Chemistry 20 Chapters 13 Lipids
... together in close parallel alignment and the have higher London dispersion forces than unsaturated fatty acids. Essential fatty acids: human body is capable of synthesizing most fatty acids from carbohydrates or other fatty acids. However, humans do not synthesize sufficient amounts of fatty acids t ...
... together in close parallel alignment and the have higher London dispersion forces than unsaturated fatty acids. Essential fatty acids: human body is capable of synthesizing most fatty acids from carbohydrates or other fatty acids. However, humans do not synthesize sufficient amounts of fatty acids t ...
Lipids - U of L Class Index
... 1. Types of Lipids Lipids are discussed in terms of their components and solubility in various solvents. Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids are described along with a comparison of their melting points. Demonstration: I introduce this chapter with examples of lipids such as margarine, butter, lar ...
... 1. Types of Lipids Lipids are discussed in terms of their components and solubility in various solvents. Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids are described along with a comparison of their melting points. Demonstration: I introduce this chapter with examples of lipids such as margarine, butter, lar ...
LIPIDS
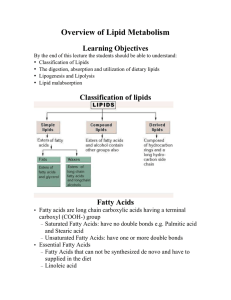
... • Double bond. – Mono unsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) (1 double bond) – • Oleic acid (18C) – Poly unsaturated fatty acid (FUFA) (2 and more double bond) • Linoleic acid (2 double bond) (18C) • Linolenic acid (3 double bond) (18 C) • Aracidonic acid (5 double bond) (20C) • Called as essential fatty aci ...
... • Double bond. – Mono unsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) (1 double bond) – • Oleic acid (18C) – Poly unsaturated fatty acid (FUFA) (2 and more double bond) • Linoleic acid (2 double bond) (18C) • Linolenic acid (3 double bond) (18 C) • Aracidonic acid (5 double bond) (20C) • Called as essential fatty aci ...
group “head” dehydration synthesis H 2 O enzyme AP
... Hydrophilic heads “attracted” to H2O Hydrophobic tails “hide” from H2O ...
... Hydrophilic heads “attracted” to H2O Hydrophobic tails “hide” from H2O ...
Biomolecules: lipids - e
... The active form of vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) induces an increase in the plasma concentration of Ca2+, thus favouring its uptake by intestinal cells. Without vitamin D, only 10 to 15% of dietary calcium and about 60% of phosphorus is absorbed. The interaction with its receptor increases the ...
... The active form of vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D) induces an increase in the plasma concentration of Ca2+, thus favouring its uptake by intestinal cells. Without vitamin D, only 10 to 15% of dietary calcium and about 60% of phosphorus is absorbed. The interaction with its receptor increases the ...
Metabolism of lipids
... a) a phospholipid bilayer on their surface b) free cholesterol in their core c) triacylglycerols in their core d) surface proteins having a role of ligands, which can bind to receptors of target cells other functions: apoproteins activate enzymes metabolizing lipoproteins, or they have a structural ...
... a) a phospholipid bilayer on their surface b) free cholesterol in their core c) triacylglycerols in their core d) surface proteins having a role of ligands, which can bind to receptors of target cells other functions: apoproteins activate enzymes metabolizing lipoproteins, or they have a structural ...
Chapter 10 Lipids
... If neural tissue - usually galactose If non-neural usually glucose Globosides 2 or more sugars Cerebrosides and globosides called neutral glycolipids because no charge at pH 7 Gangliosides (also a glygolipid, but more compliated) Oligosaccharides as polar head Typically sialic acid at terminus F. Sp ...
... If neural tissue - usually galactose If non-neural usually glucose Globosides 2 or more sugars Cerebrosides and globosides called neutral glycolipids because no charge at pH 7 Gangliosides (also a glygolipid, but more compliated) Oligosaccharides as polar head Typically sialic acid at terminus F. Sp ...
Slide 1
... They associate to form double layers called lipid bilayers, which are impermeable to polar molecules. Proteins associated with or embedded in the lipid bilayer carry out the different functions of membranes. These proteins serve as pumps, channels, receptors, energy transducers, and enzymes. Both li ...
... They associate to form double layers called lipid bilayers, which are impermeable to polar molecules. Proteins associated with or embedded in the lipid bilayer carry out the different functions of membranes. These proteins serve as pumps, channels, receptors, energy transducers, and enzymes. Both li ...
O–CH 2 - IS MU
... COX-2 activity, without the gastrointestinal (stomach ulcer) and antiplatelet side effects associated with NSAIDs Examples: celecoxib, rofecoxib ...
... COX-2 activity, without the gastrointestinal (stomach ulcer) and antiplatelet side effects associated with NSAIDs Examples: celecoxib, rofecoxib ...
没有幻灯片标题
... 5.2.4 DAG activates protein kinase C, which further activates many enzymes by phosphorylation. ...
... 5.2.4 DAG activates protein kinase C, which further activates many enzymes by phosphorylation. ...
Versatile roles of lipids and carotenoids in membranes
... ▪ structure - four rigid rings are responsible for the major functions → controlling membrane fluidity - a polar hydroxyl group → anchored the molecule to the aqueous interface - a floppy tail (function is not clear) ▪ in animals: cholesterol (Chol) - in vertebrates major location is the brain in fu ...
... ▪ structure - four rigid rings are responsible for the major functions → controlling membrane fluidity - a polar hydroxyl group → anchored the molecule to the aqueous interface - a floppy tail (function is not clear) ▪ in animals: cholesterol (Chol) - in vertebrates major location is the brain in fu ...
Membranes 1: Lipids and Lipid Bilayers
... – bilayer structure → compartments/permeability barriers – provide environment for proteins to work – electrical insulation (e.g., myelin sheath on myelinated nerve fibers, but also maintenance of electrical potential in other cells) • Membrane lipid distribution: functional significance of all the ...
... – bilayer structure → compartments/permeability barriers – provide environment for proteins to work – electrical insulation (e.g., myelin sheath on myelinated nerve fibers, but also maintenance of electrical potential in other cells) • Membrane lipid distribution: functional significance of all the ...
Membranes 1: Lipids and Lipid Bilayers
... – bilayer structure → compartments/permeability barriers – provide environment for proteins to work – electrical insulation (e.g., myelin sheath on myelinated nerve fibers, but also maintenance of electrical potential in other cells) Membrane lipid distribution: functional significance of all the di ...
... – bilayer structure → compartments/permeability barriers – provide environment for proteins to work – electrical insulation (e.g., myelin sheath on myelinated nerve fibers, but also maintenance of electrical potential in other cells) Membrane lipid distribution: functional significance of all the di ...
Overview of Lipid Metabolism
... • Glycerol can be converted to pyruvic acid which enters TCA • Fatty Acids are degraded by beta oxidation, occurs in mitochondria of liver, muscle and adipose tissue ...
... • Glycerol can be converted to pyruvic acid which enters TCA • Fatty Acids are degraded by beta oxidation, occurs in mitochondria of liver, muscle and adipose tissue ...
THE LIPIDS: TRIGLYCERIDES, PHOSPHOLIPIDS, & STEROLS
... In the mouth- the salivary glands release lipase which plays a small role in the start of digestion. In the stomach- fat floats as a layer above the other components of food, as a result little digestion takes place here. ...
... In the mouth- the salivary glands release lipase which plays a small role in the start of digestion. In the stomach- fat floats as a layer above the other components of food, as a result little digestion takes place here. ...
Lipids and Membranes The “OTHER” Solvent of Life Processes
... Different organisms have different membrane lipid head group compositions Different tissues have different membrane lipid head group compositions ...
... Different organisms have different membrane lipid head group compositions Different tissues have different membrane lipid head group compositions ...
Tomatine

Tomatine is a glycoalkaloid found in the stems and leaves of tomato plants, which has fungicidal properties. Chemically pure tomatine is a white crystalline solid at standard temperature and pressure. Tomatine as well as the a-glycone derivative Tomatidine have been shown to have multiple health benefits. Tomatine has antimicrobial properties against certain classes of microbes although some microbes produce an enzyme called tomatinase which can degrade tomatine, rendering it ineffective as an antimicrobial.