Bridges - s3.amazonaws.com
... Ch4 True/False Quiz 1) When employing virtual-circuits, packet switches are ...
... Ch4 True/False Quiz 1) When employing virtual-circuits, packet switches are ...
Congestion Control
... Three Key Features of Internet • Packet switching – A given source may have enough capacity to send data – … and yet the packets may encounter an overloaded link ...
... Three Key Features of Internet • Packet switching – A given source may have enough capacity to send data – … and yet the packets may encounter an overloaded link ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4
... “smart” end systems need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network L ...
... “smart” end systems need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network L ...
Ericsson Standard Document, Template for A4 Portrait EN
... reliable and ultra-scalable configuration. PBN is based on the following hardware platforms from Ericsson: the AXI 520 IP Core Routers, AXI 540 Edge Aggregation Router and AXD 301 High-Performance ATM Switch. PBN includes a Multiservice Management Suite (MMS) of products that includes in-house devel ...
... reliable and ultra-scalable configuration. PBN is based on the following hardware platforms from Ericsson: the AXI 520 IP Core Routers, AXI 540 Edge Aggregation Router and AXD 301 High-Performance ATM Switch. PBN includes a Multiservice Management Suite (MMS) of products that includes in-house devel ...
4th Edition: Chapter 1 - Computer Science Division
... 640,000 bits from host A to host B over a circuit-switched network? All links are 1.536 Mbps Each link uses TDM with 24 slots/sec 500 msec to establish end-to-end circuit ...
... 640,000 bits from host A to host B over a circuit-switched network? All links are 1.536 Mbps Each link uses TDM with 24 slots/sec 500 msec to establish end-to-end circuit ...
FM-Delta: Fault Management Packet Compression
... Detection (BFD) [5] control messages. Each packet type was used on half of the data set. CCMs are defined over Ethernet, while BFDs are over IPv4-over-Ethernet. Each packet included a random number of VLAN tags (either 0, 1, or 2 tags). The network topology can significantly affect the extent to whi ...
... Detection (BFD) [5] control messages. Each packet type was used on half of the data set. CCMs are defined over Ethernet, while BFDs are over IPv4-over-Ethernet. Each packet included a random number of VLAN tags (either 0, 1, or 2 tags). The network topology can significantly affect the extent to whi ...
RIP/OSPF
... • There are many IGP protocols. • The specific protocol a specific router depends on – The router manufacturer » e.g. Cisco may have a proprietary protocol that relies on a specific hardware implementation. ...
... • There are many IGP protocols. • The specific protocol a specific router depends on – The router manufacturer » e.g. Cisco may have a proprietary protocol that relies on a specific hardware implementation. ...
IP Multicast and Multicast Reliability
... • keeping the window at a fixed size in bytes • keeping the window at a fixed number of packets • keeping the window at a fixed real time duration. ...
... • keeping the window at a fixed size in bytes • keeping the window at a fixed number of packets • keeping the window at a fixed real time duration. ...
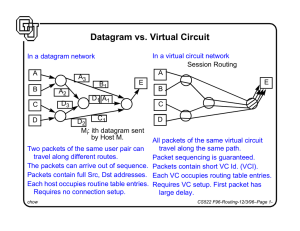
Datagram vs. Virtual Circuit
... Find the shortest paths form a given source node to all other nodes by developing paths in order of increasing path length. Let the set of nodes in a network be N. 1. start with a source node S in node set M. Let the nodes not in M be M’. 2. Let L with the set of links connecting M and M’. l Among t ...
... Find the shortest paths form a given source node to all other nodes by developing paths in order of increasing path length. Let the set of nodes in a network be N. 1. start with a source node S in node set M. Let the nodes not in M be M’. 2. Let L with the set of links connecting M and M’. l Among t ...
Datasheet - EnOcean Alliance
... 3.1.2 TCM Module The TCM 130 module is a transceiver node. It is controlled by a PIC8F452 16-Bit microcontroller. This microcontroller contains of 32KB Flash, 1,5KB RAM and 0,25KB EEPROM. It holds firmware which was enhanced with a routing algorithm and modified for debugging purposes. Therefore it' ...
... 3.1.2 TCM Module The TCM 130 module is a transceiver node. It is controlled by a PIC8F452 16-Bit microcontroller. This microcontroller contains of 32KB Flash, 1,5KB RAM and 0,25KB EEPROM. It holds firmware which was enhanced with a routing algorithm and modified for debugging purposes. Therefore it' ...
Routers - ISR - Infrastructure Systems Research Lab
... The neighboring node(s) examine this information, and compare it to what they already 'know'; anything which represents an improvement on what they already have, they insert in their own routing table(s). Over time, all the nodes in the network will discover the best next hop for all destinations, a ...
... The neighboring node(s) examine this information, and compare it to what they already 'know'; anything which represents an improvement on what they already have, they insert in their own routing table(s). Over time, all the nodes in the network will discover the best next hop for all destinations, a ...
SmartRE: An Architecture for Coordinated Network
... SmartRE is 4-5X better than the Hop-by-Hop Approach SmartRE gets 80-90% of ideal unconstrained RE Results consistent across redundancy profiles, on synthetic traces ...
... SmartRE is 4-5X better than the Hop-by-Hop Approach SmartRE gets 80-90% of ideal unconstrained RE Results consistent across redundancy profiles, on synthetic traces ...
chapter1 - Computer Science Division
... 640,000 bits from host A to host B over a circuit-switched network? All links are 1.536 Mbps Each link uses TDM with 24 slots/sec 500 msec to establish end-to-end circuit ...
... 640,000 bits from host A to host B over a circuit-switched network? All links are 1.536 Mbps Each link uses TDM with 24 slots/sec 500 msec to establish end-to-end circuit ...
Mobile IP: Introduction
... – Hawaii nodes are IP routers Assume intra-domain routing protocol is operating in the access network, allowing each node to have routes to other nodes The routing information is used to exchange explicit signaling messages, and forward packets between old and new access points during handoff ...
... – Hawaii nodes are IP routers Assume intra-domain routing protocol is operating in the access network, allowing each node to have routes to other nodes The routing information is used to exchange explicit signaling messages, and forward packets between old and new access points during handoff ...
Securing Information Transmission by Redundancy
... • Successful if at least one copy is authentically received ...
... • Successful if at least one copy is authentically received ...
Slide 1
... ICMP disabled NAT boxes / firewalls No information on route (other than TTL) No information on performance (other than RTT) ...
... ICMP disabled NAT boxes / firewalls No information on route (other than TTL) No information on performance (other than RTT) ...
Internetworking
... • if router is connected to destination network, then forward to host • if not directly connected, then forward to some router • forwarding table maps network number into next hop (router) • each host has a default router • each router maintains a forwarding table ...
... • if router is connected to destination network, then forward to host • if not directly connected, then forward to some router • forwarding table maps network number into next hop (router) • each host has a default router • each router maintains a forwarding table ...
VoCCN: Voice-over Content
... VoIP Signaling and Media paths result from a mismatch between the user’s goal and the network’s meaning of achieving it. Alice simply wants to talk to Bob but the network requires that the communication be addressed to the IP address of Bob’s phone. ...
... VoIP Signaling and Media paths result from a mismatch between the user’s goal and the network’s meaning of achieving it. Alice simply wants to talk to Bob but the network requires that the communication be addressed to the IP address of Bob’s phone. ...
OSPF
... Developed in reference to the limitation of RIP in large enterprise networks Based on open standards Runs on most routers Uses the SPF algorithm to provide a loop-free topology Fast convergence with triggered and incremental updates via LSA’s (it’s a link state protocol) Classless protocol allowing ...
... Developed in reference to the limitation of RIP in large enterprise networks Based on open standards Runs on most routers Uses the SPF algorithm to provide a loop-free topology Fast convergence with triggered and incremental updates via LSA’s (it’s a link state protocol) Classless protocol allowing ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4
... “smart” end systems need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network L ...
... “smart” end systems need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network L ...
The Network Layer
... about its neighbourhood with every routers in the area. b) However, in LSR, the link-state packet (LSP) defines the best known network topology (of an area) is sent to every routers (of other area) after it is constructed locally. Whereas RIP slowly converge to final routing list based information r ...
... about its neighbourhood with every routers in the area. b) However, in LSR, the link-state packet (LSP) defines the best known network topology (of an area) is sent to every routers (of other area) after it is constructed locally. Whereas RIP slowly converge to final routing list based information r ...