SAMARSKITE-(Yb): A NEW SPECIES OF THE SAMARSKITE
... written in quotes to indicate the group name has not received IMA approval. Electron-microprobe analyses of these minerals are challenging, as more than 30 elements need to be measured. In addition, the crystal chemistry of samarskite has been difficult to establish owing to its complex composition, ...
... written in quotes to indicate the group name has not received IMA approval. Electron-microprobe analyses of these minerals are challenging, as more than 30 elements need to be measured. In addition, the crystal chemistry of samarskite has been difficult to establish owing to its complex composition, ...
Tissues - Union County College
... strength, support and flexibility – consists of several types of fibers and cells embedded in a gel-like ground substance (matrix): • Collagen fibers--provides strength and slight flexibility • Elastic—thin and very flexible coiled elastic fibers made from the protein elastin; can stretch without br ...
... strength, support and flexibility – consists of several types of fibers and cells embedded in a gel-like ground substance (matrix): • Collagen fibers--provides strength and slight flexibility • Elastic—thin and very flexible coiled elastic fibers made from the protein elastin; can stretch without br ...
Print - Inno-Vita
... consumed, the body withdraws needed calcium from its own skeletal structure resulting in compromised bone integrity. ...
... consumed, the body withdraws needed calcium from its own skeletal structure resulting in compromised bone integrity. ...
PHYT 622 Clinical Gross Anatomy
... from bone marrow to settle down and lay down ECM which then calcifies into woven bone • With time osteoclasts resorb the woven bone and replace it with mature trabecular bone ...
... from bone marrow to settle down and lay down ECM which then calcifies into woven bone • With time osteoclasts resorb the woven bone and replace it with mature trabecular bone ...
Quantitative Biochemical Differences between
... From these observations, together with a more ma ture understanding of the mechanism of antimetabolite action, had evolved a working hypothe sis that metabolic pathways in malignant tissues can be blocked while producing minimal effects on ...
... From these observations, together with a more ma ture understanding of the mechanism of antimetabolite action, had evolved a working hypothe sis that metabolic pathways in malignant tissues can be blocked while producing minimal effects on ...
PHYT 622 Clinical Gross Anatomy
... 4. Osteoids are deposited by osteoblast and take about ten days to mineralize – matrix is collagen based ...
... 4. Osteoids are deposited by osteoblast and take about ten days to mineralize – matrix is collagen based ...
Study Guide for Tissues, Membranes, Wounds Obj. 1 Define the
... _____ b. a wound caused by pressure that is sufficient to destroy tissue structure _____ c. better know as a scrape _____ d. a wound that has been made by a sharp, slender object _____ e. a wound in which skin and tissue are partially torn away _____ f. a wound with smooth edges caused by a sharp su ...
... _____ b. a wound caused by pressure that is sufficient to destroy tissue structure _____ c. better know as a scrape _____ d. a wound that has been made by a sharp, slender object _____ e. a wound in which skin and tissue are partially torn away _____ f. a wound with smooth edges caused by a sharp su ...
Bone
... 1 Everything has to be done by cells* 2 Organs & tissues need to grow & to change shape 3 Cells age , and control systems get out of balance 4 Bone is always at the mercy of body’s need for calcium nerve-muscle priority 5 Bone needs to be loaded every day: use is essential ...
... 1 Everything has to be done by cells* 2 Organs & tissues need to grow & to change shape 3 Cells age , and control systems get out of balance 4 Bone is always at the mercy of body’s need for calcium nerve-muscle priority 5 Bone needs to be loaded every day: use is essential ...
23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants
... The cuticle and epidermal cells form a waterproof barrier that protects tissues inside the leaf and limits the loss of water through evaporation. The vascular tissues of leaves are connected directly to the vascular tissues of stems. ...
... The cuticle and epidermal cells form a waterproof barrier that protects tissues inside the leaf and limits the loss of water through evaporation. The vascular tissues of leaves are connected directly to the vascular tissues of stems. ...
The Power of the Almighty Bone Broth
... required for Collagen formation, and therefore is essential healthy cartilage, tendons, bones, ligaments and skin. Proline is also helps keep the arteries flexible and producing collagen, reducing arteriosclerosis and blood pressure. Highlights of the benefits of Proline: ๏ Collagen formation (best ...
... required for Collagen formation, and therefore is essential healthy cartilage, tendons, bones, ligaments and skin. Proline is also helps keep the arteries flexible and producing collagen, reducing arteriosclerosis and blood pressure. Highlights of the benefits of Proline: ๏ Collagen formation (best ...
pan granulated
... • Turf will absorb nutrients via the foliar route, immediately on contact • Liquid Protene ® will also be encompassed in the soil profile to feed and stimulate soil microbes • Turf will then take nutrients via the root system, due to massive stimulation of soil microbes per medium of the amino acids ...
... • Turf will absorb nutrients via the foliar route, immediately on contact • Liquid Protene ® will also be encompassed in the soil profile to feed and stimulate soil microbes • Turf will then take nutrients via the root system, due to massive stimulation of soil microbes per medium of the amino acids ...
C - IS MU
... • arterial walls, pulmonary alveoli, skin, ligamentum nuchae • composed of elastin surrounded by a microfibrillar sheath that consists of glycoprotein fibrilin and fibromodulin. During the formation of elastic fibres, those two proteins are arranged in the form of oxytalan fibrils, which serve as a ...
... • arterial walls, pulmonary alveoli, skin, ligamentum nuchae • composed of elastin surrounded by a microfibrillar sheath that consists of glycoprotein fibrilin and fibromodulin. During the formation of elastic fibres, those two proteins are arranged in the form of oxytalan fibrils, which serve as a ...
Reading - Chapter 15 and the Appendix to Chapter 15
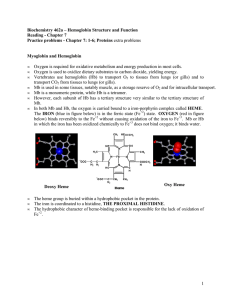
... The differences in O2 affinity between T-State (deoxy) and R-State (oxy) Hb can be understood in terms of the changes in quaternary structure that accompany the conversion of deoxy Hb to oxy Hb. o The shift from the deoxy to oxy conformation arises from the fact that in deoxy Hb the iron lies out of ...
... The differences in O2 affinity between T-State (deoxy) and R-State (oxy) Hb can be understood in terms of the changes in quaternary structure that accompany the conversion of deoxy Hb to oxy Hb. o The shift from the deoxy to oxy conformation arises from the fact that in deoxy Hb the iron lies out of ...
1 Biochemistry 462a – Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading
... 3. The presence of BPG aids the delivery of O2 by favoring the deoxy conformation. 4. Deoxy Hb binds CO2. 5. The deoxy Hb returns to the lungs where the pH is higher, the O2 content higher and the CO2 content is lower. All these factors favor reverse of carbamate formation (loss of bound CO2), depro ...
... 3. The presence of BPG aids the delivery of O2 by favoring the deoxy conformation. 4. Deoxy Hb binds CO2. 5. The deoxy Hb returns to the lungs where the pH is higher, the O2 content higher and the CO2 content is lower. All these factors favor reverse of carbamate formation (loss of bound CO2), depro ...
Review of Musculoskeletal System
... – Dominant inheritance, but frequent new mutations – Other organs develop normally – Individuals live a normal lifespan ...
... – Dominant inheritance, but frequent new mutations – Other organs develop normally – Individuals live a normal lifespan ...
Review of Musculoskeletal System
... – Involves a defect in normal cartilage development – Epiphyseal plates close early in long bones; individual has short arms and legs, but normal spine and skull – Dominant inheritance, but frequent new mutations – Other organs develop normally – Individuals live a normal lifespan ...
... – Involves a defect in normal cartilage development – Epiphyseal plates close early in long bones; individual has short arms and legs, but normal spine and skull – Dominant inheritance, but frequent new mutations – Other organs develop normally – Individuals live a normal lifespan ...
Connective Tissues
... Reticular fibers- thin fibers that form an interwoven framework in various organs Elastic fibers- contain elastin protein, are branched and waving, will return to their original length after stretching ...
... Reticular fibers- thin fibers that form an interwoven framework in various organs Elastic fibers- contain elastin protein, are branched and waving, will return to their original length after stretching ...
CHAPTER 2 (Minerals) Geojeopardy for review
... be left behind to form minerals after water in lakes or ponds ...
... be left behind to form minerals after water in lakes or ponds ...
Polypeptide and protein structure
... The Collagen Triple Helix The most abundant protein in vertebrates Organized in water-insoluble fibers Have a great strength Consists of three polypeptide chains wrapped around each other in a ropelike twist, or triple helix Has a repeating sequence of the amino acids; X1—X2(Pro, ProOH)—G ...
... The Collagen Triple Helix The most abundant protein in vertebrates Organized in water-insoluble fibers Have a great strength Consists of three polypeptide chains wrapped around each other in a ropelike twist, or triple helix Has a repeating sequence of the amino acids; X1—X2(Pro, ProOH)—G ...
Bones
... osteocytes are located, btwn each lamellae (space where osteon sits inside) Lamellae: layers of calcified bone matrix Canaliculi: small channels or canals that connect lacunae to each other & central canal to blood vessels…allows blood to go from one osteocyte to another ...
... osteocytes are located, btwn each lamellae (space where osteon sits inside) Lamellae: layers of calcified bone matrix Canaliculi: small channels or canals that connect lacunae to each other & central canal to blood vessels…allows blood to go from one osteocyte to another ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation in Homogenates of
... tion occurs only after at least one phosphate has been removed from theATP molecule. The removal ofamnioniaisevidentlynotpartofthedephosphory lation reaction, because in brain the phosphate out put is not accompanied by a corresponding out put of ammonia. Furthermore, the two reactions can be dissoc ...
... tion occurs only after at least one phosphate has been removed from theATP molecule. The removal ofamnioniaisevidentlynotpartofthedephosphory lation reaction, because in brain the phosphate out put is not accompanied by a corresponding out put of ammonia. Furthermore, the two reactions can be dissoc ...
Chapter 11
... The best candidates to donate organs are those who have died of brain injury. In cardiac death, organs deteriorate due to lack of oxygen, and thus are less suitable for transplant. Thousands of lives are saved each year through organ donation. The decision to become a donor now can save fami ...
... The best candidates to donate organs are those who have died of brain injury. In cardiac death, organs deteriorate due to lack of oxygen, and thus are less suitable for transplant. Thousands of lives are saved each year through organ donation. The decision to become a donor now can save fami ...
republic of indonesia ministry of energy and mineral resources
... nickel production, respectively). A number of major discoveries have made Indonesia as one of highly prospective region in the world (Rank 12th from 79 regions and 1st in AsiaPacific, Fraser Institute – 2011). The country is still largely under-explored and will undoubtedly will produce significant ...
... nickel production, respectively). A number of major discoveries have made Indonesia as one of highly prospective region in the world (Rank 12th from 79 regions and 1st in AsiaPacific, Fraser Institute – 2011). The country is still largely under-explored and will undoubtedly will produce significant ...
Collagen by Kati Feken - Illinois State University
... Collagen molecules stack together to form fibrils. Above is an electron micrograph of several fibrils. One molecule of collagen from these fibrils are 3000Å in length and 15Å thick. The gaps formed between the collagen molecules line up every 4 molecules, causing striations that are 640Å. ...
... Collagen molecules stack together to form fibrils. Above is an electron micrograph of several fibrils. One molecule of collagen from these fibrils are 3000Å in length and 15Å thick. The gaps formed between the collagen molecules line up every 4 molecules, causing striations that are 640Å. ...
Mineralized tissues
Mineralized tissues are biological tissues that incorporate minerals into soft matrices. Typically these tissues form a protective shield or structural support. Bone, mollusc shells, deep sea sponge Euplectella species, radiolarians, diatoms, antler bone, tendon, cartilage, tooth enamel and dentin are some examples where mineralized tissues are found.These tissues have been finely tuned to enhance their mechanical capabilities over millions of years of evolution. Thus, mineralized tissues have been the subject of many studies since there is a lot to learn from nature as seen from the growing field of biomimetics. The remarkable structural organization and engineering properties makes these tissues desirable candidates for duplication by artificial means. Mineralized tissues inspire miniaturization, adaptability and multifunctionality. While natural materials are made up of a limited number of components, a larger variety of material chemistries can be used to simulate the same properties in engineering applications. However, the success of biomimetics lies in fully grasping the performance and mechanics of these biological hard tissues before swapping the natural components with artificial materials for engineering design.Mineralized tissues combine stiffness, low weight, strength and toughness due to the presence of minerals (the inorganic part) in soft protein networks and tissues (the organic part). There are approximately 60 different minerals generated through biological processes, but the most common ones are calcium carbonate found in mollusk shells and hydroxyapatite present in teeth and bones. Although one might think that the mineral content of these tissues can make them fragile, studies have shown that mineralized tissues are 1,000 to 10,000 times tougher than the minerals they contain. The secret to this underlying strength is in the organized layering of the tissue. Due to this layering, loads and stresses are transferred throughout several length-scales, from macro to micro to nano, which results in the dissipation of energy within the arrangement. These scales or hierarchical structures are therefore able to distribute damage and resist cracking. Two types of biological tissues have been the target of extensive investigation, namely nacre from mollusk shells and bone, which are both high performance natural composites. Many mechanical and imaging techniques such as nanoindentation and atomic force microscopy are used to characterize these tissues. Although the degree of efficiency of biological hard tissues are yet unmatched by any man-made ceramic composites, some promising new techniques to synthesize them are currently under development. Not all mineralized tissues develop through normal physiologic processes and are beneficial to the organism. For example, kidney stones contain mineralized tissues that are developed through pathologic processes. Hence, biomineralization is an important process to understand how these diseases occur.