Chem101, 2nd Major Exam, term061
... The hydrogen atom has only one orbital. The size of the hydrogen 1s orbital is defined as the surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. C) The square of the wave function represents the probability distribution of the elctron in the orbital. D) In the quantum mechanical model, the ...
... The hydrogen atom has only one orbital. The size of the hydrogen 1s orbital is defined as the surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. C) The square of the wave function represents the probability distribution of the elctron in the orbital. D) In the quantum mechanical model, the ...
Proton chemical shifts in NMR. Part 8.1 Electric field effects and
... CF2 and CF3 groups 22 due to resonance forms such as F+]C]F2. On this basis the electron distribution in the CF bond would be greater between the atoms in the CF2 and CF3 groups than in the CF bond. A similar explanation has been proposed previously to explain the correction for the β and γ protons. ...
... CF2 and CF3 groups 22 due to resonance forms such as F+]C]F2. On this basis the electron distribution in the CF bond would be greater between the atoms in the CF2 and CF3 groups than in the CF bond. A similar explanation has been proposed previously to explain the correction for the β and γ protons. ...
Chemistry - RESONANCE PCCP IDEAL for NTSE, IJSO, Olympiads
... becomes less negative. The electron can have a maximum energy value of zero when n = . The zero energy means that the electron is no longer bound to the nucleus , i.e. , it is not under the force of attraction ...
... becomes less negative. The electron can have a maximum energy value of zero when n = . The zero energy means that the electron is no longer bound to the nucleus , i.e. , it is not under the force of attraction ...
Charges and Electric Fields - University of Colorado Boulder
... create or destroy electrons, protons, and other charged particles – all we can do is move them around. In high energy reactions, we can create charged particles from energy (energy = mc2), but the particles are always created or destroyed in pairs (+1 and −1) so that the net charge is conserved. Asi ...
... create or destroy electrons, protons, and other charged particles – all we can do is move them around. In high energy reactions, we can create charged particles from energy (energy = mc2), but the particles are always created or destroyed in pairs (+1 and −1) so that the net charge is conserved. Asi ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... positive charge, much more mass than negative stuff (turn out to be He nuclei) particles, attracted to positive electrode, so they have a negative charge, 1000s of times less massive (turn out to be electrons coming from nucleus). rays, no charge, no mass, ...
... positive charge, much more mass than negative stuff (turn out to be He nuclei) particles, attracted to positive electrode, so they have a negative charge, 1000s of times less massive (turn out to be electrons coming from nucleus). rays, no charge, no mass, ...
Charges and Electric Fields - University of Colorado Boulder
... Most materials can be classified as conductor or insulator. A conductor is also called a metal; an insulator also called a dielectric. Metals (Cu, Al, Au, Ag, Fe…) conduct electricity. In metals, some of the electrons (conduction electrons) can move freely through the metal. If there is an E-field, ...
... Most materials can be classified as conductor or insulator. A conductor is also called a metal; an insulator also called a dielectric. Metals (Cu, Al, Au, Ag, Fe…) conduct electricity. In metals, some of the electrons (conduction electrons) can move freely through the metal. If there is an E-field, ...
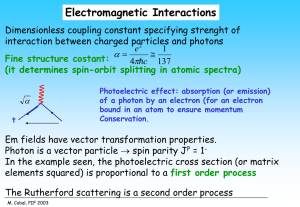
Atoms Absorb Low Frequency Electromagnetic Energy
... The atomic structure is described by the Standard Model [1]. Despite huge scientific efforts the atomic structure remains to large extent unsolved. All forces within the atom, except the Coulomb force, remain unknown; the strong force (gluon), the weak force and the graviton [2-5]. Some progress has ...
... The atomic structure is described by the Standard Model [1]. Despite huge scientific efforts the atomic structure remains to large extent unsolved. All forces within the atom, except the Coulomb force, remain unknown; the strong force (gluon), the weak force and the graviton [2-5]. Some progress has ...
jyvaskla2 - School of Chemistry
... quite transferable and additive, but do not look very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces ar ...
... quite transferable and additive, but do not look very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces ar ...
Finite-Volume Electromagnetic Corrections to the Masses of Mesons
... space is much larger than that of the hadron, keeping in mind that only the zero modes are being excluded from the photon fields, the FV corrections to the mass of the hadron will have a powerlaw dependence upon L, and vanish as L → ∞. As the modifications to the self-energy arise from the infrared ...
... space is much larger than that of the hadron, keeping in mind that only the zero modes are being excluded from the photon fields, the FV corrections to the mass of the hadron will have a powerlaw dependence upon L, and vanish as L → ∞. As the modifications to the self-energy arise from the infrared ...
H - Deans Community High School
... largein excess ofinthe EA. These energy excess of EA. increase in the number of particles with energy particles have enough above EA. Therefore a greater proportion energyof to cause successful collisions collisions will be successful. ...
... largein excess ofinthe EA. These energy excess of EA. increase in the number of particles with energy particles have enough above EA. Therefore a greater proportion energyof to cause successful collisions collisions will be successful. ...
Majorana Fermions - Physics | Oregon State University
... Just this month, Banerjee et al. have claimed to observe MFs in QSLs: Quantum spin liquids (QSLs) are topological states of matter exhibiting remarkable properties such as the capacity to protect quantum information from decoherence. Whereas their featureless ground states have precluded their strai ...
... Just this month, Banerjee et al. have claimed to observe MFs in QSLs: Quantum spin liquids (QSLs) are topological states of matter exhibiting remarkable properties such as the capacity to protect quantum information from decoherence. Whereas their featureless ground states have precluded their strai ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.