MAX14531E–MAX14534E USB 2.0 Hi-Speed and Audio Switches with General Description
... signals, low/full-speed USB signals, and analog signals such as AC-coupled audio or video through any of three channels. These devices combine the low oncapacitance (CON) and low on-resistance (RON) necessary for high-performance switching applications in portable electronics, and include an interna ...
... signals, low/full-speed USB signals, and analog signals such as AC-coupled audio or video through any of three channels. These devices combine the low oncapacitance (CON) and low on-resistance (RON) necessary for high-performance switching applications in portable electronics, and include an interna ...
LMR16030 - Texas Instruments
... from a 4.3 V to 60 V supply voltage. It integrates a 155 mΩ (typical) high-side MOSFET, and is capable of delivering up to 3 A DC load current with exceptional efficiency and thermal performance in a very small solution size. The operating current is typically 40 μA under no load condition (not swit ...
... from a 4.3 V to 60 V supply voltage. It integrates a 155 mΩ (typical) high-side MOSFET, and is capable of delivering up to 3 A DC load current with exceptional efficiency and thermal performance in a very small solution size. The operating current is typically 40 μA under no load condition (not swit ...
OIP A 67 dBm Multistacked Junction Varactor 3
... When connecting varactor stacks in series, the applied RF voltage will be divided over the stacks. Since the (remaining) nonlinearities of these varactor stacks are excited with a voltage that is times lower, their resulting nonlinear currents will be reduced. One of the key advantages of the NTSVS ...
... When connecting varactor stacks in series, the applied RF voltage will be divided over the stacks. Since the (remaining) nonlinearities of these varactor stacks are excited with a voltage that is times lower, their resulting nonlinear currents will be reduced. One of the key advantages of the NTSVS ...
A Bidirectional LLC Resonant Converter With Automatic Forward
... in Fig. 9(a). M1, M4, M5, and M8 turn ON at t0 with ZVS. The voltage across the auxiliary inductor Lm 2 is equal to Vo , so iL m 2 increases linearly. Voltage across the transformer magnetizing inductor Lm 1 is equal to Vb , and its current increases linearly, too. In this mode, Lr resonant with Cr ...
... in Fig. 9(a). M1, M4, M5, and M8 turn ON at t0 with ZVS. The voltage across the auxiliary inductor Lm 2 is equal to Vo , so iL m 2 increases linearly. Voltage across the transformer magnetizing inductor Lm 1 is equal to Vb , and its current increases linearly, too. In this mode, Lr resonant with Cr ...
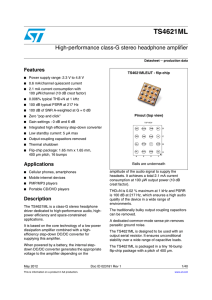
TS4621ML - STMicroelectronics
... driver dedicated to high-performance audio, highpower efficiency and space-constrained applications. It is based on the core technology of a low power dissipation amplifier combined with a highefficiency step-down DC/DC converter for supplying this amplifier. When powered by a battery, the internal ...
... driver dedicated to high-performance audio, highpower efficiency and space-constrained applications. It is based on the core technology of a low power dissipation amplifier combined with a highefficiency step-down DC/DC converter for supplying this amplifier. When powered by a battery, the internal ...
Noise in Analog Communication Systems
... The channel introduces additive noise in message and thus message received becomes corrupted. Figure of merit is defined ...
... The channel introduces additive noise in message and thus message received becomes corrupted. Figure of merit is defined ...
THS4081 Low-Power High Speed Operational
... plane noise coupling into these pins. This is especially important for the inverting pin while the amplifier is operating in the noninverting mode. Because the voltage at this pin swings directly with the noninverting input voltage, any stray capacitance would allow currents to flow into the ground ...
... plane noise coupling into these pins. This is especially important for the inverting pin while the amplifier is operating in the noninverting mode. Because the voltage at this pin swings directly with the noninverting input voltage, any stray capacitance would allow currents to flow into the ground ...
Dynamic range and sensitivity improvement in complementary metal-oxide semiconductor technology
... detectors exhibit high dynamic range (DR) and sensitivity. The disadvantage is that they only detect radiation in a small part of the near-IR range. BiCMOS detectors have shown improvements over CCD detectors because they have lower power consumption, high speed operation, and lower manufacturing co ...
... detectors exhibit high dynamic range (DR) and sensitivity. The disadvantage is that they only detect radiation in a small part of the near-IR range. BiCMOS detectors have shown improvements over CCD detectors because they have lower power consumption, high speed operation, and lower manufacturing co ...
Reference Design
... handle large amount of switching current often require far more than +/-1A drive current even for a brief moment due to mosfets’ gate drive requirement (high total gate charge, Qg). In order to facilitate this high drive current, a buffer stage is devised to source and sink this high gate charge. Th ...
... handle large amount of switching current often require far more than +/-1A drive current even for a brief moment due to mosfets’ gate drive requirement (high total gate charge, Qg). In order to facilitate this high drive current, a buffer stage is devised to source and sink this high gate charge. Th ...
TPS4021x 4.5-V to 52-V Input Current Mode Boost Controller (Rev. F)
... Soft-start time programming pin. Connect capacitor from SS pin to GND to program converter soft-start time. This pin also functions as a timeout timer when the power supply is in an overcurrent condition. ...
... Soft-start time programming pin. Connect capacitor from SS pin to GND to program converter soft-start time. This pin also functions as a timeout timer when the power supply is in an overcurrent condition. ...
Understanding Quartz Crystals
... Consequently, most of the quartz used for crystal fabrication today is of the “cultured” or synthetic variety. Cultured quartz is produced by placing small seeds of quartz mixed with an alkaline solution in an autoclave. This mixture is subjected to high heat (> 400°C) and high pressure (30,000 psi) ...
... Consequently, most of the quartz used for crystal fabrication today is of the “cultured” or synthetic variety. Cultured quartz is produced by placing small seeds of quartz mixed with an alkaline solution in an autoclave. This mixture is subjected to high heat (> 400°C) and high pressure (30,000 psi) ...
MAX9814 - Part Number Search
... microphone amplifier gain is then reduced with a selectable time constant to correct for the excessive outputvoltage amplitude. This process is known as the attack time. When the output signal subsequently lowers in amplitude, the gain is held at the reduced state for a short period before slowly in ...
... microphone amplifier gain is then reduced with a selectable time constant to correct for the excessive outputvoltage amplitude. This process is known as the attack time. When the output signal subsequently lowers in amplitude, the gain is held at the reduced state for a short period before slowly in ...
Datasheet
... signals are often received from a transmission line where long cables and system interference can degrade signal quality, the inputs have enhanced sensitivity to detect weakened signals. The receivers also feature a typical hysteresis margin of 500mV for clean reception of slowly transitioning signa ...
... signals are often received from a transmission line where long cables and system interference can degrade signal quality, the inputs have enhanced sensitivity to detect weakened signals. The receivers also feature a typical hysteresis margin of 500mV for clean reception of slowly transitioning signa ...
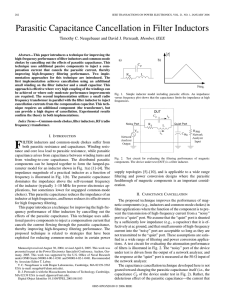
T.C. Neugebauer and D.J. Perreault, “Parasitic Capacitance Cancellation in Filter Inductors,” IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics , Vol. 21, No. 1, January 2006, pp. 282-288.
... and 59 pF when the turns ratios are 0.5 and 0.06. Note that 56 pF is much larger than the expected compensating capacitor for ...
... and 59 pF when the turns ratios are 0.5 and 0.06. Note that 56 pF is much larger than the expected compensating capacitor for ...
UNIT - WordPress.com
... During the course of signal T (x) travel it experience attenuation, time delay, additive noise. These disturbance, attenuation, interference are termed as noise. Practically Noise is always possible.Amplifying the received signal does not help. As Amplifiers amplify both signal as well as noise comp ...
... During the course of signal T (x) travel it experience attenuation, time delay, additive noise. These disturbance, attenuation, interference are termed as noise. Practically Noise is always possible.Amplifying the received signal does not help. As Amplifiers amplify both signal as well as noise comp ...
TPS62152-Q1 - Texas Instruments
... Qualified for Automotive Applications AEC-Q100 Qualified With the Following Results: – Device Temperature Grade 1: –40°C to 125°C Ambient Operating Temperature Range – Device HBM ESD Classification Level H2 – Device CDM ESD Classification Level C4B DCS-Control Topology Input Voltage Range: 4 V to 17 ...
... Qualified for Automotive Applications AEC-Q100 Qualified With the Following Results: – Device Temperature Grade 1: –40°C to 125°C Ambient Operating Temperature Range – Device HBM ESD Classification Level H2 – Device CDM ESD Classification Level C4B DCS-Control Topology Input Voltage Range: 4 V to 17 ...
II - CERN Accelerator School
... The presence of the beam phase loop enlarge the Robinson 1st stability limits since also a region with z < 0 (z > 0 for h < 0 ) becomes accessible. This is because the strong loop damping of the coherent motion overrides the Robinson antidamping. The Robinson 2nd limit is unaffected since it is a ...
... The presence of the beam phase loop enlarge the Robinson 1st stability limits since also a region with z < 0 (z > 0 for h < 0 ) becomes accessible. This is because the strong loop damping of the coherent motion overrides the Robinson antidamping. The Robinson 2nd limit is unaffected since it is a ...
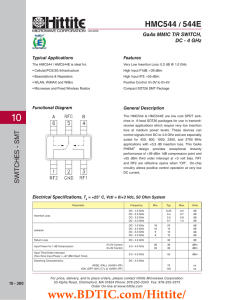
AZV321 Description Pin Assignments Applications Functional Block
... Should Customers purchase or use Diodes Incorporated products for any unintended or unauthorized application, Customers shall indemnify and hold Diodes Incorporated and its representatives harmless against all claims, damages, expenses, and attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any c ...
... Should Customers purchase or use Diodes Incorporated products for any unintended or unauthorized application, Customers shall indemnify and hold Diodes Incorporated and its representatives harmless against all claims, damages, expenses, and attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any c ...
±15kV ESD-Protected, 1µA, 3.0V to 5.5V, 250kbps, RS-232 Transceivers with AutoShutdown
... guarantee a 250kbps data rate with worst-case loads of 3kΩ in parallel with 1000pF, providing compatibility with PC-to-PC communication software such as LapLink™. Transmitters can be paralleled to drive multiple receivers. The MAX3243E has been specifically designed to drive serial mice. Figure 1 sh ...
... guarantee a 250kbps data rate with worst-case loads of 3kΩ in parallel with 1000pF, providing compatibility with PC-to-PC communication software such as LapLink™. Transmitters can be paralleled to drive multiple receivers. The MAX3243E has been specifically designed to drive serial mice. Figure 1 sh ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.