Marketing Concepts
... • The idea that you must satisfy a customers’ needs and wants in order to make a profit. • Businesses must have the right goods and services at the right time, at the right price and at the right place. Plus they must communicate this to their customers. ...
... • The idea that you must satisfy a customers’ needs and wants in order to make a profit. • Businesses must have the right goods and services at the right time, at the right price and at the right place. Plus they must communicate this to their customers. ...
PRODUCT
... 7 The set of beliefs that the public at large holds of an organization 8 Dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different requirements or buying habits ...
... 7 The set of beliefs that the public at large holds of an organization 8 Dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different requirements or buying habits ...
MARKET ANALYSIS: MARKETING PLAN
... market share will the new product take away from competitors? How will competitors respond to the new product? Will they respond by changing price? Will they change their product? Distribution of the Product or Service Distribution refers to how and when to move the product from the greenhouse to t ...
... market share will the new product take away from competitors? How will competitors respond to the new product? Will they respond by changing price? Will they change their product? Distribution of the Product or Service Distribution refers to how and when to move the product from the greenhouse to t ...
Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning
... 1. Identify groups of similar customers and potential customers 2. Prioritize the groups 3. Understand their behavior 4. Respond with appropriate marketing strategies that satisfy the different preferences of each chosen segment ...
... 1. Identify groups of similar customers and potential customers 2. Prioritize the groups 3. Understand their behavior 4. Respond with appropriate marketing strategies that satisfy the different preferences of each chosen segment ...
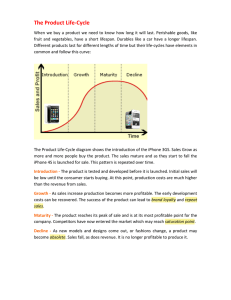
The Product Life-Cycle - NW 14-19
... The Product Life‐Cycle diagram shows the introduction of the iPhone 3GS. Sales Grow as more and more people buy the product. The sales mature and as they start to fall the iPhone 4S is launched for sale. This pattern is repeated over time. Introduction ‐ The product is tested and developed before ...
... The Product Life‐Cycle diagram shows the introduction of the iPhone 3GS. Sales Grow as more and more people buy the product. The sales mature and as they start to fall the iPhone 4S is launched for sale. This pattern is repeated over time. Introduction ‐ The product is tested and developed before ...
Product and profit life cycles
... The ability of the firm to manage the Customer Life Cycle is critical because the needs of the customer changes at various stages ...
... The ability of the firm to manage the Customer Life Cycle is critical because the needs of the customer changes at various stages ...
26 – Monopolistic Competition
... Product Differentiation: Product differentiation is the distinguishing of products by brand name, color, minor attributes, and the like. Product differentiation occurs in other than perfectly competitive markets where products are homogeneous. Each separate, differentiated product has numerous simil ...
... Product Differentiation: Product differentiation is the distinguishing of products by brand name, color, minor attributes, and the like. Product differentiation occurs in other than perfectly competitive markets where products are homogeneous. Each separate, differentiated product has numerous simil ...
the impact of price-endings on the customers perception and
... keep them sustainable and progressive with leveraged sales and profit. The price-ending or psychological pricing is the pricing strategy which has been keeping the organizations sustainable with augmented sales and profitability for more than a century, especially in the retail sector. The price-end ...
... keep them sustainable and progressive with leveraged sales and profit. The price-ending or psychological pricing is the pricing strategy which has been keeping the organizations sustainable with augmented sales and profitability for more than a century, especially in the retail sector. The price-end ...
Froeb_06 - owen.vanderbilt.edu
... (purchase) more as price falls, assuming other factors are held constant But, the marginal value of consuming each subsequent unit diminishes the more you consume Consumers attempt to maximize their surplus by using marginal analysis Consumer surplus = value to consumer less price paid Definition: D ...
... (purchase) more as price falls, assuming other factors are held constant But, the marginal value of consuming each subsequent unit diminishes the more you consume Consumers attempt to maximize their surplus by using marginal analysis Consumer surplus = value to consumer less price paid Definition: D ...
Chapter One
... Internet to widely distribute their ads to anyone willing to see or hear them. Another significant trend regarding future of advertising is the growing importance of the niche market using niche or targeted ads. Also brought about by the Internet and the theory of The Long Tail, advertisers will hav ...
... Internet to widely distribute their ads to anyone willing to see or hear them. Another significant trend regarding future of advertising is the growing importance of the niche market using niche or targeted ads. Also brought about by the Internet and the theory of The Long Tail, advertisers will hav ...
Inside the Entrepreneurial Mind: From Ideas to Reality
... delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large. (American Marketing Association) ...
... delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large. (American Marketing Association) ...
8. Efficiencies and Market Structures
... Some differentiation does not create utility but generates unnecessary waste, such as excess packaging. Advertising may also be considered wasteful, though most is informative rather than persuasive. As the diagram illustrates, assuming profit maximisation, there is allocative inefficiency in both t ...
... Some differentiation does not create utility but generates unnecessary waste, such as excess packaging. Advertising may also be considered wasteful, though most is informative rather than persuasive. As the diagram illustrates, assuming profit maximisation, there is allocative inefficiency in both t ...
Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans
... To build customer awareness of the products: ◦ Ensuring the availability, service after sale, and communicating Samsung essential value and attributes around the world, to make sure the consumers are worth the money. ...
... To build customer awareness of the products: ◦ Ensuring the availability, service after sale, and communicating Samsung essential value and attributes around the world, to make sure the consumers are worth the money. ...