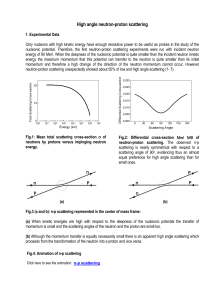
High angle neutron-proton scattering
... Let us now make the phenomenological description of the proton-neutron inversion from the orbital standpoint. It provides a straightforward answer (expressed in form of an animation of the scattering process) based on the neutron shell which is easily interchanged between protons. It presents some s ...
... Let us now make the phenomenological description of the proton-neutron inversion from the orbital standpoint. It provides a straightforward answer (expressed in form of an animation of the scattering process) based on the neutron shell which is easily interchanged between protons. It presents some s ...
posted
... EVALUATE: All points of a conductor are at the same potential. (a) IDENTIFY and SET UP: The electric field on the ring’s axis is calculated in Example 21.9. The force on the electron exerted by this field is given by Eq. (21.3). EXECUTE: When the electron is on either side of the center of the ring, ...
... EVALUATE: All points of a conductor are at the same potential. (a) IDENTIFY and SET UP: The electric field on the ring’s axis is calculated in Example 21.9. The force on the electron exerted by this field is given by Eq. (21.3). EXECUTE: When the electron is on either side of the center of the ring, ...
chem1a_ch02_lecture - Santa Rosa Junior College
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any ...
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any ...
Chemistry- CST Review
... Standard 6- Solutions 1. Define solute and solvent. Salt is dissolved in a glass of water. Which is the solute? Which is the solvent? Solute is the substance being dissolved and it is present in lesser amount. The solvent is usually a liquid and present in the greater amount. Salt is a solute and wa ...
... Standard 6- Solutions 1. Define solute and solvent. Salt is dissolved in a glass of water. Which is the solute? Which is the solvent? Solute is the substance being dissolved and it is present in lesser amount. The solvent is usually a liquid and present in the greater amount. Salt is a solute and wa ...
Chapter 6 - TeacherWeb
... • For large objects, we can calculate position and momentum with great accuracy. For electrons we are limited. • For large objects, the uncertainty is extremely small! • Our uncertainty of the whereabouts of an electron is often greater than the size of the atom itself! © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... • For large objects, we can calculate position and momentum with great accuracy. For electrons we are limited. • For large objects, the uncertainty is extremely small! • Our uncertainty of the whereabouts of an electron is often greater than the size of the atom itself! © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Bose-Einstein Condensates Bosons Liquid Helium
... Although the electron configuration is the same as ordinary helium, a neutron is unpaired in spin. The entire atom thus has spin 1/2, and is a fermion. It must obey the PauliExclusion principle. So even though the mass is nearly the same as 42 He , and the electron configuration is the same, 23 He d ...
... Although the electron configuration is the same as ordinary helium, a neutron is unpaired in spin. The entire atom thus has spin 1/2, and is a fermion. It must obey the PauliExclusion principle. So even though the mass is nearly the same as 42 He , and the electron configuration is the same, 23 He d ...
Nanoscience Student Reading Lesson 4
... –it is not just limited to light––and the wave nature has been observed in experiments. It may be hard to imagine something like a “matter wave,” but when you are talking about small particles such as electrons, it is possible to observe wave-like behavior. Quantum Tunneling Quantum tunneling is one ...
... –it is not just limited to light––and the wave nature has been observed in experiments. It may be hard to imagine something like a “matter wave,” but when you are talking about small particles such as electrons, it is possible to observe wave-like behavior. Quantum Tunneling Quantum tunneling is one ...
GHW - Louisiana Tech University
... table, Mendeleev used atomic weights not atomic numbers. a) In the periodic table what elements should have been swapped if Mendeleev was to following order of increasing atomic masses strictly? ...
... table, Mendeleev used atomic weights not atomic numbers. a) In the periodic table what elements should have been swapped if Mendeleev was to following order of increasing atomic masses strictly? ...
39 The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... Nucleons are bound together by an attractive nuclear force appropriately called the strong force. • The nuclear force of attraction is strong only over a very short distance (large force vectors). • When two nucleons are just a few nucleon diameters apart, the nuclear force they exert on each other ...
... Nucleons are bound together by an attractive nuclear force appropriately called the strong force. • The nuclear force of attraction is strong only over a very short distance (large force vectors). • When two nucleons are just a few nucleon diameters apart, the nuclear force they exert on each other ...
Paper - Revision Science
... The 82 kg mass is fired from Charon's surface to Pluto. Neglecting any losses due to resistive forces, calculate the change in kinetic energy of the 82 kg mass from the instant it was fired to the instant just before it collides with Pluto. ...
... The 82 kg mass is fired from Charon's surface to Pluto. Neglecting any losses due to resistive forces, calculate the change in kinetic energy of the 82 kg mass from the instant it was fired to the instant just before it collides with Pluto. ...
Electron
... together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons • Covalent bonds can form between atoms of the same element or atoms of different elements ...
... together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons • Covalent bonds can form between atoms of the same element or atoms of different elements ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.