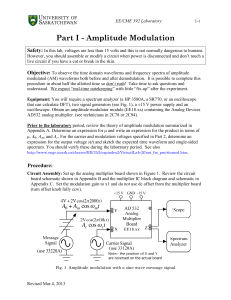
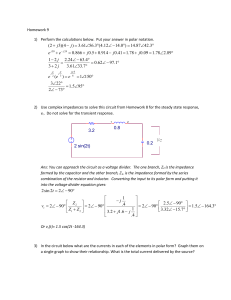
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION This is a precise, fast sample-and-hold circuit. During the sample mode, SW2 is closed, and the output, VOUT, follows the input signal, VIN. In the hold mode, SW2 is opened, and the signal is held by the hold capacitor, CH. Due to switch and capacitor leakage current, the voltage ...
... CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION This is a precise, fast sample-and-hold circuit. During the sample mode, SW2 is closed, and the output, VOUT, follows the input signal, VIN. In the hold mode, SW2 is opened, and the signal is held by the hold capacitor, CH. Due to switch and capacitor leakage current, the voltage ...
Electricity in Agriculture Unit Test
... Match the following definitions with the correct parts of the circuit ...
... Match the following definitions with the correct parts of the circuit ...
Control 1E - JBL Professional
... with built-in biamplification. A 20-watt amplifier is dedicated to the low frequency section, and a lo-watt amplifier is dedicated to the high frequency section. Frequency division is ahead of the amplifiers, and the transducers are directly connected to the amplifiers for maximum power transfer and ...
... with built-in biamplification. A 20-watt amplifier is dedicated to the low frequency section, and a lo-watt amplifier is dedicated to the high frequency section. Frequency division is ahead of the amplifiers, and the transducers are directly connected to the amplifiers for maximum power transfer and ...
90523-exm-06 - Learning on the Loop
... In the circuit shown above, the inductor has inductance 0.35 H and has internal resistance of 220 . The switch is closed, and after a time of 8.0 10–3 s, the circuit current has reached a value that is sufficiently close to the steady current value for any difference to be ignored. (a) ...
... In the circuit shown above, the inductor has inductance 0.35 H and has internal resistance of 220 . The switch is closed, and after a time of 8.0 10–3 s, the circuit current has reached a value that is sufficiently close to the steady current value for any difference to be ignored. (a) ...
What is a breadboard?
... connected by a metal strip underneath forms a node. A node is a point in a circuit where two components are connected. Connections between different components are formed by putting their legs in a common node. The long top and bottom row of holes are usually used for power supply connections. The r ...
... connected by a metal strip underneath forms a node. A node is a point in a circuit where two components are connected. Connections between different components are formed by putting their legs in a common node. The long top and bottom row of holes are usually used for power supply connections. The r ...
Instruments for Radiation Detection and Measurement
... • After g-ray interaction in the crystal, a maximum amount of light will be received by the PM tube nearest to the point of interaction ...
... • After g-ray interaction in the crystal, a maximum amount of light will be received by the PM tube nearest to the point of interaction ...
MooseFET Classic Valve Design
... the user has a reasonably competent grasp of line operated electronics at the time of sale. ...
... the user has a reasonably competent grasp of line operated electronics at the time of sale. ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-ISSN: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331,
... speaker cone to produce a sound output. The term "loudspeaker" may refer to individual transducers (known as "drivers") or to complete speaker systems consisting of an enclosure including one or more drivers. To adequately reproduce a wide range of frequencies, most loudspeaker systems employ more t ...
... speaker cone to produce a sound output. The term "loudspeaker" may refer to individual transducers (known as "drivers") or to complete speaker systems consisting of an enclosure including one or more drivers. To adequately reproduce a wide range of frequencies, most loudspeaker systems employ more t ...
Electrical System
... An electrical system uses electricity to perform some sort of work. An obvious element of an electrical system is electricity which can be defined as the flow of electrons. Electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. When electrons are carefully controlled using various compo ...
... An electrical system uses electricity to perform some sort of work. An obvious element of an electrical system is electricity which can be defined as the flow of electrons. Electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. When electrons are carefully controlled using various compo ...
Series Circuits
... doubles (Figure 2). The current flow is now half of what it was when only one lamp was in the circuit as before. The voltage across each lamp is now 60 volts due to the reduced current flow. Each bulb is operating at only one-half its intended voltage, which will reduce its brightness. Since each bu ...
... doubles (Figure 2). The current flow is now half of what it was when only one lamp was in the circuit as before. The voltage across each lamp is now 60 volts due to the reduced current flow. Each bulb is operating at only one-half its intended voltage, which will reduce its brightness. Since each bu ...
Document
... signal r(t) and determines which one of the M signals is being sent based on maximizing the likelihood function. • Define what the likelihood function is. – By employing the Gram-Schmidt procedure, we can construct a set of N (N M) orthonormal functions (all are time limited to [0; T]) which spans ...
... signal r(t) and determines which one of the M signals is being sent based on maximizing the likelihood function. • Define what the likelihood function is. – By employing the Gram-Schmidt procedure, we can construct a set of N (N M) orthonormal functions (all are time limited to [0; T]) which spans ...
EE4446 - bYTEBoss
... • Organizing subgroup, networking with group leader and other subgroup leader. • Researching on the internet and library materials for project. • Writing-up Preliminary Design. • Building up the circuit board. • Setting up the circuit on Lab. ...
... • Organizing subgroup, networking with group leader and other subgroup leader. • Researching on the internet and library materials for project. • Writing-up Preliminary Design. • Building up the circuit board. • Setting up the circuit on Lab. ...
Lecture 19: Available Power. Distortion. Emitter Degeneration. Miller
... v ic Rc Dividing (9.30) by (9.29) gives the small-signal ac gain Gv of this common-emitter amplifier to be ...
... v ic Rc Dividing (9.30) by (9.29) gives the small-signal ac gain Gv of this common-emitter amplifier to be ...
where-does-the-low-e..
... touch sensitivity and responsiveness, doubling a coupling cap's value can cause too much LF to pass through to subsequent stages, and wreak havoc on your dynamic response. lowering the 3db point does NOTHING to those frequencies which were already fairly flat in terms of response... it only makes th ...
... touch sensitivity and responsiveness, doubling a coupling cap's value can cause too much LF to pass through to subsequent stages, and wreak havoc on your dynamic response. lowering the 3db point does NOTHING to those frequencies which were already fairly flat in terms of response... it only makes th ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.