econ2 - Exalogics
... his opportunity cost of tomatoes is less than his opportunity cost of turnips Tom can grow more tomatoes than Di can his opportunity cost of tomatoes is less than Di's opportunity cost of tomatoes ...
... his opportunity cost of tomatoes is less than his opportunity cost of turnips Tom can grow more tomatoes than Di can his opportunity cost of tomatoes is less than Di's opportunity cost of tomatoes ...
Supply - Coach Gilmore
... • This is because producers are not willing to increase their supply of a good or service if they will not be able to maximize their profit. – They will, however, increase their supply if their consumers are willing and able (demand) to purchase items at high price, and thus at a higher profit margi ...
... • This is because producers are not willing to increase their supply of a good or service if they will not be able to maximize their profit. – They will, however, increase their supply if their consumers are willing and able (demand) to purchase items at high price, and thus at a higher profit margi ...
Supply and Demand
... in money. Prices are flexible as they react to the market. Rationing is an alternative to ...
... in money. Prices are flexible as they react to the market. Rationing is an alternative to ...
3.4 Market Mix - AIS-iGCSE
... price based on that charged by rivals. Setting a price above that charged by the market leader can only work if your product has better features and appearance. Costs. A business can make a profit only if the price charged eventually covers the costs of making an item. One way to try to ensure a pro ...
... price based on that charged by rivals. Setting a price above that charged by the market leader can only work if your product has better features and appearance. Costs. A business can make a profit only if the price charged eventually covers the costs of making an item. One way to try to ensure a pro ...
Answer Key
... the magnitudes of the shifts in D2 and S2. f) The demand for labour could increase because labour productivity rises or because total output for the economy increase while the decrease in the supply of labour could be caused by a decrease in population or in the labour force participation rate. 5. S ...
... the magnitudes of the shifts in D2 and S2. f) The demand for labour could increase because labour productivity rises or because total output for the economy increase while the decrease in the supply of labour could be caused by a decrease in population or in the labour force participation rate. 5. S ...
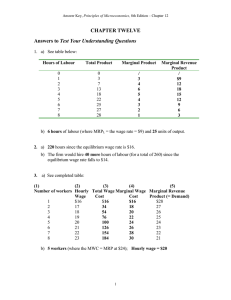
Chapter 10
... does per hour, as shown by point a. As shown by point b on the demand curve, the price required to sell this ...
... does per hour, as shown by point a. As shown by point b on the demand curve, the price required to sell this ...
Factor Markets
... MRPL (Marginal Revenue Product of Labor): a measure of whaht the next unit of a resource, such as labor, brings to the firm In a PC market structure, the marginal revenue is simply the price of the product ...
... MRPL (Marginal Revenue Product of Labor): a measure of whaht the next unit of a resource, such as labor, brings to the firm In a PC market structure, the marginal revenue is simply the price of the product ...
Student ID Name Microeconomics Exercises MULTIPLE CHOICE
... knowing which change is greater. D) A decrease in supply causes equilibrium price to rise; the increase in price then results in a decrease in demand. 12) Positive technological change in the production of LCD televisions caused the price of LCD televisions to fall. Holding everything else constant, ...
... knowing which change is greater. D) A decrease in supply causes equilibrium price to rise; the increase in price then results in a decrease in demand. 12) Positive technological change in the production of LCD televisions caused the price of LCD televisions to fall. Holding everything else constant, ...
Keegan11mmd
... than the cost of production plus an 8% profit margin or at levels below those prevailing in the producing countries To prove, both price discrimination and injury must be shown ...
... than the cost of production plus an 8% profit margin or at levels below those prevailing in the producing countries To prove, both price discrimination and injury must be shown ...
document
... revenue less total costs. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company.All rights reserved. ...
... revenue less total costs. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company.All rights reserved. ...
Slide 1
... – Arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market • At a smaller cost than could two or more firms ...
... – Arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market • At a smaller cost than could two or more firms ...
Rupp Econ 2113 3B Fall 09
... b. is most often equal to accounting profit. c. is always at least as large as accounting profit. d. is a less complete measure of profitability than accounting profit. ____ 32. Economies of scale occur when a. long-run average total costs rise as output increases. b. long-run average total costs fa ...
... b. is most often equal to accounting profit. c. is always at least as large as accounting profit. d. is a less complete measure of profitability than accounting profit. ____ 32. Economies of scale occur when a. long-run average total costs rise as output increases. b. long-run average total costs fa ...
Economics demand-supply equilibrium analysis
... profit in the cost. If selling price is increased, the profit will also increases. This increase the profit of the seller, which motivates to supply more quality .So, increase in selling price increase the supply of good. 5. Price of Raw Material: Price of raw materials directly effects the qual ...
... profit in the cost. If selling price is increased, the profit will also increases. This increase the profit of the seller, which motivates to supply more quality .So, increase in selling price increase the supply of good. 5. Price of Raw Material: Price of raw materials directly effects the qual ...
Answers to Homework #4
... (2) If the firm does not shut down in the short run when price equals 10, will the firm make a positive economic profit or a negative economic profit? What is the value of the firm's economic profit when price equals 10? (3) If the firm does not shut down in the short run when price equals 10, what ...
... (2) If the firm does not shut down in the short run when price equals 10, will the firm make a positive economic profit or a negative economic profit? What is the value of the firm's economic profit when price equals 10? (3) If the firm does not shut down in the short run when price equals 10, what ...
The 4 P`s of Marketing
... • Marketing is responsible for establishing the price of their service/product • Must consider the costs of all the inputs (materials, labour, etc) • Mark-up Price – How much profit do you want to make on every product/customer • Example: Selling Cupcakes – Every cupcake uses $1 of materials and lab ...
... • Marketing is responsible for establishing the price of their service/product • Must consider the costs of all the inputs (materials, labour, etc) • Mark-up Price – How much profit do you want to make on every product/customer • Example: Selling Cupcakes – Every cupcake uses $1 of materials and lab ...