Has the Periodic Table Been Successfully Axiomatized?
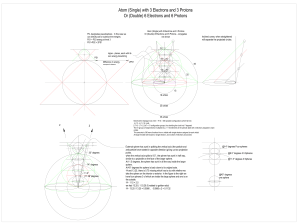
... the arrangement of electrons in rings. Thomson proposed a detailed set of atomic configurations as part of his plumb pudding model in which electrons were embedded in the main body of the atoms and were held to circulate in concentric rings (Thomson, 1904). The particular arrangement of how many ele ...
... the arrangement of electrons in rings. Thomson proposed a detailed set of atomic configurations as part of his plumb pudding model in which electrons were embedded in the main body of the atoms and were held to circulate in concentric rings (Thomson, 1904). The particular arrangement of how many ele ...
Chapter 2 Matter and Components F11 110
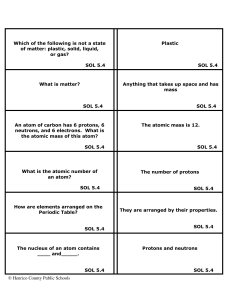
... 3. For Type II metals with only two common oxidation states an older, Latin system was once used; while it is not employed very often it is useful to know some simple rules regarding it. It is sometimes called the “-ous/-ic” system, where the LOWER charged cation will be denoted by the latin root na ...
... 3. For Type II metals with only two common oxidation states an older, Latin system was once used; while it is not employed very often it is useful to know some simple rules regarding it. It is sometimes called the “-ous/-ic” system, where the LOWER charged cation will be denoted by the latin root na ...
Perspectives of Nuclear Physics in Europe
... table, and by binding negatively charged, much lighter electrons around them form atoms. The atoms can, in turn, combine and form molecules making complex chemical and biological structures. The largest and heaviest nuclei contain up to nearly 300 protons and neutrons (collectively called nucleons). ...
... table, and by binding negatively charged, much lighter electrons around them form atoms. The atoms can, in turn, combine and form molecules making complex chemical and biological structures. The largest and heaviest nuclei contain up to nearly 300 protons and neutrons (collectively called nucleons). ...
Description, introduction, example data for Mossbauer experiments
... recoil energy is smaller than the bonding energy between atoms in the crystal, the emitting or absorbing nuclei do not leave their site in the crystal. case the recoil momentum is taken up by the lattice as a whole. ...
... recoil energy is smaller than the bonding energy between atoms in the crystal, the emitting or absorbing nuclei do not leave their site in the crystal. case the recoil momentum is taken up by the lattice as a whole. ...
Final Exam
... bromine is found as bromine-79 (78.9183 u), what is the mass of the other isotope? a. 79.82 u b. 79.97 u c. 80.91 u d. 81.93 u e. 82.91 u ...
... bromine is found as bromine-79 (78.9183 u), what is the mass of the other isotope? a. 79.82 u b. 79.97 u c. 80.91 u d. 81.93 u e. 82.91 u ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.