members managed to compete successfully on the market. Legal and economic approach Nederlandse ...
Marketing Strategies
... Two Types of People with Needs & Wants Customers vs. Consumers Customers buy a product. Consumers use the product. Example: Parents who buy video games from retailers are customers. The kids who play the video games are the consumers. ...
... Two Types of People with Needs & Wants Customers vs. Consumers Customers buy a product. Consumers use the product. Example: Parents who buy video games from retailers are customers. The kids who play the video games are the consumers. ...
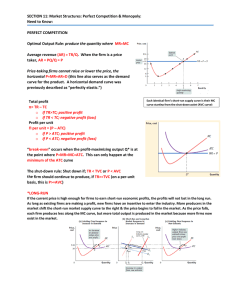
SECTION 11: Market Structures: Perfect Competition & Monopoly: Need to Know: PERFECT COMPETITION
... the point where P=MR=MC=ATC. This can only happen at the minimum of the ATC curve ...
... the point where P=MR=MC=ATC. This can only happen at the minimum of the ATC curve ...
Introduction to Business
... which are frequently bought locally, with little consideration of the price charged since purchases are usually on a small scale and convenience is rated more highly than economy ...
... which are frequently bought locally, with little consideration of the price charged since purchases are usually on a small scale and convenience is rated more highly than economy ...
PROMOTION and PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION LECTURE Promotioni
... much as they had. Where to spend it is decided in the marketing mix. Advertising: Objectives -- inform, convince, remind, motivate, and support sales team or distributor. (Another way of saying this is: Aim at immediate sale or consideration of brand or build reservoir of good will.) Directed to ult ...
... much as they had. Where to spend it is decided in the marketing mix. Advertising: Objectives -- inform, convince, remind, motivate, and support sales team or distributor. (Another way of saying this is: Aim at immediate sale or consideration of brand or build reservoir of good will.) Directed to ult ...
Name
... 1. service - the act that a person does in return for pay 2. scarcity - not enough to meet a demand; when people want more goods and services than available 3. goods - the objects that are made from resources; these objects may be sold to make money. 4. economics - the business of buying and selling ...
... 1. service - the act that a person does in return for pay 2. scarcity - not enough to meet a demand; when people want more goods and services than available 3. goods - the objects that are made from resources; these objects may be sold to make money. 4. economics - the business of buying and selling ...
Chapter Three
... tourism market, which alert coach operators have seized. Clearly, this demand did not exist until the centre was open, but the operators with good market research will profit from this new revenue earning opportunity. Competition Unless a business can obtain such a stranglehold on the market that it ...
... tourism market, which alert coach operators have seized. Clearly, this demand did not exist until the centre was open, but the operators with good market research will profit from this new revenue earning opportunity. Competition Unless a business can obtain such a stranglehold on the market that it ...
Market Equilibrium
... Many of the markets in which farmers buy inputs and sell their products however do not meet these conditions This chapter initially focuses on specific types of imperfect competitors in the farm input market, where firms are capable of setting the prices farmers must pay for specific inputs to t ...
... Many of the markets in which farmers buy inputs and sell their products however do not meet these conditions This chapter initially focuses on specific types of imperfect competitors in the farm input market, where firms are capable of setting the prices farmers must pay for specific inputs to t ...
chapt-6
... • Legal Considerations Legal factors are usually related to safety or health protection. ...
... • Legal Considerations Legal factors are usually related to safety or health protection. ...
CHAPTER 6
... Marketing to more than one market segment rather than the whole market for a product/service ...
... Marketing to more than one market segment rather than the whole market for a product/service ...