Waves - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... •Baud rate is number of bits (binary integers) that are transferred per second. •The baud rate on any electromagnetic wave is limited to approximately the frequency of the wave. •Waves with short wavelength or high frequency can transfer data at higher rates. ...
... •Baud rate is number of bits (binary integers) that are transferred per second. •The baud rate on any electromagnetic wave is limited to approximately the frequency of the wave. •Waves with short wavelength or high frequency can transfer data at higher rates. ...
X - Symek
... Power supply / location of J1251 (Pin 4 = +14V) 1=brown, 2=red, 3=orange, 4=yellow (+14V), 5=green 25. Make a connection from IFD data output to the packet-radio TNC (data input). Best is to drill a 6.5 mm hole in the rear panel near the grounding screw and install a Cynch connector there. (see bel ...
... Power supply / location of J1251 (Pin 4 = +14V) 1=brown, 2=red, 3=orange, 4=yellow (+14V), 5=green 25. Make a connection from IFD data output to the packet-radio TNC (data input). Best is to drill a 6.5 mm hole in the rear panel near the grounding screw and install a Cynch connector there. (see bel ...
Microwave Amplifiers
... For instance if the amplifier is required to drive 50Ω load the voltage across the load may be small, although the corresponding current may be large (there is current gain). For amplifiers functioning at lower frequency (such as IF frequency), it is the voltage gain that is of interest, since imped ...
... For instance if the amplifier is required to drive 50Ω load the voltage across the load may be small, although the corresponding current may be large (there is current gain). For amplifiers functioning at lower frequency (such as IF frequency), it is the voltage gain that is of interest, since imped ...
What is included in a circuit diagram? Circuit Diagrams
... • If one bulb burns out in a series circuit, it becomes an open circuit. • The bulbs in a circuit are a source of resistance. Adding bulbs to a series circuit increases the resistance. The current decreases, and each bulb shines less brightly. ...
... • If one bulb burns out in a series circuit, it becomes an open circuit. • The bulbs in a circuit are a source of resistance. Adding bulbs to a series circuit increases the resistance. The current decreases, and each bulb shines less brightly. ...
SP3485
... EXAR Corporation reserves the right to make changes to any products contained in this publication in order to improve design, performance or reliability. EXAR Corporation assumes no representation that the circuits are free of patent infringement. Charts and schedules contained herein are only for i ...
... EXAR Corporation reserves the right to make changes to any products contained in this publication in order to improve design, performance or reliability. EXAR Corporation assumes no representation that the circuits are free of patent infringement. Charts and schedules contained herein are only for i ...
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory
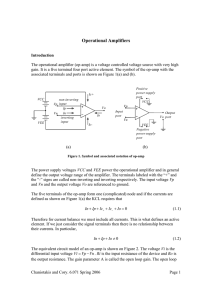
... back to its input. Op-amp open-loop gain typically exceeds 10,000. Closed-loop: A configuration that has a negative feedback path from the op-amp output back to its input. Negative feedback reduces the gain and improves many characteristics of the op-amp. • Closed-loop gain is always lower than open ...
... back to its input. Op-amp open-loop gain typically exceeds 10,000. Closed-loop: A configuration that has a negative feedback path from the op-amp output back to its input. Negative feedback reduces the gain and improves many characteristics of the op-amp. • Closed-loop gain is always lower than open ...
EXPERIMENT 2_3
... Calculate the equivalent resistance between points A and B for each circuit from the measured values in part A1, and record in Table II. ...
... Calculate the equivalent resistance between points A and B for each circuit from the measured values in part A1, and record in Table II. ...
A high conversion-gain Q-band InP DHBT subharmonic
... this, SHMs offer inherent RF/LO isolation, which is important in receiver applications where unwanted radiation of LO power from the RF port must be minimized. The most common SHM topology consists of a pair of antiparallel Schottky barrier diodes [1], [2]. However, this topology suffers from signif ...
... this, SHMs offer inherent RF/LO isolation, which is important in receiver applications where unwanted radiation of LO power from the RF port must be minimized. The most common SHM topology consists of a pair of antiparallel Schottky barrier diodes [1], [2]. However, this topology suffers from signif ...
This course contains - College of Micronesia
... 1. Describe the basic concept of voltage and current and the behavior of these parameters in simple electrical circuits. 2. Explain the purpose and identify the various types of resistors and their symbols. Identify the value, power rating and tolerance of resistors using various types of industry c ...
... 1. Describe the basic concept of voltage and current and the behavior of these parameters in simple electrical circuits. 2. Explain the purpose and identify the various types of resistors and their symbols. Identify the value, power rating and tolerance of resistors using various types of industry c ...
BUF634 250-mA High-Speed Buffer (Rev. A)
... to approximately ±350 mA; see Figure 10. For many applications, however, the continuous output current will be limited by thermal effects. The output voltage swing capability varies with junction temperature and output current (see Figure 14). Although all four package types are tested for the same ...
... to approximately ±350 mA; see Figure 10. For many applications, however, the continuous output current will be limited by thermal effects. The output voltage swing capability varies with junction temperature and output current (see Figure 14). Although all four package types are tested for the same ...
Physics 107 Recommended Demos
... connected to a demo galvanometer (Shelf C3-3), and a bar magnet is moved in and out of the coil, and varying speeds. One can pass a wooden ruler through the coil in the same way to show that there is no deflection with non-magnetic materials. (Shelf C1-4) Hand Crank generator - This generator produc ...
... connected to a demo galvanometer (Shelf C3-3), and a bar magnet is moved in and out of the coil, and varying speeds. One can pass a wooden ruler through the coil in the same way to show that there is no deflection with non-magnetic materials. (Shelf C1-4) Hand Crank generator - This generator produc ...
16826 - Public Address System
... db compression, 0.5%. Frequency response - 20 to 20 000 Hz + 1 db. Gain - [600 Ohm] at threshold of compression 51.5 + db. [Bridging] at threshold of compression 14 +2 db. Input impedance - matching 600 Ohm. Bridging 10 000 Ohm. Output impedance - 600 Ohm. Noise [threshold of compression] - 70 db. N ...
... db compression, 0.5%. Frequency response - 20 to 20 000 Hz + 1 db. Gain - [600 Ohm] at threshold of compression 51.5 + db. [Bridging] at threshold of compression 14 +2 db. Input impedance - matching 600 Ohm. Bridging 10 000 Ohm. Output impedance - 600 Ohm. Noise [threshold of compression] - 70 db. N ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.