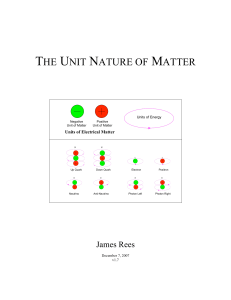
To do List
... His oil-drop experiment enabled scientists to measure the charge on the electron. ...
... His oil-drop experiment enabled scientists to measure the charge on the electron. ...
Neutron Data Booklet
... lengths vary irregularly from one nucleus to another due to their strong dependence on the details of the individual nuclear interaction. Therefore, low-energy neutrons are an important tool for the investigation of the static and dynamic properties of condensed matter since they distinguish between ...
... lengths vary irregularly from one nucleus to another due to their strong dependence on the details of the individual nuclear interaction. Therefore, low-energy neutrons are an important tool for the investigation of the static and dynamic properties of condensed matter since they distinguish between ...
Effects of electric fields on ultracold Rydberg atom interactions
... of the laser. These observations are direct experimental evidence of interacting Rydberg atom pairs and can be used as benchmark data to test calculations of Rydberg atom pair ...
... of the laser. These observations are direct experimental evidence of interacting Rydberg atom pairs and can be used as benchmark data to test calculations of Rydberg atom pair ...
Neutron Data Booklet - Institut Laue
... lengths vary irregularly from one nucleus to another due to their strong dependence on the details of the individual nuclear interaction. Therefore, low-energy neutrons are an important tool for the investigation of the static and dynamic properties of condensed matter since they distinguish between ...
... lengths vary irregularly from one nucleus to another due to their strong dependence on the details of the individual nuclear interaction. Therefore, low-energy neutrons are an important tool for the investigation of the static and dynamic properties of condensed matter since they distinguish between ...
Exam Review
... compounds of crude oil, boil at temperatures above 400ºC. The differences in boiling points of the compounds making up petroleum enable the separation of these compounds in a process called fractional distillation, or fractionation. When crude oil is heated to 500ºC in the absence of air, most of it ...
... compounds of crude oil, boil at temperatures above 400ºC. The differences in boiling points of the compounds making up petroleum enable the separation of these compounds in a process called fractional distillation, or fractionation. When crude oil is heated to 500ºC in the absence of air, most of it ...
Physics Mechanics
... If the speeds of the interacting objects are very large, we must replace Classical mechanics with Einstein’s special theory of relativity, which hold at any speed, including those near the speed of light. If the interacting bodies are on the scale of atomic structure, we must replace Classical mecha ...
... If the speeds of the interacting objects are very large, we must replace Classical mechanics with Einstein’s special theory of relativity, which hold at any speed, including those near the speed of light. If the interacting bodies are on the scale of atomic structure, we must replace Classical mecha ...
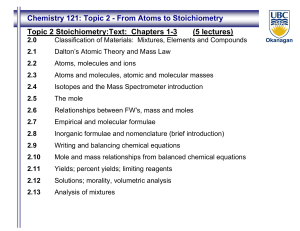
TOPIC 7. CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I
... CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I - atomic and formula weights. Atomic structure revisited. In Topic 2, atoms were described as ranging from the simplest atom, H, containing a single proton and usually no neutrons in its nucleus with one electron orbiting outside that nucleus, through to very large atoms such ...
... CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I - atomic and formula weights. Atomic structure revisited. In Topic 2, atoms were described as ranging from the simplest atom, H, containing a single proton and usually no neutrons in its nucleus with one electron orbiting outside that nucleus, through to very large atoms such ...
TOPIC 7. CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I
... CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I - atomic and formula weights. Atomic structure revisited. In Topic 2, atoms were described as ranging from the simplest atom, H, containing a single proton and usually no neutrons in its nucleus with one electron orbiting outside that nucleus, through to very large atoms such ...
... CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I - atomic and formula weights. Atomic structure revisited. In Topic 2, atoms were described as ranging from the simplest atom, H, containing a single proton and usually no neutrons in its nucleus with one electron orbiting outside that nucleus, through to very large atoms such ...
Subject Area Standard Area Organizing Category Grade Level
... CHEM.A.1.2.5: Describe how chemical bonding can affect whether a substance dissolves in a given liquid. ...
... CHEM.A.1.2.5: Describe how chemical bonding can affect whether a substance dissolves in a given liquid. ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry
... As you have learned, ions are atoms or molecules bearing an electrical charge. A cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative ion) forms when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons in its valence shell. Compounds c ...
... As you have learned, ions are atoms or molecules bearing an electrical charge. A cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative ion) forms when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons in its valence shell. Compounds c ...
Chemistry Review 2 answer key
... Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brother and sister team, Charles and Julia Hall, found that molten (melted) c ...
... Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brother and sister team, Charles and Julia Hall, found that molten (melted) c ...
PC_Chemistry_Macomb_April08
... Explain why it is necessary for a molecule to absorb energy in order to break a chemical bond. ...
... Explain why it is necessary for a molecule to absorb energy in order to break a chemical bond. ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.