Marketing, Chapter 2 - Cole
... •You want to create Value: the personal satisfaction gained from the use of a good/service. Consumers compare the price they pay for a product with all the benefits that come with it. •Ranges from support services offered to how customers are treated. •Value is NOT defined by a business; its by the ...
... •You want to create Value: the personal satisfaction gained from the use of a good/service. Consumers compare the price they pay for a product with all the benefits that come with it. •Ranges from support services offered to how customers are treated. •Value is NOT defined by a business; its by the ...
Document
... Internet sellers engage in price discrimination when they charge different consumers different prices for identical goods or by charging the same consumer different prices for the same good depending on how many units the consumer purchased. From the firm’s perspective, the idea behind price discrim ...
... Internet sellers engage in price discrimination when they charge different consumers different prices for identical goods or by charging the same consumer different prices for the same good depending on how many units the consumer purchased. From the firm’s perspective, the idea behind price discrim ...
4.2 Marketing Planning Part 1 PPT
... Packaging may be a part of promotion (usually part of PLACE) because it can reinforce image or create a product preference. Can you think of any promotion activities that encouraged you to make a purchase? Can you think of any creative packaging that would make you purchase one product over another? ...
... Packaging may be a part of promotion (usually part of PLACE) because it can reinforce image or create a product preference. Can you think of any promotion activities that encouraged you to make a purchase? Can you think of any creative packaging that would make you purchase one product over another? ...
4.2 Marketing Planning
... Process: Satisfying customer needs as part of marketing services (automatically renewing a membership) Physical Evidence: Customers can see for themselves the quality of the product (a clean lobby at a hotel, table clothes used a nice ...
... Process: Satisfying customer needs as part of marketing services (automatically renewing a membership) Physical Evidence: Customers can see for themselves the quality of the product (a clean lobby at a hotel, table clothes used a nice ...
L10 HANDOUT
... Pricing strategy can affect consumer perceptions of a brand’s position in its product category and of its overall quality. Many firms now employ value pricing, in which a brand’s price is based on considerations of product quality, product costs, and product prices that satisfy consumer needs as wel ...
... Pricing strategy can affect consumer perceptions of a brand’s position in its product category and of its overall quality. Many firms now employ value pricing, in which a brand’s price is based on considerations of product quality, product costs, and product prices that satisfy consumer needs as wel ...
slides - Editorial Express
... • However, the PRC has specified a different treatment for revenues associated with discounted volumes under NSAs: – “Mail volumes sent at rates under negotiated service agreements are to be included in the calculation of percentage change in rates as though they paid the appropriate rates of genera ...
... • However, the PRC has specified a different treatment for revenues associated with discounted volumes under NSAs: – “Mail volumes sent at rates under negotiated service agreements are to be included in the calculation of percentage change in rates as though they paid the appropriate rates of genera ...
CHARACTERISTICS OF OLIGOPOLY An oligopoly is a market
... proportion of the market. An oligopolistic market must possess the following characteristics. (i) A few large firms Oligopoly is “competition among the few”. The industry is dominated by a few large firms which control a large proportion of the industry’s output. However, a special case of duopoly o ...
... proportion of the market. An oligopolistic market must possess the following characteristics. (i) A few large firms Oligopoly is “competition among the few”. The industry is dominated by a few large firms which control a large proportion of the industry’s output. However, a special case of duopoly o ...
Things I should have learned in marketing
... Distribution and logistics are part of this element of the marketing mix ...
... Distribution and logistics are part of this element of the marketing mix ...
Marketing Identify customers` needs and wants Anticipate changes
... PR – important element is publicity – unlike advertising it is not paid for directly Varies between industry – attractive to music & tourist trade Corporate Communication – Influencing the way an organisation behaves & communicating the benefits of this behaviour to the public Research suggest ...
... PR – important element is publicity – unlike advertising it is not paid for directly Varies between industry – attractive to music & tourist trade Corporate Communication – Influencing the way an organisation behaves & communicating the benefits of this behaviour to the public Research suggest ...
trading stocks on saxotrader platform
... that the price at which your order is filled may differ from the price you set for the order if the opening price of the market is better than your limit price. In the case of Futures, the order will be filled if possible, and any remaining volume will remain in the market as a limit order.In the ca ...
... that the price at which your order is filled may differ from the price you set for the order if the opening price of the market is better than your limit price. In the case of Futures, the order will be filled if possible, and any remaining volume will remain in the market as a limit order.In the ca ...
Distribution Strategies
... the promotional activities on the distributor (usually retailer) The Marketer hopes to convince the distributor to display the product prominently in the store Buying incentives such as discounts, prizes, samples, product knowledge seminars are used This strategy is used mostly for unglamorous g ...
... the promotional activities on the distributor (usually retailer) The Marketer hopes to convince the distributor to display the product prominently in the store Buying incentives such as discounts, prizes, samples, product knowledge seminars are used This strategy is used mostly for unglamorous g ...
Marketing Fundamentals - Marcie Smith and Rebecca Lynn Moss, April 2012
... target market will find access to our products and services ...
... target market will find access to our products and services ...
Market Segmentation
... Provide a bridge between producers & consumers so exchange of goods & services can occur ...
... Provide a bridge between producers & consumers so exchange of goods & services can occur ...
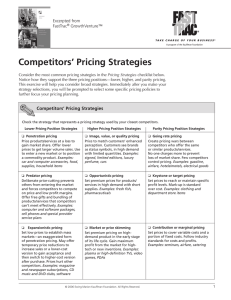
Pricing Strategies - Business Lincolnshire
... lengthy telephone bills that include numerous contingent costs, which depend on location, use, and service features. Consequently, competitors in the corporate long distance telephone service market do not use lower pricing as the primary pricing strategy, as they do in the consumer and small-busine ...
... lengthy telephone bills that include numerous contingent costs, which depend on location, use, and service features. Consequently, competitors in the corporate long distance telephone service market do not use lower pricing as the primary pricing strategy, as they do in the consumer and small-busine ...