Chapter 7
... cycle. • When the relatively fast growth has tapered, there will be some "shake-out" of the competition that built during the growth stage. • As the strategic window of opportunity has all but closed for the product/market, no more firms will enter the market unless they have found some product inno ...
... cycle. • When the relatively fast growth has tapered, there will be some "shake-out" of the competition that built during the growth stage. • As the strategic window of opportunity has all but closed for the product/market, no more firms will enter the market unless they have found some product inno ...
First Midterm (Afternoon Lecture) with answers
... d. Neither country has the comparative advantage in the production of Tshirts. 33. Suppose France and Germany specialize and trade with each other. For which of the following prices will both countries agree to trade? a. 1/2 T-shirts for a sweater b. 2/3 T-shirts for a sweater c. 3/2 sweaters for a ...
... d. Neither country has the comparative advantage in the production of Tshirts. 33. Suppose France and Germany specialize and trade with each other. For which of the following prices will both countries agree to trade? a. 1/2 T-shirts for a sweater b. 2/3 T-shirts for a sweater c. 3/2 sweaters for a ...
ECON4925 Resource economics, Autumn 2008
... T1 . Knowing this, the firms in the fringe would hold back some of their production potential in order to take advantage of this price rise. The price path and extraction policy is chosen and announced by the cartel in order to speed up the exhaustion of the deposit of the competitive fringe. Howeve ...
... T1 . Knowing this, the firms in the fringe would hold back some of their production potential in order to take advantage of this price rise. The price path and extraction policy is chosen and announced by the cartel in order to speed up the exhaustion of the deposit of the competitive fringe. Howeve ...
International Marketing - Glendale Community College
... • It also conveys an image of the consumer, such as lifestyle, social status and level of wealth. • Building brand loyalty is key for brand owners – brand equity is the added value which accrues to the brand and its owner. • Brand extension – applying a brand associated with one product to other pro ...
... • It also conveys an image of the consumer, such as lifestyle, social status and level of wealth. • Building brand loyalty is key for brand owners – brand equity is the added value which accrues to the brand and its owner. • Brand extension – applying a brand associated with one product to other pro ...
Who`s on the Other Side?
... So what happens if everyone who has a long portfolio of S&P stocks decides on the same day to hedge their portfolio 1:1 with /ES futures? Suddenly there is massive selling pressure in the /ES, and if everyone is selling, the only one buying is Jane Wallstreet, who is hedging by selling the actual eq ...
... So what happens if everyone who has a long portfolio of S&P stocks decides on the same day to hedge their portfolio 1:1 with /ES futures? Suddenly there is massive selling pressure in the /ES, and if everyone is selling, the only one buying is Jane Wallstreet, who is hedging by selling the actual eq ...
Price Competition
... • It is the most readily changeable characteristic (under favorable circumstances) of a product. • It is a key element in the marketing mix because it relates directly to generation of revenues and quantities sold. ...
... • It is the most readily changeable characteristic (under favorable circumstances) of a product. • It is a key element in the marketing mix because it relates directly to generation of revenues and quantities sold. ...
armstrong08_media
... – Move into larger market channels – Offer new or improved services to buyers ...
... – Move into larger market channels – Offer new or improved services to buyers ...
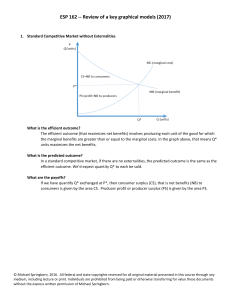
Review of key models used
... The socially efficient outcome (that maximizes social net benefits) involves producing each unit of the good for which the marginal social benefits are greater than or equal to the marginal social costs. (Since there is no external benefit here, we don’t distinguish between private and social benefi ...
... The socially efficient outcome (that maximizes social net benefits) involves producing each unit of the good for which the marginal social benefits are greater than or equal to the marginal social costs. (Since there is no external benefit here, we don’t distinguish between private and social benefi ...
lecture 1 - Vanderbilt University
... • Market equilibrium is the price at which quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. If price is above the equilibrium price, there are too many sellers, forcing price down, and vice versa. • Prices are a primary way that market participants communicate with one another. High prices tell consumers ...
... • Market equilibrium is the price at which quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. If price is above the equilibrium price, there are too many sellers, forcing price down, and vice versa. • Prices are a primary way that market participants communicate with one another. High prices tell consumers ...
GCSE OCR Economics Chapter1 - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... my own food and clothing, and therefore be selfsufficient, I could only produce what I needed. I would never really become skilled at producing one item, because my tasks would be changing all the time. If I specialised in making one item, I would become better at it (more productive) and therefore ...
... my own food and clothing, and therefore be selfsufficient, I could only produce what I needed. I would never really become skilled at producing one item, because my tasks would be changing all the time. If I specialised in making one item, I would become better at it (more productive) and therefore ...
Positioning and Differentiating the market offering
... Sales growth tends to be slow at this stage because it takes time to roll out a new product and fill dealer pipelines. Costs are high per customer as customers are not that much in introduction stage, and promotional expenditures are at their highest ratio to sales. Profits are negative or low i ...
... Sales growth tends to be slow at this stage because it takes time to roll out a new product and fill dealer pipelines. Costs are high per customer as customers are not that much in introduction stage, and promotional expenditures are at their highest ratio to sales. Profits are negative or low i ...
Marketing Chapter 9 Lecture Presentation - MyBC
... What Is a Price? Narrowly defined, price is the amount of money charged for a product or service. Broadly defined, price is the sum of all of the values that consumers give up in order to gain the benefits of using the product or service. Price vs. Value – Cutting cost in tough economic times ...
... What Is a Price? Narrowly defined, price is the amount of money charged for a product or service. Broadly defined, price is the sum of all of the values that consumers give up in order to gain the benefits of using the product or service. Price vs. Value – Cutting cost in tough economic times ...
Announcements
... decides to use personal selling and advertising to convince customers to buy their bulbs. So, the firm increases its advertising budget by 50 percent and doubles its sales staff to pressure the consumers to buy the product. This company is operating as if it were in which of the following paradigms? ...
... decides to use personal selling and advertising to convince customers to buy their bulbs. So, the firm increases its advertising budget by 50 percent and doubles its sales staff to pressure the consumers to buy the product. This company is operating as if it were in which of the following paradigms? ...
Using this module:
... buyers are paying $110. Consequently they buy fewer than 100 houses when the price (to the seller) is $100. On the supply side, the price of commercial building represents an opportunity cost to home builders. They could use the same resources to build either homes of commercial buildings, so the h ...
... buyers are paying $110. Consequently they buy fewer than 100 houses when the price (to the seller) is $100. On the supply side, the price of commercial building represents an opportunity cost to home builders. They could use the same resources to build either homes of commercial buildings, so the h ...
sample problems
... SAMPLE PROBLEMS 1. A large shipment of a single product can be sent from St. Louis to Los Angeles by train or by water (down the Mississippi and through the Panama Canal). What characteristics of the product would cause the ship to be preferred over rail? 2. An airline may lower their costs between ...
... SAMPLE PROBLEMS 1. A large shipment of a single product can be sent from St. Louis to Los Angeles by train or by water (down the Mississippi and through the Panama Canal). What characteristics of the product would cause the ship to be preferred over rail? 2. An airline may lower their costs between ...
Pricing Laws
... 5. JCPenny’s advertised a winter coat for $50, but when a customer came in looking for the coat in the advertisement, they were told this item was not in stock, but they could purchase this other coat for $75. a. What type of pricing is this? __________________________________________ b. What law pr ...
... 5. JCPenny’s advertised a winter coat for $50, but when a customer came in looking for the coat in the advertisement, they were told this item was not in stock, but they could purchase this other coat for $75. a. What type of pricing is this? __________________________________________ b. What law pr ...
Elasticity of Supply
... Time lags in the production process – fixed supply available to the market in momentary period (i.e. the daily catch) Longer term; change in the number of vessels, length of time at sea ...
... Time lags in the production process – fixed supply available to the market in momentary period (i.e. the daily catch) Longer term; change in the number of vessels, length of time at sea ...
Marketing and Distribution Systems
... Insurance Market Intermediaries Unique characteristics of insurance marketing Legal status of agent Agent - represents insurer ...
... Insurance Market Intermediaries Unique characteristics of insurance marketing Legal status of agent Agent - represents insurer ...