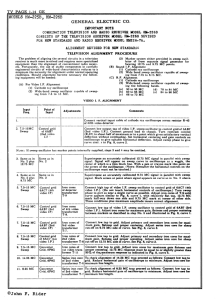
Chapter 11: Overvoltage Effects on Analog Integrated Circuits
... Many factors contribute to the current-voltage characteristic of an amplifier’s input stage: internal differential clamping diodes, current-limiting series resistances, substrate potential connections, and differential input stage topologies (BJTs or FETs). Input protection diodes used as differenti ...
... Many factors contribute to the current-voltage characteristic of an amplifier’s input stage: internal differential clamping diodes, current-limiting series resistances, substrate potential connections, and differential input stage topologies (BJTs or FETs). Input protection diodes used as differenti ...
RF2472G 2.4GHz LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER WITH ENABLE Features
... high-frequency gain, the designer must take care to ensure that the device will remain stable outside the desired operating frequency. The RF2472G is capable of providing outstanding linearity, but to achieve this high performance, the circuit designer must pay attention to the terminations that are ...
... high-frequency gain, the designer must take care to ensure that the device will remain stable outside the desired operating frequency. The RF2472G is capable of providing outstanding linearity, but to achieve this high performance, the circuit designer must pay attention to the terminations that are ...
Dog-Legs Status
... – Much bigger bandwidth than Cu cables (bandwidth of a links is speed * distance). ...
... – Much bigger bandwidth than Cu cables (bandwidth of a links is speed * distance). ...
MAX9181 Low-Jitter, Low-Noise LVPECL-to-LVDS Level Translator in an SC70 Package General Description
... Note 1: All devices are 100% tested at TA = +25°C. Limits over temperature are guaranteed by design and characterization. Note 2: Current into a pin is defined as positive. Current out of a pin is defined as negative. All voltages are referenced to ground except VTH, VTL, VOD, and ∆VOD. Note 3: Guar ...
... Note 1: All devices are 100% tested at TA = +25°C. Limits over temperature are guaranteed by design and characterization. Note 2: Current into a pin is defined as positive. Current out of a pin is defined as negative. All voltages are referenced to ground except VTH, VTL, VOD, and ∆VOD. Note 3: Guar ...
LT5557 - 400MHz to 3.8GHz 3.3V Active Downconverting Mixer.
... transformer, which has low DC resistance to ground. If the RF source is not DC blocked, then a series blocking capacitor must be used. The RF input is internally matched from 1.6GHz to 2.3GHz. Operation down to 400MHz or up to 3.8GHz is possible with simple external matching. ...
... transformer, which has low DC resistance to ground. If the RF source is not DC blocked, then a series blocking capacitor must be used. The RF input is internally matched from 1.6GHz to 2.3GHz. Operation down to 400MHz or up to 3.8GHz is possible with simple external matching. ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-ISSN: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331,
... The main FRA test types are given below. 3.1 End-to-end or End-to-end open In the „end-to-end open„ test, the signal is applied to one end of each winding in turn, and the transmitted signal is measured at the other end. The magnetizing impedance of the transformer is the main parameter characterizi ...
... The main FRA test types are given below. 3.1 End-to-end or End-to-end open In the „end-to-end open„ test, the signal is applied to one end of each winding in turn, and the transmitted signal is measured at the other end. The magnetizing impedance of the transformer is the main parameter characterizi ...
MAX16936 36V, 220kHz to 2.2MHz Step-Down Converter with 28µA Quiescent Current General Description
... The MAX16936 is a 2.5A current-mode step-down converter with integrated high-side and low-side MOSFETs designed to operate with an external Schottky diode for better efficiency. The low-side MOSFET enables fixed-frequency forced-PWM (FPWM) operation under light-load applications. The device operates ...
... The MAX16936 is a 2.5A current-mode step-down converter with integrated high-side and low-side MOSFETs designed to operate with an external Schottky diode for better efficiency. The low-side MOSFET enables fixed-frequency forced-PWM (FPWM) operation under light-load applications. The device operates ...
analytical prediction of noise of magnetic origin produced by
... The magnetomotive force (MMF) space harmonics, time harmonics, slot harmonics, eccentricity harmonics, and saturation harmonics produce parasitic higher harmonic forces and torques. The amplitude of the radial force of the order r is Fmr = πDin Li Pmr where Din is the stator core inner diameter, Li ...
... The magnetomotive force (MMF) space harmonics, time harmonics, slot harmonics, eccentricity harmonics, and saturation harmonics produce parasitic higher harmonic forces and torques. The amplitude of the radial force of the order r is Fmr = πDin Li Pmr where Din is the stator core inner diameter, Li ...
E1000059-v3 - DCC - LIGO Document Control Center Portal
... The following Test Procedure describes the test of proper operation of the Frequency Locking Slave which locks the frequency of an external oscillator to the 1PPS ...
... The following Test Procedure describes the test of proper operation of the Frequency Locking Slave which locks the frequency of an external oscillator to the 1PPS ...
AN-376 Logic-System Design Techniques Reduce Switching-CMOS Power AN-
... In Equation 5, load capacitances CL1, CL2, etc. are not simply the sum of all individual output loads. CL is actually dependent on device type. Why? Different devices switch a different number of outputs simultaneously. What's more, these outputs can toggle at a different rate from that of the IC's ...
... In Equation 5, load capacitances CL1, CL2, etc. are not simply the sum of all individual output loads. CL is actually dependent on device type. Why? Different devices switch a different number of outputs simultaneously. What's more, these outputs can toggle at a different rate from that of the IC's ...
Equation 7
... proprietary D-CAP™ mode control combined with an adaptive on-time architecture. This combination is ideal for building modern low duty ratio, ultra-fast load step response DC-DC converters. The output voltage ranges from 0.6 V to 5.5 V. The conversion input voltage range is from 3 V up to 28V. The D ...
... proprietary D-CAP™ mode control combined with an adaptive on-time architecture. This combination is ideal for building modern low duty ratio, ultra-fast load step response DC-DC converters. The output voltage ranges from 0.6 V to 5.5 V. The conversion input voltage range is from 3 V up to 28V. The D ...
HMC578LC3B Datasheet
... The HMC578LC3B is a x2 active broadband frequency multiplier utilizing GaAs PHEMT technology in a leadless RoHS compliant SMT package. When driven by a +3 dBm signal, the multiplier provides +15 dBm typical output power from 23 to 33 GHz. The Fo and 3Fo isolations are >20 dBc and >30 dBc respectivel ...
... The HMC578LC3B is a x2 active broadband frequency multiplier utilizing GaAs PHEMT technology in a leadless RoHS compliant SMT package. When driven by a +3 dBm signal, the multiplier provides +15 dBm typical output power from 23 to 33 GHz. The Fo and 3Fo isolations are >20 dBc and >30 dBc respectivel ...
AN-162 LM2907 Tachometer/Speed Switch Building Block
... The ground referenced input capability of the LM2907-8 allows direct coupling to transformer inputs, or variable reluctance pickups. Figure 5(a) illustrates this connection. In many cases, the frequency signal must be obtained from another circuit whose output may not go below ground. This may be re ...
... The ground referenced input capability of the LM2907-8 allows direct coupling to transformer inputs, or variable reluctance pickups. Figure 5(a) illustrates this connection. In many cases, the frequency signal must be obtained from another circuit whose output may not go below ground. This may be re ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.