Introduction to Supply and Demand
... downward because • Income effect-when prices are lower, consumers purchase larger quantities • Substitute effect-as price goes up, consumers will find substitutes, thus demand goes down ...
... downward because • Income effect-when prices are lower, consumers purchase larger quantities • Substitute effect-as price goes up, consumers will find substitutes, thus demand goes down ...
12.1 Consumer and Producer surplus
... Under this new assumption, both he reasoning and the graph made in (a) still hold. However, the main difference is that the area under the marginal costs (supply) curve, up to Q*, is the total variable costs to the producer. Total variable costs are the firm’s total costs less its (unavoidable) fixe ...
... Under this new assumption, both he reasoning and the graph made in (a) still hold. However, the main difference is that the area under the marginal costs (supply) curve, up to Q*, is the total variable costs to the producer. Total variable costs are the firm’s total costs less its (unavoidable) fixe ...
Monopolistic Competition
... – Each firm produces a product that is at least slightly different from those of other firms. – Rather than being a price taker, each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve. ...
... – Each firm produces a product that is at least slightly different from those of other firms. – Rather than being a price taker, each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve. ...
Where Do Cities Develop? - Pomona College Economics
... • In single output/single input model, firm will tend to locate at one of the endpoints. This tendency is reinforced if there are terminal costs of line haul economies. • In single input/output model, if monetary weight of input exceeds monetary weight of output, firm will locate at the source of in ...
... • In single output/single input model, firm will tend to locate at one of the endpoints. This tendency is reinforced if there are terminal costs of line haul economies. • In single input/output model, if monetary weight of input exceeds monetary weight of output, firm will locate at the source of in ...
Slides - Tamu.edu
... 1. Distinguish among three types of imperfectly competitive industries and describe how imperfect competition differs from perfect competition 2. Identify the five sources of monopoly power and describe why economies of scale are the most enduring of the various sources of market power 3. Apply the ...
... 1. Distinguish among three types of imperfectly competitive industries and describe how imperfect competition differs from perfect competition 2. Identify the five sources of monopoly power and describe why economies of scale are the most enduring of the various sources of market power 3. Apply the ...
File - Ms. Rixie`s Website
... ■You should always continue to do something as long as the benefits outweigh the costs ■Marginal means additional ■Should I eat the next slice of pizza?? Is it worth it? ...
... ■You should always continue to do something as long as the benefits outweigh the costs ■Marginal means additional ■Should I eat the next slice of pizza?? Is it worth it? ...
AP MP - Missouri State University
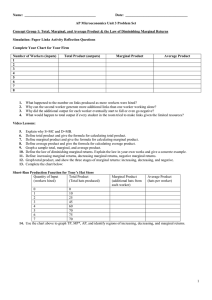
... A. both statements are true. B. both statements are false. C. I is true while II is false. D. I is false while II is true. 15. When the marginal product of labor is increasing: A. the total product of labor is increasing. B. marginal cost is decreasing. C. the average product of labor is increasing. ...
... A. both statements are true. B. both statements are false. C. I is true while II is false. D. I is false while II is true. 15. When the marginal product of labor is increasing: A. the total product of labor is increasing. B. marginal cost is decreasing. C. the average product of labor is increasing. ...
econlastminuteitems
... • Imperfectly Competitive Seller Demand Curve – Slopes Downward – Marginal Product & Product Price fall as resource employment and output rise. ...
... • Imperfectly Competitive Seller Demand Curve – Slopes Downward – Marginal Product & Product Price fall as resource employment and output rise. ...
Profit Maximazization in Pure Competition
... • Yves and Zoe are price-taking producers because their actions cannot affect the market price of the good or service they sell • When there is enough competition (when competition is “perfect”) every producer is a price-taker ...
... • Yves and Zoe are price-taking producers because their actions cannot affect the market price of the good or service they sell • When there is enough competition (when competition is “perfect”) every producer is a price-taker ...
Unit3ProblemSet
... Fixed, Variable, and Marginal Cost: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance-domain/microeconomics/firmeconomic-profit/average-costs-tutorial/v/fixed-variable-and-marginal-cost Marginal Cost & Average Total Cost: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-financedomain/microeconomics/firm-econom ...
... Fixed, Variable, and Marginal Cost: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance-domain/microeconomics/firmeconomic-profit/average-costs-tutorial/v/fixed-variable-and-marginal-cost Marginal Cost & Average Total Cost: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-financedomain/microeconomics/firm-econom ...
Lesson 7
... Monopolistic Competition: Environment and Implications • Numerous buyers and sellers • Differentiated products – Implication: Since products are differentiated, each firm faces a downward sloping demand curve. • Consumers view differentiated products as close substitutes: there exists some willingn ...
... Monopolistic Competition: Environment and Implications • Numerous buyers and sellers • Differentiated products – Implication: Since products are differentiated, each firm faces a downward sloping demand curve. • Consumers view differentiated products as close substitutes: there exists some willingn ...
Marketing Mix
... • They need to focus on the customer and understand who their customers are. • They must identify the customers needs • They must anticipate their needs in the future • They must also meet those needs when the customer requires it. ...
... • They need to focus on the customer and understand who their customers are. • They must identify the customers needs • They must anticipate their needs in the future • They must also meet those needs when the customer requires it. ...
ECON 2010-100 Principles of Microeconomics
... theory, producer theory, and market's successes and failures in efficient allocation of resources. The consumer theory analyzes buying behavior of consumers, whereas the producer theory analyzes selling behavior of producers. The third part of the course evaluates market's performance in allocation ...
... theory, producer theory, and market's successes and failures in efficient allocation of resources. The consumer theory analyzes buying behavior of consumers, whereas the producer theory analyzes selling behavior of producers. The third part of the course evaluates market's performance in allocation ...
Antitrust Policy
... and tobacco industries o Trust – monopolies o Firms often used questionable tactics to monopolize these industries and then charged monopoly prices to customers and extracted price concessions from resource suppliers. o Government concluded in the late 1800s and early 1900s that market forces in mon ...
... and tobacco industries o Trust – monopolies o Firms often used questionable tactics to monopolize these industries and then charged monopoly prices to customers and extracted price concessions from resource suppliers. o Government concluded in the late 1800s and early 1900s that market forces in mon ...
Elasticity of Demand
... Fixed Costs are those cost items which do not change with changes in level of output, that means, they are independent of output. Fixed costs are contractually fixed. Variable Costs are those items of costs which change with changes in the level of output in the short run i.e. they increase or decre ...
... Fixed Costs are those cost items which do not change with changes in level of output, that means, they are independent of output. Fixed costs are contractually fixed. Variable Costs are those items of costs which change with changes in the level of output in the short run i.e. they increase or decre ...