Chemistry Lecture No.4______By : Asst. Led Tariq-H-AL
... For a bombardment reaction to occur, the bombarding particles must have enough energy to overcome the highly charged nucleus of the target atom, especially when the target atom has a high atomic mass. Most particles emitted by natural radioactive isotopes do not have enough energy to do this, so the ...
... For a bombardment reaction to occur, the bombarding particles must have enough energy to overcome the highly charged nucleus of the target atom, especially when the target atom has a high atomic mass. Most particles emitted by natural radioactive isotopes do not have enough energy to do this, so the ...
Chapter 2 - profpaz.com
... The number of protons in an atom is its atomic number and is designated by symbol Z. Each element identified by its unique atomic number, is represented by a unique chemical symbol, a one- or two-letter abbreviation. ...
... The number of protons in an atom is its atomic number and is designated by symbol Z. Each element identified by its unique atomic number, is represented by a unique chemical symbol, a one- or two-letter abbreviation. ...
DAY 4 CHEMISTRY SUMMER SCIENCE INSTITUTE ATOMS: HOW
... Back in the early 1900’s a scientist named Rutherford shot some alpha particles (something like atomic bullets) into some very thin pieces of gold. He thought that atoms were similar to the circular particles that you have drawn and that the bullets would all interact with all the gold atoms in abou ...
... Back in the early 1900’s a scientist named Rutherford shot some alpha particles (something like atomic bullets) into some very thin pieces of gold. He thought that atoms were similar to the circular particles that you have drawn and that the bullets would all interact with all the gold atoms in abou ...
Recreating_the_beginning_of_the_Universe_at_the_LHC
... 3) Why is there no more antimatter? • Everything we see in the Universe is made of matter. • Antimatter has opposite electric charge, but identical in every other way. • At the birth of the Universe, more matter than antimatter was produced in the Big Bang. ...
... 3) Why is there no more antimatter? • Everything we see in the Universe is made of matter. • Antimatter has opposite electric charge, but identical in every other way. • At the birth of the Universe, more matter than antimatter was produced in the Big Bang. ...
Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... Atomic Models: Philosophers: Democritus (believed in atoms) and Aristotle (didn’t believe in atoms) Scientists: What was the contribution of each one’s atomic model? Draw a model of each. John Dalton List the four postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory: ...
... Atomic Models: Philosophers: Democritus (believed in atoms) and Aristotle (didn’t believe in atoms) Scientists: What was the contribution of each one’s atomic model? Draw a model of each. John Dalton List the four postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory: ...
CHEMISTRY 1 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
... A. a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler substances B. a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat or light C. a reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of a cation in a compound D. a reaction in which two or more su ...
... A. a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler substances B. a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat or light C. a reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of a cation in a compound D. a reaction in which two or more su ...
atoms-chemical
... • While all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons (atomic number), they may differ in the number of neutrons and atomic mass. • Two atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are called isotopes. • For example, 99% of carbon atoms have 6 neutrons (12C). 1% of ...
... • While all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons (atomic number), they may differ in the number of neutrons and atomic mass. • Two atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are called isotopes. • For example, 99% of carbon atoms have 6 neutrons (12C). 1% of ...
Science Olympiad
... (A) ionization energy decreases due to increases shielding effect. (B) atomic radius decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (C) electronegativity decreases due to an increase in atomic radius. (D) electron affinity decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (E) ioni ...
... (A) ionization energy decreases due to increases shielding effect. (B) atomic radius decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (C) electronegativity decreases due to an increase in atomic radius. (D) electron affinity decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (E) ioni ...
Name: Period:______ PHYSICAL SCIENCE 1st Semester Final
... Thomson’s experiments provided the first evidence that atoms are made up of smaller particles called subatomic particles (electrons, neutrons, protons). According to Rutherford’s model, all of an atom’s positive charge is located in its nucleus. Protons, electrons, and neutrons can be distingu ...
... Thomson’s experiments provided the first evidence that atoms are made up of smaller particles called subatomic particles (electrons, neutrons, protons). According to Rutherford’s model, all of an atom’s positive charge is located in its nucleus. Protons, electrons, and neutrons can be distingu ...
7A SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW - MERRICK 7th SCIENCE REVIEW
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
... ___ Describe the difference between atoms and molecules. ___ Define elements, compounds, and mixtures. ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe th ...
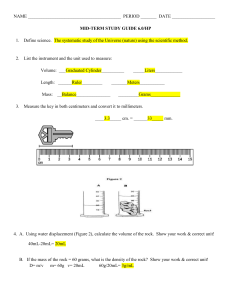
NAME PERIOD ______ DATE MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE 6.0/HP
... Solid: Definite shape, definite volume, particles move slowest (coolest temperature), particles packed closely together, particles cannot change positions- most dense for almost all substances Liquid: No definite shape, has definite volume, particles move faster than solid- but slower than gases, pa ...
... Solid: Definite shape, definite volume, particles move slowest (coolest temperature), particles packed closely together, particles cannot change positions- most dense for almost all substances Liquid: No definite shape, has definite volume, particles move faster than solid- but slower than gases, pa ...
Matter—anything that has mass and occupies space Weight—pull of
... Protons, neutrons, electrons Protons and neutrons found in nucleus Electrons orbit nucleus in an electron cloud ...
... Protons, neutrons, electrons Protons and neutrons found in nucleus Electrons orbit nucleus in an electron cloud ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.