Opportunity Analysis, Market Segmentation & Market Targeting
... segments. • Tackle most attractive segment first. • Using profits earned from this segment, then target the next most attractive segment. • Runs the risk of allowing potential competitors into a market. ...
... segments. • Tackle most attractive segment first. • Using profits earned from this segment, then target the next most attractive segment. • Runs the risk of allowing potential competitors into a market. ...
Chapter 5
... The belief that consumer wants & needs are the driving force behind any product development or marketing effort. There was a time when marketing decisions were made primarily on investment reasoning. Today, it is based on customer’s needs and wants. Consumers are more educated today especial ...
... The belief that consumer wants & needs are the driving force behind any product development or marketing effort. There was a time when marketing decisions were made primarily on investment reasoning. Today, it is based on customer’s needs and wants. Consumers are more educated today especial ...
Methods to Price Your Product
... competitive markets this strategy will sell product quickly, creating economies of scale and market penetration. As you increase production, some of your costs will decrease because of economies of scale. You’ll save when you buy materials and ingredients in larger quantities. The lower costs per un ...
... competitive markets this strategy will sell product quickly, creating economies of scale and market penetration. As you increase production, some of your costs will decrease because of economies of scale. You’ll save when you buy materials and ingredients in larger quantities. The lower costs per un ...
What is Marketing PPt
... Place – available where customers can get it Time – available when customers want it Possession – able to take it home Information – know about the product/service ...
... Place – available where customers can get it Time – available when customers want it Possession – able to take it home Information – know about the product/service ...
The Marketing Mix for Tourism Services Objective
... producer ( who aim to achieve predetermined sales volume and revenue objectives) and prospective customers ( who aim to maximize the value for money in choices they make between alternative products). In tourism there is generally a regular or standard price for a product. In addition, there are dis ...
... producer ( who aim to achieve predetermined sales volume and revenue objectives) and prospective customers ( who aim to maximize the value for money in choices they make between alternative products). In tourism there is generally a regular or standard price for a product. In addition, there are dis ...
7 Key Marketing Functions
... pizza smaller for a snack not a meal. Also offered non-traditional toppings such as corn & tuna. ...
... pizza smaller for a snack not a meal. Also offered non-traditional toppings such as corn & tuna. ...
Mktg 1.02 Marketing Mix PPT
... Should we offer one product-or more than one? Is the product a good, service, or idea? Does the product have special features? Does the product have multiple uses? What resources are necessary to research and develop the product? What level of quality should be produced or provided? Which brands sho ...
... Should we offer one product-or more than one? Is the product a good, service, or idea? Does the product have special features? Does the product have multiple uses? What resources are necessary to research and develop the product? What level of quality should be produced or provided? Which brands sho ...
Chapter 4 Marketing Begins with Customers Study Guide
... • Many competitors, some differences among the choices • It is important for the companies to have clearlyidentified differences that result in customers selecting their brands • Companies in monopolistic competition find the marketing concept to be of most value • Focus different groups of customer ...
... • Many competitors, some differences among the choices • It is important for the companies to have clearlyidentified differences that result in customers selecting their brands • Companies in monopolistic competition find the marketing concept to be of most value • Focus different groups of customer ...
THE APPLICATION OF THE GAME THEORY TO THE
... A game is any situation in which players, i.e. participants in the game, make strategic decisions, taking into account actions and reactions of others. A strategy is a rule or plan of action for playing the game. For example, for an oligopoly company which needs to determine the price of its product ...
... A game is any situation in which players, i.e. participants in the game, make strategic decisions, taking into account actions and reactions of others. A strategy is a rule or plan of action for playing the game. For example, for an oligopoly company which needs to determine the price of its product ...
10.2 HSC topic: Marketing -> Total system of
... monitoring –work in progress checks, -bugets, sales analysis, targets and controlling –cash flow statements, balance sheets, profit and loss developing a financial forecast; comparing actual and ...
... monitoring –work in progress checks, -bugets, sales analysis, targets and controlling –cash flow statements, balance sheets, profit and loss developing a financial forecast; comparing actual and ...
Organic Rice Marketing Concepts and Issues (Dr Nerlie Manalili)
... • Marketing ones product is the hardest part of being a farmer •Most farmers: * lack the skills and are not familiar with marketing if they need technical assistance in production which they have been doing all their productive lives, then more so in marketing which is new to them * not ...
... • Marketing ones product is the hardest part of being a farmer •Most farmers: * lack the skills and are not familiar with marketing if they need technical assistance in production which they have been doing all their productive lives, then more so in marketing which is new to them * not ...
Market Analysis
... business model’s value proposition is strongest Target Market: (Usually) demographic segment of the SAM with the most direct path to success Target market should be proportionally larger than cost of development! ...
... business model’s value proposition is strongest Target Market: (Usually) demographic segment of the SAM with the most direct path to success Target market should be proportionally larger than cost of development! ...
KotlerMM_ch10
... is the soft drink that gives you more energy than any other brand because it has the highest level of caffeine. ...
... is the soft drink that gives you more energy than any other brand because it has the highest level of caffeine. ...
Download Syllabus
... preference). It is important that you attend all classes, arrive on time, and give speakers and your fellow classmates your full attention. If you cannot attend a specific class or have to arrive late let Prof. Cramer know in advance by email. Please refrain from using laptops, IPads, cellphones, et ...
... preference). It is important that you attend all classes, arrive on time, and give speakers and your fellow classmates your full attention. If you cannot attend a specific class or have to arrive late let Prof. Cramer know in advance by email. Please refrain from using laptops, IPads, cellphones, et ...
2. MKT Strategy and Planning
... Used with permission by MTV 2010 MTV Networks All Rights Reserved MTV, all related titles, characters and logos are trademarks owned by MTV Networks, a division of Viacom International Inc. ...
... Used with permission by MTV 2010 MTV Networks All Rights Reserved MTV, all related titles, characters and logos are trademarks owned by MTV Networks, a division of Viacom International Inc. ...
GE Sr. Marketing Manager_Job Posting
... Own the value proposition. Develop defendable and differentiated value propositions, messaging, and position for the product line Be the market expert. Understand and communicate the market environment including: market opportunity, size, competition, macro and micro level trends, pricing dynami ...
... Own the value proposition. Develop defendable and differentiated value propositions, messaging, and position for the product line Be the market expert. Understand and communicate the market environment including: market opportunity, size, competition, macro and micro level trends, pricing dynami ...
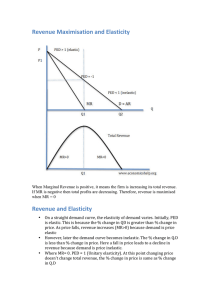
Revenue Maximisation and Elasticity Revenue
... Increase profit. Higher profit enables higher wages and more money for investment. Economies of Scale. In industries with high fixed costs, increased market sales leads to lower average costs enabling a f ...
... Increase profit. Higher profit enables higher wages and more money for investment. Economies of Scale. In industries with high fixed costs, increased market sales leads to lower average costs enabling a f ...
download
... To be successful, this strategy usually requires a considerable market share advantage or preferential access to raw materials, components, labour, or some other important input. Without one or more of these advantages, the strategy can easily be mimicked by competitors. Successful implementation a ...
... To be successful, this strategy usually requires a considerable market share advantage or preferential access to raw materials, components, labour, or some other important input. Without one or more of these advantages, the strategy can easily be mimicked by competitors. Successful implementation a ...
Marketing Concept
... o Explain the advantage of small businesses in providing customer service The Role Of Marketing o Marketing Functions—Groups of marketing activities 1. Product/Service Planning—assists in design/development by gathering information and testing ideas 2. Purchasing—identifies & obtains products 3. F ...
... o Explain the advantage of small businesses in providing customer service The Role Of Marketing o Marketing Functions—Groups of marketing activities 1. Product/Service Planning—assists in design/development by gathering information and testing ideas 2. Purchasing—identifies & obtains products 3. F ...
Consumers Rule
... Step 6: Selecting the Final Price • Additional factors to select final price: Impact of other marketing activities Company pricing policies Gain-and-risk-sharing pricing Impact of price on other parties ...
... Step 6: Selecting the Final Price • Additional factors to select final price: Impact of other marketing activities Company pricing policies Gain-and-risk-sharing pricing Impact of price on other parties ...
Service parts pricing

Service Parts Pricing refers to the aspect of Service Lifecycle Management that deals with setting prices for service parts in the after-sales market. Like other streams of Pricing, Service Parts Pricing is a scientific pursuit aimed at aligning service part prices internally to be logical and consistent, and at the same time aligning them externally with the market. This is done with the overarching aim of extracting the maximum possible price from service parts and thus maximize the profit margins. Pricing analysts have to be cognizant of possible repercussions of pricing their parts too high or too low in the after-sales market; they constantly have to strive to get the prices just right towards achieving maximum margins and maximum possible volumes.The after-sales market consists of service part and after-sales service. These areas often account for a low share in total sales, but for a relatively high share in total profits. It is important to understand that the after-sales supply chain is very different from the manufacturing supply chain, and hence rules that apply to pricing manufacturing parts do not hold good for pricing service parts. Service Parts Pricing requires a different outlook and approach.Service networks deal with a considerably higher number of SKUs and a heterogeneous product portfolio, are more complex, have a sporadic nature of demand AND have minimal response times and strict SLAs. Companies have traditionally been content with outsourcing the after-sales side of their business and have encouraged third-party parts and service providers in the market. The result has been a bevy of these operators in the market with strict price competition and low margins.Increasingly, however, companies are realizing the importance of the after-sales market and its impact on customer retention and loyalty. Increasingly, also, companies have realized that they can extract higher profit margins from the after-sales services market due to the intangible nature of services. Companies are investing in their after-sales service networks to deliver high levels of customer service and in return command higher prices for their parts and services. Customers are being sold the concept of total cost of ownership (TCO) and are being made to realize that buying from OEMs comes packaged with better distribution channels, shorter response times, better knowledge on products, and ultimately higher product uptime.The challenge for companies is to provide reliable service levels in an environment of uncertainty. Unlike factories, businesses can’t produce services in advance of demand. They can manufacture them only when an unpredictable event, such as a product failure, triggers a need. The challenge for Service Parts Pricing is to put a value to this customer need. Parts that are critical, for example, can command higher prices. So can parts that only the OEM provides in the market. Parts that are readily available in the market cannot, and must not, be priced to high. Another problem with after-sales market is that demand cannot be stimulated with price discounts, customers do not stock up service parts just because they are on discount. On the up-side, the fact that most service parts are inelastic means pricing analysts can raise prices without the adverse effects that manufacturing or retail networks witness.These and other characteristics of the after-sales market give Service Parts Pricing a life of its own. Companies are realizing that they can use the lever of service part pricing to increase profitability and don't have to take prices as market determined. Understanding customer needs and expectations, along with the company's internal strengths and weaknesses, goes a long way in designing an effective service part pricing strategy.