915U-D Serial Modem
... The only controlled copy of this Data Sheet is the electronic read-only version located on the Cooper Bussmann Network Drive. All other copies of this document are by definition uncontrolled. This bulletin is intended to clearly present comprehensive product data and provide technical information th ...
... The only controlled copy of this Data Sheet is the electronic read-only version located on the Cooper Bussmann Network Drive. All other copies of this document are by definition uncontrolled. This bulletin is intended to clearly present comprehensive product data and provide technical information th ...
i C
... frequencies ferrosilicon cores should be used due to high saturation flux density Bs (windings with smaller number of turns – lower „copper” losses), modern technological solutions – nanocrystallic or amorphic cores may be used up to the frequencies of 100 kHz as they combine adavantages of ferrite ...
... frequencies ferrosilicon cores should be used due to high saturation flux density Bs (windings with smaller number of turns – lower „copper” losses), modern technological solutions – nanocrystallic or amorphic cores may be used up to the frequencies of 100 kHz as they combine adavantages of ferrite ...
Encoder Signal Broadcaster
... Signals are optically isolated for high noise immunity Compact package saves installation costs ...
... Signals are optically isolated for high noise immunity Compact package saves installation costs ...
Active Components
... Micrel Inc. has added to its family of highcurrent protected power switches with the MIC2014/15/16 chips, all featuring Kickstart current limiting. The chips are part of the family of MIC20xx power distribution switches. The new product line is aimed at applications requiring current limiting as pro ...
... Micrel Inc. has added to its family of highcurrent protected power switches with the MIC2014/15/16 chips, all featuring Kickstart current limiting. The chips are part of the family of MIC20xx power distribution switches. The new product line is aimed at applications requiring current limiting as pro ...
DATASHEET SEARCH SITE | WWW.ALLDATASHEET.COM
... frequency response for individual applications. For example we can compensate poor speaker bass response by frequency shaping the feedback path. This is done with a series RC from pin 1 to 5 (paralleling the internal 15 kΩ resistor). For 6 dB effective bass boost: R=15 kΩ, the lowest value for good ...
... frequency response for individual applications. For example we can compensate poor speaker bass response by frequency shaping the feedback path. This is done with a series RC from pin 1 to 5 (paralleling the internal 15 kΩ resistor). For 6 dB effective bass boost: R=15 kΩ, the lowest value for good ...
The design of a low noise amplifier revolves
... common-source circuit has superior power gain performance. Due to the capacitiveand high-ohmic characteristics, impedance matching is mandatory to achieve maximum performances at 50-Ω terminations. The high power gain cannot be exploited towards high frequencies due to the large Miller capacitance s ...
... common-source circuit has superior power gain performance. Due to the capacitiveand high-ohmic characteristics, impedance matching is mandatory to achieve maximum performances at 50-Ω terminations. The high power gain cannot be exploited towards high frequencies due to the large Miller capacitance s ...
Voltage Dividers and Oscilloscope Probes Phys 3610/6610 Lab 02 Student: TA:
... Task 3: Repeat task 2, but draw only (1.2±0.1) mA. Task 4: Repeat task 2, but draw only (1.2±1) µA. What is wrong with task 4? Identify the problem and discuss with your TA. Task 5: Connect a 1 MΩ resistor to the clock signal on your breadboard. Set the frequency selector to 1 kHz and use the scope ...
... Task 3: Repeat task 2, but draw only (1.2±0.1) mA. Task 4: Repeat task 2, but draw only (1.2±1) µA. What is wrong with task 4? Identify the problem and discuss with your TA. Task 5: Connect a 1 MΩ resistor to the clock signal on your breadboard. Set the frequency selector to 1 kHz and use the scope ...
Chapter 3. High-Frequency (>100 GHz) and High
... Such ultrahigh-speed devices speed response. could be useful in easing the electronic "bottleneck" in the current fiber optical communication systems, in which only a small fraction of the 20-THz bandwidth of optical fibers are utilized because of the slow speed of electronic devices. In addition to ...
... Such ultrahigh-speed devices speed response. could be useful in easing the electronic "bottleneck" in the current fiber optical communication systems, in which only a small fraction of the 20-THz bandwidth of optical fibers are utilized because of the slow speed of electronic devices. In addition to ...
experiment number 9 inductor current
... The large value of R1 assures that, vL, the voltage across the inductor, is small compared to v1. Since vL is small compared to v1 the current, i, will be proportional to v1. 2. Set the oscilloscope triggering to positive slope, and channel 1. Set the vertical mode to dual trace. Set the signal gene ...
... The large value of R1 assures that, vL, the voltage across the inductor, is small compared to v1. Since vL is small compared to v1 the current, i, will be proportional to v1. 2. Set the oscilloscope triggering to positive slope, and channel 1. Set the vertical mode to dual trace. Set the signal gene ...
chapter #4 - oscillator
... The crystal-controlled oscillator is the most stable and accurate of all oscillators. A crystal has a natural frequency of resonance. Quartz material can be cut or shaped to have a certain frequency. We can better understand the use of a crystal in the operation of an oscillator by viewing its ...
... The crystal-controlled oscillator is the most stable and accurate of all oscillators. A crystal has a natural frequency of resonance. Quartz material can be cut or shaped to have a certain frequency. We can better understand the use of a crystal in the operation of an oscillator by viewing its ...
Discrete time Fourier transform and its Properties
... In the previous lecture we defined digital signal processing and understood its features. The general procedure is to convert the Continuous Time signal into Discrete Time signal. Then we try to obtain back the original signal. In this lecture we will study the concepts of Discrete time Fourier Tran ...
... In the previous lecture we defined digital signal processing and understood its features. The general procedure is to convert the Continuous Time signal into Discrete Time signal. Then we try to obtain back the original signal. In this lecture we will study the concepts of Discrete time Fourier Tran ...
“conducted immunity” mean?
... Only two CDNs required. One has the signal injected, the other is terminated, providing a 150 ohm impedance. Selection of which port to terminate. (See 7.2) Pick the port with the lowest circuit impedance. If clamp injection is used, must adhere to sections 7.3 or 7.4. Emphasis is on maintaining a 1 ...
... Only two CDNs required. One has the signal injected, the other is terminated, providing a 150 ohm impedance. Selection of which port to terminate. (See 7.2) Pick the port with the lowest circuit impedance. If clamp injection is used, must adhere to sections 7.3 or 7.4. Emphasis is on maintaining a 1 ...
RFVC1844 数据资料DataSheet下载
... RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change component circuitry, recommended application circuitry and specifications at any time without prior notice. RFMD Green: RoHS compliant per EU Directive 2002/95/EC, halogen free per IEC 61249-2-21, < 1000ppm each of antimony trioxide in polymeric materials and ...
... RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change component circuitry, recommended application circuitry and specifications at any time without prior notice. RFMD Green: RoHS compliant per EU Directive 2002/95/EC, halogen free per IEC 61249-2-21, < 1000ppm each of antimony trioxide in polymeric materials and ...
Review Sheet for Final
... 24. The difference in electrical potential (potential difference) between two places along a circuit is also referred to as: a. Resistance ...
... 24. The difference in electrical potential (potential difference) between two places along a circuit is also referred to as: a. Resistance ...
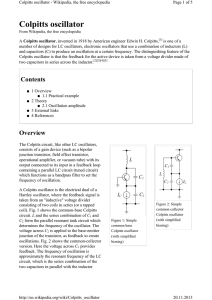
Colpitts oscillator
... consists of a gain device (such as a bipolar junction transistor, field effect transistor, operational amplifier, or vacuum tube) with its output connected to its input in a feedback loop containing a parallel LC circuit (tuned circuit) which functions as a bandpass filter to set the frequency of os ...
... consists of a gain device (such as a bipolar junction transistor, field effect transistor, operational amplifier, or vacuum tube) with its output connected to its input in a feedback loop containing a parallel LC circuit (tuned circuit) which functions as a bandpass filter to set the frequency of os ...
Why a Mini Inverter?
... A modified sine wave (sometimes referred to as a “simulated” sine wave is an AC current that is not a pure sine wave. Modified sine waves have some load limitations in regards to electronic equipment. Lighting loads, however, are typically unaffected by modified sine wave current (see note at the bo ...
... A modified sine wave (sometimes referred to as a “simulated” sine wave is an AC current that is not a pure sine wave. Modified sine waves have some load limitations in regards to electronic equipment. Lighting loads, however, are typically unaffected by modified sine wave current (see note at the bo ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.