Supply and Demand: The demand curve
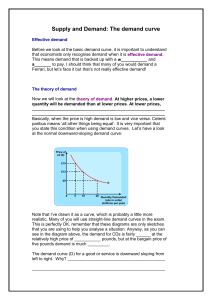
... advertising in the industry. This will shift the demand curve to the right, ceteris paribus (D2). The price will not stay at P1 for much longer. We have an excess demand situation (A to C). As stated above, this will cause the price to be bid up, and this will keep going until we reach the new equil ...
... advertising in the industry. This will shift the demand curve to the right, ceteris paribus (D2). The price will not stay at P1 for much longer. We have an excess demand situation (A to C). As stated above, this will cause the price to be bid up, and this will keep going until we reach the new equil ...
Semester Two Exam Key
... B. A computer system performs warehouse functions that are usually executed by humans. C. A technological system creates an efficient routing plan for transportation companies. D. A dispatcher has current knowledge of a delivery truck's location and destination. ...
... B. A computer system performs warehouse functions that are usually executed by humans. C. A technological system creates an efficient routing plan for transportation companies. D. A dispatcher has current knowledge of a delivery truck's location and destination. ...
A Stakeholder-Unifying, Cocreation Philosophy for Marketing
... While Peter Drucker was advocating putting the customer’s interest first, with profit as a reward for doing so, others were arguing for a view of business strategy that focused on the central importance of shareholders. The fundamental argument was that financial control over the allocation of resou ...
... While Peter Drucker was advocating putting the customer’s interest first, with profit as a reward for doing so, others were arguing for a view of business strategy that focused on the central importance of shareholders. The fundamental argument was that financial control over the allocation of resou ...
Marketing Associate Degree Sample Lesson Plan
... During the production-oriented era, the dominant attitude was that quality products would sell themselves. ...
... During the production-oriented era, the dominant attitude was that quality products would sell themselves. ...
Chapter012PowerPointSlides
... An approach requiring organizations to gather information about customer needs, share information across firm, use information to build long-term relationships with customers ...
... An approach requiring organizations to gather information about customer needs, share information across firm, use information to build long-term relationships with customers ...
Antitrust Compliance Policy
... The antitrust laws are complex, and there is no single global competition statute. Rather, competition and antitrust laws are enforced in over 100 countries including China, the European Union, Japan, Korea, Taiwan, and the United States. For the competition rules of a particular country to be appli ...
... The antitrust laws are complex, and there is no single global competition statute. Rather, competition and antitrust laws are enforced in over 100 countries including China, the European Union, Japan, Korea, Taiwan, and the United States. For the competition rules of a particular country to be appli ...
Marketing Program Planning for Cultural Differentiation Isabelle Kispotta
... It is the authors‟ belief that this is the first work of its kind to recommend a program blueprint for marketing strategy planning. The authors have not identified a significant number of references and influential papers as most of this work is experiential in nature; the correlations drawn between ...
... It is the authors‟ belief that this is the first work of its kind to recommend a program blueprint for marketing strategy planning. The authors have not identified a significant number of references and influential papers as most of this work is experiential in nature; the correlations drawn between ...
SIRUS GASIMI INTERNATIONAL MARKETING STRATEGY OF
... innovative ways to interest buyers, where to realize the production, how to present it and distinguish from other competitors. In many countries where the economy is based on the market-based approach, developed and applied marketing strategy consists of business basics, which are indispensable for ...
... innovative ways to interest buyers, where to realize the production, how to present it and distinguish from other competitors. In many countries where the economy is based on the market-based approach, developed and applied marketing strategy consists of business basics, which are indispensable for ...
Strategic Assortment Decisions in Information-Intensive and
... how economic downturns impact category assortment composition. In some categories not only private label sales increase but total category expenditures surge as well. As consumers often postpone the purchase of bigger-ticket items during economic downturns, the increased discretionary income can be ...
... how economic downturns impact category assortment composition. In some categories not only private label sales increase but total category expenditures surge as well. As consumers often postpone the purchase of bigger-ticket items during economic downturns, the increased discretionary income can be ...
The Dynamics of Rivalry
... is substantially hastened by the existence of complementary resources, e.g. the installed base of PC users, the shared infrastructure of software dealers, and the large community of buyers who expect to discover useful new products on the internet. Such mechanisms further undermine any chance of dis ...
... is substantially hastened by the existence of complementary resources, e.g. the installed base of PC users, the shared infrastructure of software dealers, and the large community of buyers who expect to discover useful new products on the internet. Such mechanisms further undermine any chance of dis ...
Data Mining For Customer Loyalty
... will whimsically switch companies or brands if provided a better offer. Their socalled loyalty is not really due to any attachment or affinity to the company or brand but because switching to another organization for the same products and services simply involves too much effort and/or risk. This ac ...
... will whimsically switch companies or brands if provided a better offer. Their socalled loyalty is not really due to any attachment or affinity to the company or brand but because switching to another organization for the same products and services simply involves too much effort and/or risk. This ac ...
Online Branding
... In the 21st century, this is what your job is all about: • Find ways to make your brand more experiential and hence more memorable! – careful spatial planning – live, real-time, event-based nature of the brand interaction ...
... In the 21st century, this is what your job is all about: • Find ways to make your brand more experiential and hence more memorable! – careful spatial planning – live, real-time, event-based nature of the brand interaction ...
Table of Contents
... of the offer that the marketer is making. There are many ways to price a product depending on the situation faced by the marketer vis-à-vis his customer or the competition. 1.112 Place Another element of Neil H.Borden's Marketing Mix is Place. Place is also known as channel, distribution, or interme ...
... of the offer that the marketer is making. There are many ways to price a product depending on the situation faced by the marketer vis-à-vis his customer or the competition. 1.112 Place Another element of Neil H.Borden's Marketing Mix is Place. Place is also known as channel, distribution, or interme ...
Regional Exam
... 39. Which of the following is an internal source of marketing information that a specialty food store uses: A. Employee handbooks C. Trade journals B. Government web sites D. Inventory records 40. Food distributors use the information from sales representatives to make decisions. One type of report ...
... 39. Which of the following is an internal source of marketing information that a specialty food store uses: A. Employee handbooks C. Trade journals B. Government web sites D. Inventory records 40. Food distributors use the information from sales representatives to make decisions. One type of report ...
Omnichannel approach – The secret ingredient of the marketing mix
... these have evolved with the changing business environment. In this paper, we talk about the foundation of marketing models – the 4 Ps, namely, Product, Price, Place and Promotion – and discuss ways of making these more effective for brand growth. We have identified an additional element beyond the a ...
... these have evolved with the changing business environment. In this paper, we talk about the foundation of marketing models – the 4 Ps, namely, Product, Price, Place and Promotion – and discuss ways of making these more effective for brand growth. We have identified an additional element beyond the a ...
Evaluation of efficiency of orange marketing system in Tanzania
... marketing costs and profit share; another was to evaluate the operational efficiency of marketing by examining the net returns on capital invested and the commission received. A study on market efficiency done by Sindh (Toaha, 1974), also support marketing efficiency could evaluated by using cost of ...
... marketing costs and profit share; another was to evaluate the operational efficiency of marketing by examining the net returns on capital invested and the commission received. A study on market efficiency done by Sindh (Toaha, 1974), also support marketing efficiency could evaluated by using cost of ...
what is strategy
... goal of any enterprise. But they work in very different ways. A company can outperform rivals only if it can establish a difference that it can preserve. It must deliver greater value to customers or create comparable value at a lower cost, or do both. The arithmetic of superior profitability then f ...
... goal of any enterprise. But they work in very different ways. A company can outperform rivals only if it can establish a difference that it can preserve. It must deliver greater value to customers or create comparable value at a lower cost, or do both. The arithmetic of superior profitability then f ...
PDF - Department of State Development
... be segmental in their own right. (Of course there are numerous occasions where the customer is the consumer of the purchased product/service.) This section will look at consumers only. Customers will need a similar approach. Close evaluation of typical consumers in the market segments being targeted ...
... be segmental in their own right. (Of course there are numerous occasions where the customer is the consumer of the purchased product/service.) This section will look at consumers only. Customers will need a similar approach. Close evaluation of typical consumers in the market segments being targeted ...
Service parts pricing

Service Parts Pricing refers to the aspect of Service Lifecycle Management that deals with setting prices for service parts in the after-sales market. Like other streams of Pricing, Service Parts Pricing is a scientific pursuit aimed at aligning service part prices internally to be logical and consistent, and at the same time aligning them externally with the market. This is done with the overarching aim of extracting the maximum possible price from service parts and thus maximize the profit margins. Pricing analysts have to be cognizant of possible repercussions of pricing their parts too high or too low in the after-sales market; they constantly have to strive to get the prices just right towards achieving maximum margins and maximum possible volumes.The after-sales market consists of service part and after-sales service. These areas often account for a low share in total sales, but for a relatively high share in total profits. It is important to understand that the after-sales supply chain is very different from the manufacturing supply chain, and hence rules that apply to pricing manufacturing parts do not hold good for pricing service parts. Service Parts Pricing requires a different outlook and approach.Service networks deal with a considerably higher number of SKUs and a heterogeneous product portfolio, are more complex, have a sporadic nature of demand AND have minimal response times and strict SLAs. Companies have traditionally been content with outsourcing the after-sales side of their business and have encouraged third-party parts and service providers in the market. The result has been a bevy of these operators in the market with strict price competition and low margins.Increasingly, however, companies are realizing the importance of the after-sales market and its impact on customer retention and loyalty. Increasingly, also, companies have realized that they can extract higher profit margins from the after-sales services market due to the intangible nature of services. Companies are investing in their after-sales service networks to deliver high levels of customer service and in return command higher prices for their parts and services. Customers are being sold the concept of total cost of ownership (TCO) and are being made to realize that buying from OEMs comes packaged with better distribution channels, shorter response times, better knowledge on products, and ultimately higher product uptime.The challenge for companies is to provide reliable service levels in an environment of uncertainty. Unlike factories, businesses can’t produce services in advance of demand. They can manufacture them only when an unpredictable event, such as a product failure, triggers a need. The challenge for Service Parts Pricing is to put a value to this customer need. Parts that are critical, for example, can command higher prices. So can parts that only the OEM provides in the market. Parts that are readily available in the market cannot, and must not, be priced to high. Another problem with after-sales market is that demand cannot be stimulated with price discounts, customers do not stock up service parts just because they are on discount. On the up-side, the fact that most service parts are inelastic means pricing analysts can raise prices without the adverse effects that manufacturing or retail networks witness.These and other characteristics of the after-sales market give Service Parts Pricing a life of its own. Companies are realizing that they can use the lever of service part pricing to increase profitability and don't have to take prices as market determined. Understanding customer needs and expectations, along with the company's internal strengths and weaknesses, goes a long way in designing an effective service part pricing strategy.























