AD8571,72,74 - Analog Devices
... external capacitors are required.) Using a spread-spectrum, auto-zero technique, the AD8571/AD8572/AD8574 eliminate the intermodulation effects from interaction of the chopping function with the signal frequency in ac applications. With an offset voltage of only 1 μV and drift of 0.005 μV/°C, the AD ...
... external capacitors are required.) Using a spread-spectrum, auto-zero technique, the AD8571/AD8572/AD8574 eliminate the intermodulation effects from interaction of the chopping function with the signal frequency in ac applications. With an offset voltage of only 1 μV and drift of 0.005 μV/°C, the AD ...
ta2022 stereo 90w
... VN10 generator filter capacitors. The high frequency capacitor (0.1uF) must be located close to pin 2 (VN10) to maximize device performance. The value of the bulk capacitor should be sized appropriately such that the VN10 voltage does not overshoot with respect to VNN during TA2022 turn on. Tripath ...
... VN10 generator filter capacitors. The high frequency capacitor (0.1uF) must be located close to pin 2 (VN10) to maximize device performance. The value of the bulk capacitor should be sized appropriately such that the VN10 voltage does not overshoot with respect to VNN during TA2022 turn on. Tripath ...
DET-L SERIES Oriel ® Amplified Detectors
... accessories and instruments. They may also be rod mounted, if desired. Each of these detectors comes with a low-noise transimpedance amplifier (TIA) built into the detector case, simplifying setup and operation. Switch selection of transimpedance gain and time constant are provided on most models. T ...
... accessories and instruments. They may also be rod mounted, if desired. Each of these detectors comes with a low-noise transimpedance amplifier (TIA) built into the detector case, simplifying setup and operation. Switch selection of transimpedance gain and time constant are provided on most models. T ...
CMOS Mixed Signal Design - Part I: OpAmp Design
... input DC level. This causes problems with direct connection to the next stage, or with DC feed back to itself. These problems can be reduced if we use a complementary arrangement of n and p channel transistors for cascoding. The upper transistor of the cascode arrangement can be thought of as a sour ...
... input DC level. This causes problems with direct connection to the next stage, or with DC feed back to itself. These problems can be reduced if we use a complementary arrangement of n and p channel transistors for cascoding. The upper transistor of the cascode arrangement can be thought of as a sour ...
Accuracy Contour Plots
... curve. Afterwards, the specific frequencies are marked where the impedance exceeds the 1% and 10% accuracy limit. The same is done with the phase curve. The one specific frequency is marked where phase varies more than 2° and 10° from its ideal. For resistors this value is 0° and for capacitors -90° ...
... curve. Afterwards, the specific frequencies are marked where the impedance exceeds the 1% and 10% accuracy limit. The same is done with the phase curve. The one specific frequency is marked where phase varies more than 2° and 10° from its ideal. For resistors this value is 0° and for capacitors -90° ...
model sr830 - Stanford Research Systems
... Set when battery backup fails Set when RAM Memory test finds an error Set when ROM Memory test finds an error Set when GPIB binary data transfer aborts Set when DSP test finds an error Set when an internal math error occurs ...
... Set when battery backup fails Set when RAM Memory test finds an error Set when ROM Memory test finds an error Set when GPIB binary data transfer aborts Set when DSP test finds an error Set when an internal math error occurs ...
MAX3384E ±15kV ESD-Protected, 3.0V to 5.5V, Low-Power, ________________General Description
... The transceiver has a proprietary low-dropout transmitter output stage, delivering true RS-232 performance from a +3.0V to +5.5V supply with a dual charge pump. The charge pump requires only four small 0.1µF capacitors for operation from a +3.3V supply. Each device is guaranteed to run at data rates ...
... The transceiver has a proprietary low-dropout transmitter output stage, delivering true RS-232 performance from a +3.0V to +5.5V supply with a dual charge pump. The charge pump requires only four small 0.1µF capacitors for operation from a +3.3V supply. Each device is guaranteed to run at data rates ...
vacon 10 complete user manual ac drives
... EN61800-3 defines the division of frequency converters into four classes according to the level of electromagnetic disturbances emitted, the requirements of a power system network and the installation environment (see below). The EMC class of each product is defined in the type designation code. Cat ...
... EN61800-3 defines the division of frequency converters into four classes according to the level of electromagnetic disturbances emitted, the requirements of a power system network and the installation environment (see below). The EMC class of each product is defined in the type designation code. Cat ...
LTC3400-1 - 600mA, 1.2MHz Micropower Synchronous Boost
... to provide a peak current control command for the PWM. Peak switch current is limited to approximately 850mA independent of input or output voltage. The current signal is blanked for 40ns to enhance noise rejection. Zero Current Comparator: The zero current comparator monitors the inductor current t ...
... to provide a peak current control command for the PWM. Peak switch current is limited to approximately 850mA independent of input or output voltage. The current signal is blanked for 40ns to enhance noise rejection. Zero Current Comparator: The zero current comparator monitors the inductor current t ...
Lecture 19
... in which we used the relation bi = /vmi. This shows that if the proper encoder, decoder and equalizer can be implemented, all signals can be perfectly reconstructed, with no crosstalk, no attenuation and no dispersion. In the special case where the lines are lossless, ai = 0, Q= I (the identity mat ...
... in which we used the relation bi = /vmi. This shows that if the proper encoder, decoder and equalizer can be implemented, all signals can be perfectly reconstructed, with no crosstalk, no attenuation and no dispersion. In the special case where the lines are lossless, ai = 0, Q= I (the identity mat ...
Introduction to Alternating Current, Voltage and Power
... amount of heat in a resistive circuit) • It is sometimes called the resistive DC equivalent value • It takes into account that the AC source passes through zero twice in each cycle where it does no work at all Vrms = 0.707Vp Irms = 0.707Ip Vp = 1.414Vrms Ip = 1.414Irms ...
... amount of heat in a resistive circuit) • It is sometimes called the resistive DC equivalent value • It takes into account that the AC source passes through zero twice in each cycle where it does no work at all Vrms = 0.707Vp Irms = 0.707Ip Vp = 1.414Vrms Ip = 1.414Irms ...
250MHz to 4000MHz Dual, Analog Voltage Variable Attenuator MAX19790 General Description Features
... Note 4: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a fourlayer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maxim-ic.com/thermal-tutorial. Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings ...
... Note 4: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a fourlayer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maxim-ic.com/thermal-tutorial. Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings ...
Modified Derivative Superposition Method for Linearizing FET Low-Noise Amplifiers , Fellow, IEEE [4]–[7].
... high gain, and low current consumption. The LNA linearity is usually specified as an input-referred third-order intercept . For example, a typical cellular CDMA LNA must point dBm, a nominal NF of 1.6 dB, and power gain have of 16 dB with the power consumption less than 30 mW. This design challenge ...
... high gain, and low current consumption. The LNA linearity is usually specified as an input-referred third-order intercept . For example, a typical cellular CDMA LNA must point dBm, a nominal NF of 1.6 dB, and power gain have of 16 dB with the power consumption less than 30 mW. This design challenge ...
C-V Measurement Tips, Tricks, and Traps
... The ramp rate technique requires the use of only two source-measure units (SMUs). With the first SMU, one forces a constant current into one node of the device under test (DUT). That SMU also measures the voltage and the time on that node. Simultaneously, the second SMU is measuring the current bein ...
... The ramp rate technique requires the use of only two source-measure units (SMUs). With the first SMU, one forces a constant current into one node of the device under test (DUT). That SMU also measures the voltage and the time on that node. Simultaneously, the second SMU is measuring the current bein ...
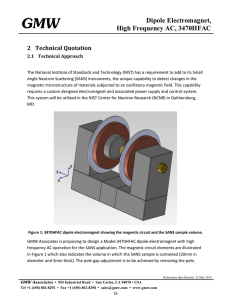
Dipole Electromagnet, High Frequency AC
... connected in series or individually excited. This allows for several operating configurations depending on how the coils and amplifiers are connected. One key advantage of this approach is to provide an initial configuration for assessment and then to add amplifiers later as greater performance is r ...
... connected in series or individually excited. This allows for several operating configurations depending on how the coils and amplifiers are connected. One key advantage of this approach is to provide an initial configuration for assessment and then to add amplifiers later as greater performance is r ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.
















![Modified Derivative Superposition Method for Linearizing FET Low-Noise Amplifiers , Fellow, IEEE [4]–[7].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008933224_1-2d88e15357b12c718a7f6ce155a9c9cc-300x300.png)