Exam I Fall 2008 with answers
... Assume the following scenario: we are selling a product, call it X, and we observe how our sales are affected by the prices of several other products (Y, W, and Z), all else held constant. Each time the producers of Y increase the price, our sales suffer substantial losses, while each time the produ ...
... Assume the following scenario: we are selling a product, call it X, and we observe how our sales are affected by the prices of several other products (Y, W, and Z), all else held constant. Each time the producers of Y increase the price, our sales suffer substantial losses, while each time the produ ...
BUSINESS UNIT 4
... Freedom of trade - When there are no barriers to trade between nations. The EU is a free trade area where member states don't have to pay tariffs (tax on imports) or meet quotas (a limit on the volume of imports). Comparative advantage is the theory that countries produce what they are good at beca ...
... Freedom of trade - When there are no barriers to trade between nations. The EU is a free trade area where member states don't have to pay tariffs (tax on imports) or meet quotas (a limit on the volume of imports). Comparative advantage is the theory that countries produce what they are good at beca ...
CHAPTER 12 Pricing CHAPTER OUTLINE 12.1 Why and How Firms
... Because the reseller can transport goods from Market 1 to Market 2 for $4 per unit, the reseller could under price the monopolist in Market 2 by $1. This forces the monopolist to reduce the market price to $34 per unit. Output increases to 39 units, and revenue increases to $1326 from $1312.50, but ...
... Because the reseller can transport goods from Market 1 to Market 2 for $4 per unit, the reseller could under price the monopolist in Market 2 by $1. This forces the monopolist to reduce the market price to $34 per unit. Output increases to 39 units, and revenue increases to $1326 from $1312.50, but ...
(a) Firm
... exit, firms that remain must be making zero economic profit. The process of entry & exit ends only when price and average total cost are driven to equality. Long-run equilibrium must have firms operating at their efficient scale. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcour ...
... exit, firms that remain must be making zero economic profit. The process of entry & exit ends only when price and average total cost are driven to equality. Long-run equilibrium must have firms operating at their efficient scale. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcour ...
Supply and Demand PPT
... good or service as a result of changes in the price for some other related good or service. • Scarcity- situation in markets whereby either less goods are available than the demand for them, or too little money is available to their potential buyers for making the purchase. ...
... good or service as a result of changes in the price for some other related good or service. • Scarcity- situation in markets whereby either less goods are available than the demand for them, or too little money is available to their potential buyers for making the purchase. ...
1. Formation of economic rent in mining
... According to Tilton (2001) this ranked series of deposits can be considered as a "cumulative availability curve" that shows the cumulative available capacity for a mineral commodity at a certain marginal cost or market price. Thus the cumulative availability curve can be used as a supply curve for t ...
... According to Tilton (2001) this ranked series of deposits can be considered as a "cumulative availability curve" that shows the cumulative available capacity for a mineral commodity at a certain marginal cost or market price. Thus the cumulative availability curve can be used as a supply curve for t ...
The Basics of Supply and Demand
... REVENUE = P × QD = 8 × 2 = 16 < 24. Cite as: Chia-Hui Chen, course materials for 14.01 Principles of Microeconomics, Fall 2007. MIT OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu), Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Downloaded on [DD Month YYYY]. ...
... REVENUE = P × QD = 8 × 2 = 16 < 24. Cite as: Chia-Hui Chen, course materials for 14.01 Principles of Microeconomics, Fall 2007. MIT OpenCourseWare (http://ocw.mit.edu), Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Downloaded on [DD Month YYYY]. ...
Change in supply
... answer the questions WHAT, HOW, and for WHOM to produce. • 4.) You have known it your entire life. ...
... answer the questions WHAT, HOW, and for WHOM to produce. • 4.) You have known it your entire life. ...
FinalSS-207 - UC Davis economics
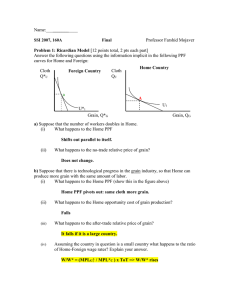
... Consider the long-run trade equilibrium in the monopolistic competition model as illustrated below. Consider a situation where the foreign and domestic demand for a particular good decrease. For instance, suppose that this is the market for cars and higher gasoline prices result in lower demand. a) ...
... Consider the long-run trade equilibrium in the monopolistic competition model as illustrated below. Consider a situation where the foreign and domestic demand for a particular good decrease. For instance, suppose that this is the market for cars and higher gasoline prices result in lower demand. a) ...
PPT
... The first two features implied a horizontal demand curve for individual firms, while the third implied zero long-run profit. Monopolistically competitive firms share features 1. and 3.; but their products are not identical to their competitors’. So we expect monopolistically competitive firms to hav ...
... The first two features implied a horizontal demand curve for individual firms, while the third implied zero long-run profit. Monopolistically competitive firms share features 1. and 3.; but their products are not identical to their competitors’. So we expect monopolistically competitive firms to hav ...
THE DEMAND FOR CAPITAL
... Suppose the firm has borrowed its funds from a bank, and the bank charged 11% for operating funds (like an operating loan) The firm can meet the payment of 11% because it derives a 12 % return on the capital ...
... Suppose the firm has borrowed its funds from a bank, and the bank charged 11% for operating funds (like an operating loan) The firm can meet the payment of 11% because it derives a 12 % return on the capital ...
Chapter 9 Profit Maximization
... Begin with the FOC’s for choosing K and L to maximize : v = p(MPK) and w = p(MPL). Solving these simultaneously shows that the profit-maximizing amounts of K and L are functions of p, v, and w for a given production function. Thus, K* = K (p,w,v) and L* = L (p,w,v). These are derived demand functio ...
... Begin with the FOC’s for choosing K and L to maximize : v = p(MPK) and w = p(MPL). Solving these simultaneously shows that the profit-maximizing amounts of K and L are functions of p, v, and w for a given production function. Thus, K* = K (p,w,v) and L* = L (p,w,v). These are derived demand functio ...
global firms
... improving their products, expanding into foreign markets, and becoming global firms. Global firms face several major problems: ...
... improving their products, expanding into foreign markets, and becoming global firms. Global firms face several major problems: ...
Feb. 5
... 6. Resource allocation models – • Porter: strategic choices are set of basic generic strategies • (low cost, differentiation, market focus) ...
... 6. Resource allocation models – • Porter: strategic choices are set of basic generic strategies • (low cost, differentiation, market focus) ...
Econ*1050 Introductory Microeconomics Instructor: Vitali Alexeev
... When we move up or down a given demand curve, a. only price is held constant. b. income and the price of the good are held constant. c. all nonprice determinants of demand are assumed to be constant. d. all determinants of quantity demanded are held constant. e. None of the above are correct. ...
... When we move up or down a given demand curve, a. only price is held constant. b. income and the price of the good are held constant. c. all nonprice determinants of demand are assumed to be constant. d. all determinants of quantity demanded are held constant. e. None of the above are correct. ...
chapter 2
... 3. The customer is placed in the center of the four P’s because this strategy is showing that all of these variables are necessary to effectively target a customer. Example of mine is this Christmas I was shopping for my son a Nintendo dsi looking for the best available price. Wal-Mart had a great p ...
... 3. The customer is placed in the center of the four P’s because this strategy is showing that all of these variables are necessary to effectively target a customer. Example of mine is this Christmas I was shopping for my son a Nintendo dsi looking for the best available price. Wal-Mart had a great p ...