File
... Chain reaction a self-sustaining reaction , where the release of one or more neutrons causes further fission Nuclear fusion: The joining together of two light nuclei to form a larger nucleus with the emission of large amounts of energy. Energy-mass equivalence: E = mc2 ...
... Chain reaction a self-sustaining reaction , where the release of one or more neutrons causes further fission Nuclear fusion: The joining together of two light nuclei to form a larger nucleus with the emission of large amounts of energy. Energy-mass equivalence: E = mc2 ...
Synchrotron - schoolphysics
... The Proton Synchrotron at CERN in Geneva has an orbit diameter of 172m, deflecting magnets of 1.4T and accelerates protons to 28 GeV. Each proton pulse contains about 1011 protons and during the acceleration the protons travel some 80 000 km (50 000 miles)! Protons from the synchrotron are shot into ...
... The Proton Synchrotron at CERN in Geneva has an orbit diameter of 172m, deflecting magnets of 1.4T and accelerates protons to 28 GeV. Each proton pulse contains about 1011 protons and during the acceleration the protons travel some 80 000 km (50 000 miles)! Protons from the synchrotron are shot into ...
Chapter 30 - Planet Holloway
... attracted toward an negatively charged grid Some of the positive particles collide and fuse ...
... attracted toward an negatively charged grid Some of the positive particles collide and fuse ...
research project #1 - Soudan Underground Laboratory
... Scientist- a person skilled in science. Neutrino- fundamental particle with very little mass and no charge. ...
... Scientist- a person skilled in science. Neutrino- fundamental particle with very little mass and no charge. ...
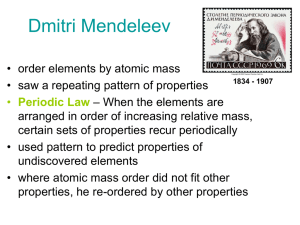
Dmitri Mendeleev
... The mass of an atom is measured relative to the mass of a chosen standard (carbon-12 atom), and is expressed in atomic mass units (amu). The average atomic mass of an element is the mass of that element’s natural occurring ...
... The mass of an atom is measured relative to the mass of a chosen standard (carbon-12 atom), and is expressed in atomic mass units (amu). The average atomic mass of an element is the mass of that element’s natural occurring ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... atomic nuclei, but they have different mass number. So, these atoms are said to be containing unstable combinations of protons and neutrons. Now, if there is unstable atomic nuclei it may it will spontaneously decompose to form a nuclei with higher stability. Now, this decomposition process where an ...
... atomic nuclei, but they have different mass number. So, these atoms are said to be containing unstable combinations of protons and neutrons. Now, if there is unstable atomic nuclei it may it will spontaneously decompose to form a nuclei with higher stability. Now, this decomposition process where an ...
chapter30
... attracted toward an negatively charged grid Some of the positive particles collide and fuse ...
... attracted toward an negatively charged grid Some of the positive particles collide and fuse ...
Atomic Structure
... 1) The next development came about 10 years later. Two of Ernest Rutherford's students, Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, were doing an experiment at Manchester University with radiation. They were using the dense, positively charged particles (called alpha particles) as 'bullets' to fire at a very th ...
... 1) The next development came about 10 years later. Two of Ernest Rutherford's students, Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, were doing an experiment at Manchester University with radiation. They were using the dense, positively charged particles (called alpha particles) as 'bullets' to fire at a very th ...
Mid-Term OR Study Guide
... A) Identify the trend for atomic radius as the atomic number increases (moving down the group) or decreases (moving up a group). Be able to explain this trend as we did in class. B) What type of charge will the elements in this group tend to achieve? C) Identify how the atomic radius compares to the ...
... A) Identify the trend for atomic radius as the atomic number increases (moving down the group) or decreases (moving up a group). Be able to explain this trend as we did in class. B) What type of charge will the elements in this group tend to achieve? C) Identify how the atomic radius compares to the ...
Day 4 - Academic Computer Center
... Back in the early 1900’s a scientist named Rutherford shot some alpha particles (something like atomic bullets) into some very thin pieces of gold. He thought that atoms were similar to the circular particles that you have drawn and that the bullets would all interact with all the gold atoms in abou ...
... Back in the early 1900’s a scientist named Rutherford shot some alpha particles (something like atomic bullets) into some very thin pieces of gold. He thought that atoms were similar to the circular particles that you have drawn and that the bullets would all interact with all the gold atoms in abou ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.