here.
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Sub-atomic/nuclear means of size less than atomi ...
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Sub-atomic/nuclear means of size less than atomi ...
Notes for course on Physics of Particles and Fields, CMI, Autumn
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Subatomic/nuclear means of size less than atomic ...
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Subatomic/nuclear means of size less than atomic ...
Chemistry 2008 Multiple Choice
... also form H-bonds with other ethanol molecules because of the presence of the OH-. Since H-bonds are stronger than London dispersion and dipole forces, the energy (temperature) needed to break the bond is higher for ethanol than it is for dimethyl ether. ...
... also form H-bonds with other ethanol molecules because of the presence of the OH-. Since H-bonds are stronger than London dispersion and dipole forces, the energy (temperature) needed to break the bond is higher for ethanol than it is for dimethyl ether. ...
Current Status of Nuclear Physics Research
... Nuclear Physics evolved in a rather logical manner; from simple ordered shell model tailored in accordance with atomic structure to reproduce the magic numbers [1, 2], to collective models needed to describe vibrations and cases involving non-spherical nuclei. The collective model is now considered ...
... Nuclear Physics evolved in a rather logical manner; from simple ordered shell model tailored in accordance with atomic structure to reproduce the magic numbers [1, 2], to collective models needed to describe vibrations and cases involving non-spherical nuclei. The collective model is now considered ...
Electricity: 1) Static electricity 2) Electrical charges and its properties
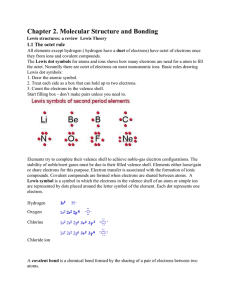
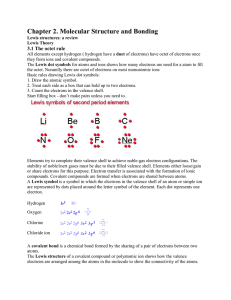
... these materials are classified as elements and compounds. The smallest particle of the element is known as ‘atom’ and smallest particle of the compound is known as ‘molecule’. Molecules are formed when two or more than two atoms come together under specific conditions. We also know that the ‘atoms a ...
... these materials are classified as elements and compounds. The smallest particle of the element is known as ‘atom’ and smallest particle of the compound is known as ‘molecule’. Molecules are formed when two or more than two atoms come together under specific conditions. We also know that the ‘atoms a ...
Spectroscopy with trapped francium: advances and perspectives for
... transported as ions to a region where after neutralization they are trapped in a magneto optical trap (MOT) for further measurements. The apparatus used to trap francium at Stony Brook is based on the same principles as the one they used to trap radioactive 79 Rb [43]. Beams of 18 O from the Stony B ...
... transported as ions to a region where after neutralization they are trapped in a magneto optical trap (MOT) for further measurements. The apparatus used to trap francium at Stony Brook is based on the same principles as the one they used to trap radioactive 79 Rb [43]. Beams of 18 O from the Stony B ...
chem481chp
... 24 electrons would be needed to satisfy the valencies independently. 24-17 = 7. The odd number of electrons is a signal that there will be a place where we would normally expect to find another electron. When you have some experience with these situations, you probably will have no problem in assign ...
... 24 electrons would be needed to satisfy the valencies independently. 24-17 = 7. The odd number of electrons is a signal that there will be a place where we would normally expect to find another electron. When you have some experience with these situations, you probably will have no problem in assign ...
Slides - Agenda INFN
... Commissioning of EAR2 The new beam line has been characterized in terms of flux and beam profile by means of several detection systems, namely silicon based devices and gaseous detectors. The detectors are equipped with different neutron converters placed in front of the sensible layer or volume ...
... Commissioning of EAR2 The new beam line has been characterized in terms of flux and beam profile by means of several detection systems, namely silicon based devices and gaseous detectors. The detectors are equipped with different neutron converters placed in front of the sensible layer or volume ...
Fundamentals Diagnostic Quiz
... a) A homogeneous mixture can also be referred to as a solution. b) Within a solution, the component in the least amount is called the solute. *c) Within a solution, the component in the least amount is called the solvent. d) A solution in which the solute is water is called an aqueous solution. e) S ...
... a) A homogeneous mixture can also be referred to as a solution. b) Within a solution, the component in the least amount is called the solute. *c) Within a solution, the component in the least amount is called the solvent. d) A solution in which the solute is water is called an aqueous solution. e) S ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.









![arXiv:1412.5987v1 [hep-ex] 18 Dec 2014](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008057205_1-733500b8b6bd2637f9a7ffd625392271-300x300.png)