Exp04rev
... Today's experiment provides practical experience with the meaning of magnitude and phase in a linear circuits and the use of phasor algebra to predict the response of a linear system to a sinusoidal input. Using the digital oscilloscopes, we can better understand the true implications of amplitude a ...
... Today's experiment provides practical experience with the meaning of magnitude and phase in a linear circuits and the use of phasor algebra to predict the response of a linear system to a sinusoidal input. Using the digital oscilloscopes, we can better understand the true implications of amplitude a ...
5.2 Circuit Timing
... A timing diagram illustrates the behavior of signals in a digital circuit as a function of time. Timing diagrams are an important part of the documentation of any digital system. They can be used both to explain the timing relationships among signals within a system and to define the timing requirem ...
... A timing diagram illustrates the behavior of signals in a digital circuit as a function of time. Timing diagrams are an important part of the documentation of any digital system. They can be used both to explain the timing relationships among signals within a system and to define the timing requirem ...
ece2201_lab5_modified
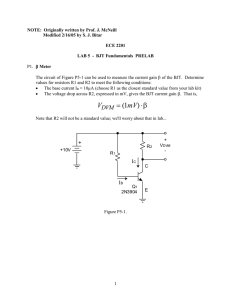
... L6. For the input signal source (a 10kHz, 0.1V peak sine wave riding on a 1.0V DC level) use the function generator with the DC offset enabled (pull out the DC OFFSET knob). Display vIN on oscilloscope channel 1; set the horizontal time scale to show a few cycles of the sine wave. To set the DC offs ...
... L6. For the input signal source (a 10kHz, 0.1V peak sine wave riding on a 1.0V DC level) use the function generator with the DC offset enabled (pull out the DC OFFSET knob). Display vIN on oscilloscope channel 1; set the horizontal time scale to show a few cycles of the sine wave. To set the DC offs ...
Radio Equipment - Model Yachting Association
... transmitter, the receiver’s worst enemy is moisture. Depending on the space available and style of boat the receiver is usually protected from moisture by placing it in a radio pot, film can or a simple balloon. After sailing it is important to ventilate the enclosure to ensure there can be no build ...
... transmitter, the receiver’s worst enemy is moisture. Depending on the space available and style of boat the receiver is usually protected from moisture by placing it in a radio pot, film can or a simple balloon. After sailing it is important to ventilate the enclosure to ensure there can be no build ...
Ohms Law and Circuits WKSHT
... 3. Fill out the table for the circuit diagramed at the right. Circuit Position ...
... 3. Fill out the table for the circuit diagramed at the right. Circuit Position ...
Lecture 4: RL Circuits. Inductive Kick. Diode Snubbers.
... when they turn off electric motors. (I had a switch in a vacuum cleaner burn a hole through beryllium-copper sliding contacts due to this source of arcing.) In sensitive electronic circuits, such inductive kick can be catastrophic and burn out transistors, for example. You will study this phenomenon ...
... when they turn off electric motors. (I had a switch in a vacuum cleaner burn a hole through beryllium-copper sliding contacts due to this source of arcing.) In sensitive electronic circuits, such inductive kick can be catastrophic and burn out transistors, for example. You will study this phenomenon ...
asynchronous analog-discrete converter using an analog signal
... analog signals processor that functions stabilized round an inflection point, in substitution to the operational amplifiers used in the first version of the converter and that allowed to work with high gain and slew-rate. This processor is also described in this article. Keywords: converter, asynchr ...
... analog signals processor that functions stabilized round an inflection point, in substitution to the operational amplifiers used in the first version of the converter and that allowed to work with high gain and slew-rate. This processor is also described in this article. Keywords: converter, asynchr ...
LABORATORY VI : Flip-Flops 1 Introduction 2 Laboratory Preliminaries
... amplitudes are at least 4.5V. More precisely, if the digital supply voltage range is larger 4.5 V (VDD − VSS > 4.5 V), then analog output swings are possible with amplitudes set by the supply voltage range VDD − VEE and VDD − VEE ≤ 20 V. The advantage of analog multiplexers is that they have a low O ...
... amplitudes are at least 4.5V. More precisely, if the digital supply voltage range is larger 4.5 V (VDD − VSS > 4.5 V), then analog output swings are possible with amplitudes set by the supply voltage range VDD − VEE and VDD − VEE ≤ 20 V. The advantage of analog multiplexers is that they have a low O ...
Feb 2000 ADSL Line Driver/Receiver Design Guide, Part 1
... looks basically like white noise, because many different frequencies of rapidly changing amplitude and phase are combined simultaneously. The changes of each tone are considered random as they result from an arbitrary sequence of data bits comprising the transmitted information. Over time, the signa ...
... looks basically like white noise, because many different frequencies of rapidly changing amplitude and phase are combined simultaneously. The changes of each tone are considered random as they result from an arbitrary sequence of data bits comprising the transmitted information. Over time, the signa ...
Auto-Zero Amplifiers
... compensation techniques result in dynamic performance improvements while minimizing total die area. The result, amplifiers that retain the high gain and DC precision of the auto-zero approach while minimizing the negative effects of digital switching on the analog signal — at half the cost. Typical ...
... compensation techniques result in dynamic performance improvements while minimizing total die area. The result, amplifiers that retain the high gain and DC precision of the auto-zero approach while minimizing the negative effects of digital switching on the analog signal — at half the cost. Typical ...
stonz basic manual
... IN Jack, LEVEL Pot: Audio input and attenuator pot. Maximum gain is unity. FREQ CV Jack and Pot: Sets the center frequency of the phasing effect. Typically, use 0-10V. Negative voltages will cancel the effect (unless biased with the pot) but allow the unprocessed signal through the module. Regenerat ...
... IN Jack, LEVEL Pot: Audio input and attenuator pot. Maximum gain is unity. FREQ CV Jack and Pot: Sets the center frequency of the phasing effect. Typically, use 0-10V. Negative voltages will cancel the effect (unless biased with the pot) but allow the unprocessed signal through the module. Regenerat ...
ma 2.2 true class a microphone amplifier. users manual.
... Buzz Audio guarantees the MA2.2 True Class A Microphone Amplifier to be free of defective materials and/or workmanship for a period of 1 year (12 months) from the date of sale, and will replace defective parts and repair malfunctioning products under this warranty when the defect occurs under normal ...
... Buzz Audio guarantees the MA2.2 True Class A Microphone Amplifier to be free of defective materials and/or workmanship for a period of 1 year (12 months) from the date of sale, and will replace defective parts and repair malfunctioning products under this warranty when the defect occurs under normal ...
Spectral Efficiency and Receiver Sensitivity in Direct Detection Optical-OFDM
... reaches 1800. For fixed bias, carrier power is fixed, too. Now, the amplitude of the zero-mean driving signal is varied. Obviously, there is a trade-off: For low amplitude, carrier power is much higher than the power in the sideband yielding low sensitivity. Increasing the signal amplitude improves ...
... reaches 1800. For fixed bias, carrier power is fixed, too. Now, the amplitude of the zero-mean driving signal is varied. Obviously, there is a trade-off: For low amplitude, carrier power is much higher than the power in the sideband yielding low sensitivity. Increasing the signal amplitude improves ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.