Marketing Seminar Notes
... are making less and buying more Firms are under intense quality and time pressure To get what they need, firms are concentrating their purchases with fewer suppliers and developing longterm “partnering” relationships ...
... are making less and buying more Firms are under intense quality and time pressure To get what they need, firms are concentrating their purchases with fewer suppliers and developing longterm “partnering” relationships ...
Example #1 - West Salem High School
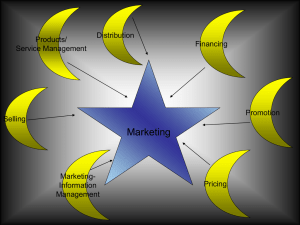
... distribute the product and make many copies of the item, then you design a way to promote the product. Next decided how you are going to sell it and then make decisions on how to market the product. Next you finance the product and price it. Now you promote it and get people to purchase your product ...
... distribute the product and make many copies of the item, then you design a way to promote the product. Next decided how you are going to sell it and then make decisions on how to market the product. Next you finance the product and price it. Now you promote it and get people to purchase your product ...
12-Price Determination
... Different types of retailers require different percentage mark-ups because of the nature of the products handled and the services offered: Low-turnover products (jewellery) need much larger mark-ups than high-turnover products (groceries). Retailers that offer many services require larger mark-ups t ...
... Different types of retailers require different percentage mark-ups because of the nature of the products handled and the services offered: Low-turnover products (jewellery) need much larger mark-ups than high-turnover products (groceries). Retailers that offer many services require larger mark-ups t ...
The Marketing Mix - PowerPoint Presentation
... Products may be sold at a price lower than the cost to produce it. Often used by supermarkets to encourage people into the store where it is hoped they will buy other products. ...
... Products may be sold at a price lower than the cost to produce it. Often used by supermarkets to encourage people into the store where it is hoped they will buy other products. ...
Market Opportunity
... Homework • Identify where you are priced, and what market that puts you in (list the competition based on that specific price point) • Identify your target market and their preferred market mediums • Provide at least 3 supporting documents to justify your product, price point, and target market ...
... Homework • Identify where you are priced, and what market that puts you in (list the competition based on that specific price point) • Identify your target market and their preferred market mediums • Provide at least 3 supporting documents to justify your product, price point, and target market ...
Marketing is the Marketing Mix
... Price - what you'll charge customers for products and services. May be affected by supply and demand, your costs, and/or your competition. ...
... Price - what you'll charge customers for products and services. May be affected by supply and demand, your costs, and/or your competition. ...
Economic Survey
... o Goods in a command economy were inexpensive o Consumers could not always find what they needed § Consumers had to wait years for apartments, or telephones § Make long lines for bread, meat, and poultry § Price controls were instituted Rationing in the United States – only in times of desperate nee ...
... o Goods in a command economy were inexpensive o Consumers could not always find what they needed § Consumers had to wait years for apartments, or telephones § Make long lines for bread, meat, and poultry § Price controls were instituted Rationing in the United States – only in times of desperate nee ...
Chapter 9 material - Loyola University Maryland
... less sensitive to the price. This is why Michelin advertises safety of babies in their ads. How much is the child's safety worth? Doesn't this make the price difference between a Michelin and another brand seem small? This is especially useful as a tool for segmentation since many products can be us ...
... less sensitive to the price. This is why Michelin advertises safety of babies in their ads. How much is the child's safety worth? Doesn't this make the price difference between a Michelin and another brand seem small? This is especially useful as a tool for segmentation since many products can be us ...
chapter4B
... Introduction Phrase Features: brand-new products or service a baby in the market low consumer awareness, low sales, no competitors Examples: iris-based personal identify card 虹膜个人识别卡 third-generation mobile phone 天翼3G, I Pad 2 Marketing ★ low consumer/product awareness →low sales Strategies: → mass ...
... Introduction Phrase Features: brand-new products or service a baby in the market low consumer awareness, low sales, no competitors Examples: iris-based personal identify card 虹膜个人识别卡 third-generation mobile phone 天翼3G, I Pad 2 Marketing ★ low consumer/product awareness →low sales Strategies: → mass ...
3.03 Guided Notes D
... Demand forecasting is the activity of ________________________________ the quantity of a product or service that consumers will purchase. Demand forecasting involves techniques including both ___________________________ methods, such as educated guesses, and _______________________ methods, such as ...
... Demand forecasting is the activity of ________________________________ the quantity of a product or service that consumers will purchase. Demand forecasting involves techniques including both ___________________________ methods, such as educated guesses, and _______________________ methods, such as ...
Promotion and Pricing Strategies
... • Encourage retailers in several ways: • To stock new products. • To continue carrying existing ones. • To promote both new and existing products effectively to consumers. • Point-of-purchase (POP) adver tising Displays or demonstrations that promote products when and where consumers buy them, such ...
... • Encourage retailers in several ways: • To stock new products. • To continue carrying existing ones. • To promote both new and existing products effectively to consumers. • Point-of-purchase (POP) adver tising Displays or demonstrations that promote products when and where consumers buy them, such ...
Business Studies Revison Guide
... Income tax- a tax on the income earned by workers. National insurance contributions- a tax on the earning of workers. Business takes it from the employees pay and give it to the government. Sole traders have to pay this tax themselves. Corporate tax- a tax on the profits of a company. Sole traders d ...
... Income tax- a tax on the income earned by workers. National insurance contributions- a tax on the earning of workers. Business takes it from the employees pay and give it to the government. Sole traders have to pay this tax themselves. Corporate tax- a tax on the profits of a company. Sole traders d ...
3.02-GuidedNotes
... Market Segmentation is the division of a total market into __________________ specific groups as a way to meet the customers’ needs Advantages _____________________________ Allows for a finely tuned product, appropriate price, and ease of distribution Disadvantages More complex, difficul ...
... Market Segmentation is the division of a total market into __________________ specific groups as a way to meet the customers’ needs Advantages _____________________________ Allows for a finely tuned product, appropriate price, and ease of distribution Disadvantages More complex, difficul ...
Product Price Promotion Place
... your customers and competitors, so that you can provide the right products at the right price in the right place, promoted in the right way to achieve your business objectives. ...
... your customers and competitors, so that you can provide the right products at the right price in the right place, promoted in the right way to achieve your business objectives. ...
Service parts pricing

Service Parts Pricing refers to the aspect of Service Lifecycle Management that deals with setting prices for service parts in the after-sales market. Like other streams of Pricing, Service Parts Pricing is a scientific pursuit aimed at aligning service part prices internally to be logical and consistent, and at the same time aligning them externally with the market. This is done with the overarching aim of extracting the maximum possible price from service parts and thus maximize the profit margins. Pricing analysts have to be cognizant of possible repercussions of pricing their parts too high or too low in the after-sales market; they constantly have to strive to get the prices just right towards achieving maximum margins and maximum possible volumes.The after-sales market consists of service part and after-sales service. These areas often account for a low share in total sales, but for a relatively high share in total profits. It is important to understand that the after-sales supply chain is very different from the manufacturing supply chain, and hence rules that apply to pricing manufacturing parts do not hold good for pricing service parts. Service Parts Pricing requires a different outlook and approach.Service networks deal with a considerably higher number of SKUs and a heterogeneous product portfolio, are more complex, have a sporadic nature of demand AND have minimal response times and strict SLAs. Companies have traditionally been content with outsourcing the after-sales side of their business and have encouraged third-party parts and service providers in the market. The result has been a bevy of these operators in the market with strict price competition and low margins.Increasingly, however, companies are realizing the importance of the after-sales market and its impact on customer retention and loyalty. Increasingly, also, companies have realized that they can extract higher profit margins from the after-sales services market due to the intangible nature of services. Companies are investing in their after-sales service networks to deliver high levels of customer service and in return command higher prices for their parts and services. Customers are being sold the concept of total cost of ownership (TCO) and are being made to realize that buying from OEMs comes packaged with better distribution channels, shorter response times, better knowledge on products, and ultimately higher product uptime.The challenge for companies is to provide reliable service levels in an environment of uncertainty. Unlike factories, businesses can’t produce services in advance of demand. They can manufacture them only when an unpredictable event, such as a product failure, triggers a need. The challenge for Service Parts Pricing is to put a value to this customer need. Parts that are critical, for example, can command higher prices. So can parts that only the OEM provides in the market. Parts that are readily available in the market cannot, and must not, be priced to high. Another problem with after-sales market is that demand cannot be stimulated with price discounts, customers do not stock up service parts just because they are on discount. On the up-side, the fact that most service parts are inelastic means pricing analysts can raise prices without the adverse effects that manufacturing or retail networks witness.These and other characteristics of the after-sales market give Service Parts Pricing a life of its own. Companies are realizing that they can use the lever of service part pricing to increase profitability and don't have to take prices as market determined. Understanding customer needs and expectations, along with the company's internal strengths and weaknesses, goes a long way in designing an effective service part pricing strategy.