IC Technology and Device Models
... zero base current level for better power efficiency. Class C The output of a class C amplifier is biased for operation at less than 180 of the cycle and is used in special areas of tuned circuits, such as radio or communications. Class D This operating class is a form of amplifier operation using p ...
... zero base current level for better power efficiency. Class C The output of a class C amplifier is biased for operation at less than 180 of the cycle and is used in special areas of tuned circuits, such as radio or communications. Class D This operating class is a form of amplifier operation using p ...
Word - ITU
... A numerical example may serve to clarify this definition. The alignment signal has an r.m.s. voltage of 0.775 V and a peak amplitude of 1.1 V at a zero relative level point. The instantaneous peak amplitude of the sound-programme signal at this point should only rarely exceed 3.1 V. Although it is i ...
... A numerical example may serve to clarify this definition. The alignment signal has an r.m.s. voltage of 0.775 V and a peak amplitude of 1.1 V at a zero relative level point. The instantaneous peak amplitude of the sound-programme signal at this point should only rarely exceed 3.1 V. Although it is i ...
A Low-Cost and Low-Power CMOS Receiver Front-End for MB-OFDM Ultra-Wideband Systems
... offset and sensitivity to narrowband jammers. A DC offset at the output of the receiver can degrade the SNR of the digitized baseband signal. In addition, it can introduce second-order distortion in the baseband signal, which further degrades the SNR. Since the LO can vary from 3.5 to 8 GHz, the DC ...
... offset and sensitivity to narrowband jammers. A DC offset at the output of the receiver can degrade the SNR of the digitized baseband signal. In addition, it can introduce second-order distortion in the baseband signal, which further degrades the SNR. Since the LO can vary from 3.5 to 8 GHz, the DC ...
Modal Interference and Dynamical Instability in a Solid
... pairs within many eigenmodes are coupled with each other and produce intensity pulsations at beat frequencies corresponding to the energy (i.e., eigenfrequency) differences between eigenmode pairs. In the case of Fig. 3(a), mode pairs, which are indicated by the bridge sign below the arrows, induce ...
... pairs within many eigenmodes are coupled with each other and produce intensity pulsations at beat frequencies corresponding to the energy (i.e., eigenfrequency) differences between eigenmode pairs. In the case of Fig. 3(a), mode pairs, which are indicated by the bridge sign below the arrows, induce ...
lect01 course overview transducer characteristics
... transducer (for example, due to thermal fluctuations of carrier concentrations in a semiconductor), or be generated by interaction with the environment (for example, by RF pickup). threshold: The minimum value for which a noticeable or measurable response is produced. A relevant consideration especi ...
... transducer (for example, due to thermal fluctuations of carrier concentrations in a semiconductor), or be generated by interaction with the environment (for example, by RF pickup). threshold: The minimum value for which a noticeable or measurable response is produced. A relevant consideration especi ...
Chapter 15:AC Fundamentals
... • Effective value or RMS value of an ac waveform is an equivalent dc value – It tells how many volts or amps of dc that an ac waveform supplies in terms of its ability to produce the same average power ...
... • Effective value or RMS value of an ac waveform is an equivalent dc value – It tells how many volts or amps of dc that an ac waveform supplies in terms of its ability to produce the same average power ...
hamtronics® td-3 subaudible tone decoder module
... Encoder designed especially for use with Hamtronics Receiver modules in repeater use, but allowing also for general use in other radios. It is tunable to cover the entire range of tone frequencies from 63 to 250 Hz. The unit normally is used to inhibit a repeater transmitter from responding to recei ...
... Encoder designed especially for use with Hamtronics Receiver modules in repeater use, but allowing also for general use in other radios. It is tunable to cover the entire range of tone frequencies from 63 to 250 Hz. The unit normally is used to inhibit a repeater transmitter from responding to recei ...
AD8041
... The AD8041 has a high speed disable feature useful for multiplexing or for reducing power consumption (1.5 mA). The disable logic interface is compatible with CMOS or opencollector logic. The AD8041 offers a low power supply current of 5.8 mA maximum and can run on a single 3 V power supply. These f ...
... The AD8041 has a high speed disable feature useful for multiplexing or for reducing power consumption (1.5 mA). The disable logic interface is compatible with CMOS or opencollector logic. The AD8041 offers a low power supply current of 5.8 mA maximum and can run on a single 3 V power supply. These f ...
COMP3221: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems
... Consider changing the output code of a 8-bit D/A from 10000000 to 01111111. These code are adjacent, and we expect the output to go from one-half full-scale to one resolution value less than that. However, if the switches can switch faster from a one to a zero, the output code will go through a tr ...
... Consider changing the output code of a 8-bit D/A from 10000000 to 01111111. These code are adjacent, and we expect the output to go from one-half full-scale to one resolution value less than that. However, if the switches can switch faster from a one to a zero, the output code will go through a tr ...
CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter 2003 Lecture 01
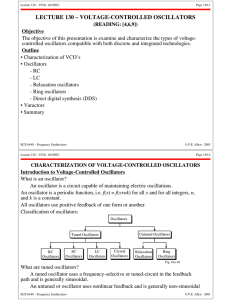
... dependent on characteristics of the open-loop (no-feedback) amplifier; eventually depend only on properties of the feedback network itself A “self-balancing mechanism” that allows amplifier to preserve zero potential difference between its input terminals Feedback can also be positive (oscillators, ...
... dependent on characteristics of the open-loop (no-feedback) amplifier; eventually depend only on properties of the feedback network itself A “self-balancing mechanism” that allows amplifier to preserve zero potential difference between its input terminals Feedback can also be positive (oscillators, ...
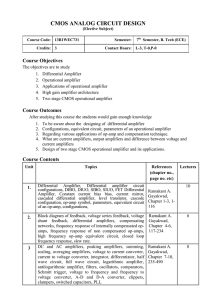
CMOS ANALOG CIRCUIT DESIGN
... Course Outcomes After studying this course the students would gain enough knowledge ...
... Course Outcomes After studying this course the students would gain enough knowledge ...
SUBELEMENT E4 - Tukwila Radio Club
... to measure intermodulation distortion in an SSB transmitter? A. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically related radio frequencies and observe the RF output with a spectrum analyzer B. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically related audio frequencies and observe the RF output wi ...
... to measure intermodulation distortion in an SSB transmitter? A. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically related radio frequencies and observe the RF output with a spectrum analyzer B. Modulate the transmitter with two non-harmonically related audio frequencies and observe the RF output wi ...
Dual 160 MHz Rail-to-Rail Amplifier AD8042
... CCD Imaging systems Ultrasound equipment (multichannel) ...
... CCD Imaging systems Ultrasound equipment (multichannel) ...
a AN-534 APPLICATION NOTE
... carrier detection, waveshaping and bandpass filtering to implement the protocol on-chip. The HART protocol communicates without interrupting the 4 mA–20 mA signal and allows a host application (master) to get two or more digital updates per second from a field device. As the digital FSK signal is ph ...
... carrier detection, waveshaping and bandpass filtering to implement the protocol on-chip. The HART protocol communicates without interrupting the 4 mA–20 mA signal and allows a host application (master) to get two or more digital updates per second from a field device. As the digital FSK signal is ph ...
Analog or digital? Chapter 12 12.1 Is the world ‘analog’?
... information. In fact we could say the same thing about the ‘waves’ and ‘particles’ we use so much in physics. Although it's easy to forget the fact, both waves and particles are mental models or ‘pictures’ we use to help us grasp how the real world behaves. Although useful as concepts, they don't ne ...
... information. In fact we could say the same thing about the ‘waves’ and ‘particles’ we use so much in physics. Although it's easy to forget the fact, both waves and particles are mental models or ‘pictures’ we use to help us grasp how the real world behaves. Although useful as concepts, they don't ne ...
Measuring Output VSWR For An Active Levelled Source
... introduced to students as part of basic circuit theory for the case of a DC voltage source and resistive load. For maximum power transfer to the load, the source and load resistances must be equal. The concept of maximum power transfer appears again when considering transmission line theory, often a ...
... introduced to students as part of basic circuit theory for the case of a DC voltage source and resistive load. For maximum power transfer to the load, the source and load resistances must be equal. The concept of maximum power transfer appears again when considering transmission line theory, often a ...
Word Version - DCC - LIGO Document Control Center Portal
... signals on the diode segments are used for beam centering on the quadrant diodes. The DC photocurrent is pulled out through a transimpedance amplifier stage, with a nominal transimpedance of 100 ohms (kept relatively low in order to handle up to 100 ma of photocurrent; this could be increased for th ...
... signals on the diode segments are used for beam centering on the quadrant diodes. The DC photocurrent is pulled out through a transimpedance amplifier stage, with a nominal transimpedance of 100 ohms (kept relatively low in order to handle up to 100 ma of photocurrent; this could be increased for th ...
NB4N441 - Serial Input PLL Clock Synthesizer
... designed to target this range. The key parameter that needs to be met in the final filter design is the DC voltage drop that will be seen between the VCC supply and the PLL_VCC pin of the NB4N441. From the data sheet, the PLL_VCC current (the current sourced through the PLL_VCC Pin) is typically 26 ...
... designed to target this range. The key parameter that needs to be met in the final filter design is the DC voltage drop that will be seen between the VCC supply and the PLL_VCC pin of the NB4N441. From the data sheet, the PLL_VCC current (the current sourced through the PLL_VCC Pin) is typically 26 ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.