INTRODUCTION - Atlas 180 Atlas 215 Atlas 210 Atlas 350 Atlas 110
... F.E.T. amplifiers. With its advanced front end design the Atlas 180 will continue receiving signals in the presence of extremely strong adjacent channel stations that would overload, cross modulate, or desensitize other receivers. Sensitivity: As with most new developments in technology, it may be d ...
... F.E.T. amplifiers. With its advanced front end design the Atlas 180 will continue receiving signals in the presence of extremely strong adjacent channel stations that would overload, cross modulate, or desensitize other receivers. Sensitivity: As with most new developments in technology, it may be d ...
Sound
... as intensity increases. We cannot equate frequency and pitch, but they are analogous. The same situation exists between intensity and loudness. The relationship between the two is not linear. Similarly, the relationship between waveform (or spectrum) and perceived quality (or timbre) is complicated ...
... as intensity increases. We cannot equate frequency and pitch, but they are analogous. The same situation exists between intensity and loudness. The relationship between the two is not linear. Similarly, the relationship between waveform (or spectrum) and perceived quality (or timbre) is complicated ...
ADC, FFT and Noise. p. 1 ADC, FFT, and Noise
... White noise has equal power per unit frequency. That is, the spectral density measured in watts per Hertz is the same for all frequencies. The zener diode noise source makes noise that is white over a very broad frequency range. (1) Show that noise cannot be absolutely white by showing that if the s ...
... White noise has equal power per unit frequency. That is, the spectral density measured in watts per Hertz is the same for all frequencies. The zener diode noise source makes noise that is white over a very broad frequency range. (1) Show that noise cannot be absolutely white by showing that if the s ...
Twitter - Texas Instruments
... type of board would seem to lend itself to easier routing because it has two layers of foil, and it is possible to route signals by crossing traces on different layers. While that is certainly possible, it is not recommended for analog circuitry. Wherever possible, the bottom layer should be devoted ...
... type of board would seem to lend itself to easier routing because it has two layers of foil, and it is possible to route signals by crossing traces on different layers. While that is certainly possible, it is not recommended for analog circuitry. Wherever possible, the bottom layer should be devoted ...
Optical Transceiver reference guide
... physical compactness and pin-thru hole soldering onto a host board. They are available with several configurations including industry standard 2x5 / 2x10, and de-facto 2x6 and 2x7 pinouts. ...
... physical compactness and pin-thru hole soldering onto a host board. They are available with several configurations including industry standard 2x5 / 2x10, and de-facto 2x6 and 2x7 pinouts. ...
Elec - eHam
... Modulation, bandwidth, and emission types The basic principle of radio communications is: a radio wave (an RF carrier) is combined with an information signal and is transmitted; a receiver separates the two. The information signal can be analog, which means continuous, or digital, which means it occ ...
... Modulation, bandwidth, and emission types The basic principle of radio communications is: a radio wave (an RF carrier) is combined with an information signal and is transmitted; a receiver separates the two. The information signal can be analog, which means continuous, or digital, which means it occ ...
Aalborg Universitet Model Predictive Current Control for High-Power Grid-Connected Converters with
... generated by the resonance in ~i1 and to modify the cost Gi2 in order to consider the energy put in frequencies close to the resonance. Based on [11], where frequency dependant weight functions have been used to obtain a pulse-width-modulation like current spectrum; to avoid any resonance in the ran ...
... generated by the resonance in ~i1 and to modify the cost Gi2 in order to consider the energy put in frequencies close to the resonance. Based on [11], where frequency dependant weight functions have been used to obtain a pulse-width-modulation like current spectrum; to avoid any resonance in the ran ...
Analyzing Data Streams by Online DFT
... and their generalizations (ARMA etc.). They can be used for forecasting, but usually they fail in streaming environments and often have a number of limitations (see [11] for more details on this). There are also approaches for nonlinear forecasting, but they always require human intervention [12]. P ...
... and their generalizations (ARMA etc.). They can be used for forecasting, but usually they fail in streaming environments and often have a number of limitations (see [11] for more details on this). There are also approaches for nonlinear forecasting, but they always require human intervention [12]. P ...
tach model research paper
... 50%, the switch will be closed for only half of the carrier signal period and, as power is time dependant (power in Watts = Joules / second), the motor will receive half as much power. It follows, that the carrier frequency has no apparent effect on the long-term power delivered to the motor, but is ...
... 50%, the switch will be closed for only half of the carrier signal period and, as power is time dependant (power in Watts = Joules / second), the motor will receive half as much power. It follows, that the carrier frequency has no apparent effect on the long-term power delivered to the motor, but is ...
Unit Number- 3471587
... evidence that they have met all the performance criteria for each outcome within the range specified. Details of these requirements are given for each outcome. The assessment instruments used should follow the general guidance offered by the SQA assessment model and an integrative approach to assess ...
... evidence that they have met all the performance criteria for each outcome within the range specified. Details of these requirements are given for each outcome. The assessment instruments used should follow the general guidance offered by the SQA assessment model and an integrative approach to assess ...
A 40Gb/s Clock and Data Recovery Circuit in 0.18um
... flipflops efficiently; and (3) isolate the VCO from the data edges coupled through the phase detectors. The PD employs eight flipflops to strobe the data at 12.5ps intervals (Fig. 13.7.3). In a manner similar to an Alexander topology [3], the PD compares every two consecutive samples by means of an ...
... flipflops efficiently; and (3) isolate the VCO from the data edges coupled through the phase detectors. The PD employs eight flipflops to strobe the data at 12.5ps intervals (Fig. 13.7.3). In a manner similar to an Alexander topology [3], the PD compares every two consecutive samples by means of an ...
Evaluation of Magnetic Materials for Very High Frequency Power
... determination of inductor QL . Drive level can be adjusted by varying the amplitude of the rf source. The current of the inductor is equal to the capacitor current and can be calculated from the output voltage and the known capacitor impedance. (These considerations motivate the use of high-precisio ...
... determination of inductor QL . Drive level can be adjusted by varying the amplitude of the rf source. The current of the inductor is equal to the capacitor current and can be calculated from the output voltage and the known capacitor impedance. (These considerations motivate the use of high-precisio ...
A 40Gb/s clock and data recovery circuit in 0.18/spl mu/m CMOS
... flipflops efficiently; and (3) isolate the VCO from the data edges coupled through the phase detectors. The PD employs eight flipflops to strobe the data at 12.5ps intervals (Fig. 13.7.3). In a manner similar to an Alexander topology [3], the PD compares every two consecutive samples by means of an ...
... flipflops efficiently; and (3) isolate the VCO from the data edges coupled through the phase detectors. The PD employs eight flipflops to strobe the data at 12.5ps intervals (Fig. 13.7.3). In a manner similar to an Alexander topology [3], the PD compares every two consecutive samples by means of an ...
Lab 73 Measuring Phase Difference
... PART B: Measuring the Phase Angle 1. Turn the function generator on. Using the frequency control, set the input signal to approximately 850 Hz. Set channels 1 and 2 of the oscilloscope to AC. Increase the signal strength (of the function generator) until the input signal (channel 1) spans 4 vertical ...
... PART B: Measuring the Phase Angle 1. Turn the function generator on. Using the frequency control, set the input signal to approximately 850 Hz. Set channels 1 and 2 of the oscilloscope to AC. Increase the signal strength (of the function generator) until the input signal (channel 1) spans 4 vertical ...
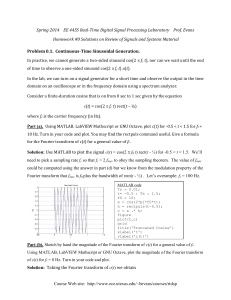
Solutions
... the initial values in the delay-by-one-sample blocks, which are denoted by z -1. The impulse response is given as h[n] = sin( 0 n) u[n]. That is, for x[n] = [n], the output is y[n] = h[n], which gives y[-1] = h[-1] = 0 and y[-2] = h[-2] = 0 and x[-1] = [-1] = 0, For the system to satisfy the line ...
... the initial values in the delay-by-one-sample blocks, which are denoted by z -1. The impulse response is given as h[n] = sin( 0 n) u[n]. That is, for x[n] = [n], the output is y[n] = h[n], which gives y[-1] = h[-1] = 0 and y[-2] = h[-2] = 0 and x[-1] = [-1] = 0, For the system to satisfy the line ...
MAX44281 Ultra-Small, Ultra-Thin, 4-Bump Op Amp General Description Benefits and Features
... The MAX44281 features shutdown functionality by pulling VDD to ground. During shutdown, both the input and the output are high-impedance. The input and output of the MAX44281 enter a high-impedance state when the device enters shutdown. Since shutdown is triggered by lowering the supply voltage to b ...
... The MAX44281 features shutdown functionality by pulling VDD to ground. During shutdown, both the input and the output are high-impedance. The input and output of the MAX44281 enter a high-impedance state when the device enters shutdown. Since shutdown is triggered by lowering the supply voltage to b ...
Keep your Switch Mode Supply stable with a Critical-Mode
... D’ (1-D). A linearization process will finally lead to a set of continuous linear equations. The reader interested by an in-depth and pedagogical description of these methods will find all the necessary information in Daniel MITCHELL's book [3]. As one can see from figure 3, the SSA models the conve ...
... D’ (1-D). A linearization process will finally lead to a set of continuous linear equations. The reader interested by an in-depth and pedagogical description of these methods will find all the necessary information in Daniel MITCHELL's book [3]. As one can see from figure 3, the SSA models the conve ...
RF2057 HIGH PERFORMANCE WIDEBAND RF PLL/VCO WITH Features
... chip with integrated local oscillator (LO) generation and a pair of RF mixers. The RF synthesizer includes an integrated fractional-N phase locked loop with voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) and dividers to produce a low-phase noise LO signal with a very fine frequency resolution. The buffered LO ...
... chip with integrated local oscillator (LO) generation and a pair of RF mixers. The RF synthesizer includes an integrated fractional-N phase locked loop with voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) and dividers to produce a low-phase noise LO signal with a very fine frequency resolution. The buffered LO ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.