Chapter 3
... In the market equilibrium for such goods whose production generate pollution, the benefit to buyers of the last good produced is, as before, equal to the cost incurred by sellers to produce that good. But since producing that good also resulted in the costs of the associated pollution, we know t ...
... In the market equilibrium for such goods whose production generate pollution, the benefit to buyers of the last good produced is, as before, equal to the cost incurred by sellers to produce that good. But since producing that good also resulted in the costs of the associated pollution, we know t ...
3.01 Outline Content
... Marketing strategies are important because they show how goals will be reached. There may be more than one option to achieve desired goals. Marketers must consider the following when choosing a strategy: o How the marketing concept applies to their situation? o When they want to reach their goal? o ...
... Marketing strategies are important because they show how goals will be reached. There may be more than one option to achieve desired goals. Marketers must consider the following when choosing a strategy: o How the marketing concept applies to their situation? o When they want to reach their goal? o ...
Chap003
... the tradeoff rate between goods is constant, a fact that is true if each consumer is a price taker in the market and can buy all she can afford at the constant market price. This graphical model can be shown algebraically if it is recognized that all income must go to only two commodities in a two-d ...
... the tradeoff rate between goods is constant, a fact that is true if each consumer is a price taker in the market and can buy all she can afford at the constant market price. This graphical model can be shown algebraically if it is recognized that all income must go to only two commodities in a two-d ...
Monopoly
... It is more efficient to regulate natural monopoly than to break it up and make the industry competitive. Strengthening the Incentives to Innovate Monopoly might be more innovative than competition. Innovation can create a monopoly. ...
... It is more efficient to regulate natural monopoly than to break it up and make the industry competitive. Strengthening the Incentives to Innovate Monopoly might be more innovative than competition. Innovation can create a monopoly. ...
segment 7 : market segmentation
... COMPETITION-to not go after segment with lots of competition, and entry to market, same point as above, (apple and not going after mainframe, but concentrating on different segment because competition) COST-each time we develop a marketing program for specific segment cost more money, product, ...
... COMPETITION-to not go after segment with lots of competition, and entry to market, same point as above, (apple and not going after mainframe, but concentrating on different segment because competition) COST-each time we develop a marketing program for specific segment cost more money, product, ...
Opening Case: Extending the Wintel Monopoly to Wireless
... completely replaced by the new technology in time. The contest to decide which firm will own the technical standard is called a “format war.” Standards may emerge as a result of government policy, through an agreement made by firms with in an industry, or gradually emerge based on consumer buying pa ...
... completely replaced by the new technology in time. The contest to decide which firm will own the technical standard is called a “format war.” Standards may emerge as a result of government policy, through an agreement made by firms with in an industry, or gradually emerge based on consumer buying pa ...
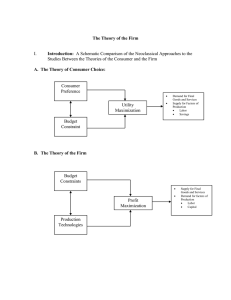
B. The Theory of the Firm
... isoquant implies that, as a general rule, the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital tends to decrease as an increasing amount of labor is substituted for capital. This is known as the law of diminishing marginal rate of technical substitution. This law can be easily verified ...
... isoquant implies that, as a general rule, the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital tends to decrease as an increasing amount of labor is substituted for capital. This is known as the law of diminishing marginal rate of technical substitution. This law can be easily verified ...
Chapter 3
... In this chapter you will learn how to 1. Explain what determines “quantity demanded,” the amount of some product that consumers want to purchase. 2. Describe the difference between a shift in a demand curve and a movement along a demand curve. 3. Explain what determines “quantity supplied,” the amo ...
... In this chapter you will learn how to 1. Explain what determines “quantity demanded,” the amount of some product that consumers want to purchase. 2. Describe the difference between a shift in a demand curve and a movement along a demand curve. 3. Explain what determines “quantity supplied,” the amo ...
Sports_and_Entertainment_Marketing
... TV revenue due to advertising, naming rights to stadiums, programs and more ...
... TV revenue due to advertising, naming rights to stadiums, programs and more ...
L10 HANDOUT
... E*Trade was founded in 1991 and partnered with America Online and CompuServe in 1992 to offer trading to users of those portals. In 1996, E*Trade established its own Internet site. That year, E*Trade spent $25 million on its first national advertising television campaign, which attempted to convince ...
... E*Trade was founded in 1991 and partnered with America Online and CompuServe in 1992 to offer trading to users of those portals. In 1996, E*Trade established its own Internet site. That year, E*Trade spent $25 million on its first national advertising television campaign, which attempted to convince ...
Document
... for non-profit hospitals. Such hospitals seem to hire more high-wage labor (physicians) and less lower-wage labor (nurses) than do for-profit hospitals. One explanation for this result may be that nonprofit hospitals are run by physicians who gain utility from high-quality (high-cost) surroundings w ...
... for non-profit hospitals. Such hospitals seem to hire more high-wage labor (physicians) and less lower-wage labor (nurses) than do for-profit hospitals. One explanation for this result may be that nonprofit hospitals are run by physicians who gain utility from high-quality (high-cost) surroundings w ...
lecture notes
... Optimal Combination of Resources A. Two questions are considered. 1. What is the least-cost combination of resources to use in producing any given output? 2. What combination of resources (and output) will maximize a firm’s profits? B. The least-cost rule states that costs are minimized where the ma ...
... Optimal Combination of Resources A. Two questions are considered. 1. What is the least-cost combination of resources to use in producing any given output? 2. What combination of resources (and output) will maximize a firm’s profits? B. The least-cost rule states that costs are minimized where the ma ...
Chapter 2
... maximized at a level of $2,500. Prior to that point, the added sales from a decrease in price more than compensate for the loss in revenue from charging current customers a lower price. At prices lower than $250, the loss in revenue from charging current customers a lesser price is greater than the ...
... maximized at a level of $2,500. Prior to that point, the added sales from a decrease in price more than compensate for the loss in revenue from charging current customers a lower price. At prices lower than $250, the loss in revenue from charging current customers a lesser price is greater than the ...
2 Supply - Mr. Davidson`s IB Economics Page
... each given price level. When you think of supply think of firms, businesses, producers – the economic agents that are producing the goods or services to sell. Note in the definition that is says plan – just as we said with demand it is planned not actual supply. Consumers might not actually buy al ...
... each given price level. When you think of supply think of firms, businesses, producers – the economic agents that are producing the goods or services to sell. Note in the definition that is says plan – just as we said with demand it is planned not actual supply. Consumers might not actually buy al ...
Targeting your Consumer
... – Value-personal satisfaction gained from use of a good or service – goal is to develop a relationship w/ the customer ...
... – Value-personal satisfaction gained from use of a good or service – goal is to develop a relationship w/ the customer ...
ECON211 Midterm I_an..
... c. consumption is the dependent variable and income is the independent variable d. there is no relationship between the variables e. income is the dependent variable and family consumption is the independent variable 24. The "law of demand" hypothesizes that, other things being equal, a. price and d ...
... c. consumption is the dependent variable and income is the independent variable d. there is no relationship between the variables e. income is the dependent variable and family consumption is the independent variable 24. The "law of demand" hypothesizes that, other things being equal, a. price and d ...