Physics Notes for Class 12 Chapter 12 Atoms
... 1. It could not explain the origin of spectral series of hydrogen and other atoms. 2. It could not explain large angle scattering of α – particles. Rutherford’s Atomic Model On the basis of this experiment, Rutherford made following observations (i) The entire positive charge and almost entire mass ...
... 1. It could not explain the origin of spectral series of hydrogen and other atoms. 2. It could not explain large angle scattering of α – particles. Rutherford’s Atomic Model On the basis of this experiment, Rutherford made following observations (i) The entire positive charge and almost entire mass ...
Student Guide - Quarknet
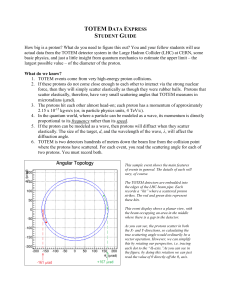
... What do we know? 1. TOTEM events come from very high-energy proton collisions. 2. If these protons do not come close enough to each other to interact via the strong nuclear force, then they will simply scatter elastically as though they were rubber balls. Protons that scatter elastically, therefore, ...
... What do we know? 1. TOTEM events come from very high-energy proton collisions. 2. If these protons do not come close enough to each other to interact via the strong nuclear force, then they will simply scatter elastically as though they were rubber balls. Protons that scatter elastically, therefore, ...
Geography - aps mhow
... executing S.H.M. In what positions, the energy is wholly kinetic or wholly potential? (b). Plot a graph of kinetic energy, potential energy and total energy of the oscillator with ...
... executing S.H.M. In what positions, the energy is wholly kinetic or wholly potential? (b). Plot a graph of kinetic energy, potential energy and total energy of the oscillator with ...
parity-violating electron scattering
... us to derive the electroweak charges of leptons and quarks. We then describe the formalism of probing nuclear and nucleon structure using fixed-target electron scattering, with particular emphasis on parity-violation. This is followed by an introduction to the experimental technique of parity-violat ...
... us to derive the electroweak charges of leptons and quarks. We then describe the formalism of probing nuclear and nucleon structure using fixed-target electron scattering, with particular emphasis on parity-violation. This is followed by an introduction to the experimental technique of parity-violat ...
Rusov-Presentation-Sofia-Mateev-NuclearFission
... fission, which was based on the newest experimental data for alpha-decay of even-even super heavy nuclei (Z=114, 116, 118) have shown the good coincidence of the experimental and theoretical half-life depend on of alphadecay energy. ...
... fission, which was based on the newest experimental data for alpha-decay of even-even super heavy nuclei (Z=114, 116, 118) have shown the good coincidence of the experimental and theoretical half-life depend on of alphadecay energy. ...
Atomic Collisions and Backscattering Spectrometry
... scattering of alpha particles by the positively charged nucleus not only established this model but also forms the basis for one modern analytical technique, Rutherford backscattering spectrometry. In this chapter, we will develop the physical concepts underlying Coulomb scattering of a fast light i ...
... scattering of alpha particles by the positively charged nucleus not only established this model but also forms the basis for one modern analytical technique, Rutherford backscattering spectrometry. In this chapter, we will develop the physical concepts underlying Coulomb scattering of a fast light i ...
Electrical Force - Scarsdale Schools
... • A positron (the electron’s antiparticle) has mass 9.1 x 10^-31 kg and charge q = 1.6 x 10^-19 C. Suppose a positron moves in the vicinity of an (alpha) particle, which has charge 3.2 x 10^-19 C. The alpha particle’s mass is more than 7000 times that of the positron, so we assume that the particle ...
... • A positron (the electron’s antiparticle) has mass 9.1 x 10^-31 kg and charge q = 1.6 x 10^-19 C. Suppose a positron moves in the vicinity of an (alpha) particle, which has charge 3.2 x 10^-19 C. The alpha particle’s mass is more than 7000 times that of the positron, so we assume that the particle ...
Lipatov, A.S. - ISSS-9
... We suggest a merging procedure for the Complex Particle Kinetic (CPK) model in case of interpenetrating flow (multiple plasma beams). Each CPK macro-particle includes a Maxwellian distribution in velocity and Gaussian distribution in space with internal dynamics (see [1], for details). It is assumed ...
... We suggest a merging procedure for the Complex Particle Kinetic (CPK) model in case of interpenetrating flow (multiple plasma beams). Each CPK macro-particle includes a Maxwellian distribution in velocity and Gaussian distribution in space with internal dynamics (see [1], for details). It is assumed ...
Solutions Fall 2004 Due 5:01 PM, Monday 2004/11/22
... Solution: The eigenfunction of the time-independent Schroedinger equation is the spatial part of the wave function which is a solution to the Schroedinger equation for a time-independent potential energy function. Since the wave function is used to calculate actual quantities that can be measured in ...
... Solution: The eigenfunction of the time-independent Schroedinger equation is the spatial part of the wave function which is a solution to the Schroedinger equation for a time-independent potential energy function. Since the wave function is used to calculate actual quantities that can be measured in ...
Physics League Across Nume ous Countries for Kick
... DNA is a rather stiff polymer. Its mechanical properties can be well approximated by the wormlike chain model, that describes DNA as an elastic rod with fixed contour length and a local bending energy (per length) that is given by (A/2) · (1/R2 ). Here A denotes the bending modulus of the rod and R ...
... DNA is a rather stiff polymer. Its mechanical properties can be well approximated by the wormlike chain model, that describes DNA as an elastic rod with fixed contour length and a local bending energy (per length) that is given by (A/2) · (1/R2 ). Here A denotes the bending modulus of the rod and R ...
Document
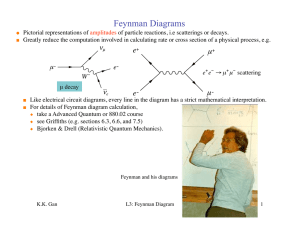
... External lines represent physical particles (observable). Internal lines represent virtual particles ( A virtual particle is just like a physical particle except its mass can assume any value i.e. not on mass-shell). Vertices represent interactions. 4-momentum p must be conserved at each vertex; i ...
... External lines represent physical particles (observable). Internal lines represent virtual particles ( A virtual particle is just like a physical particle except its mass can assume any value i.e. not on mass-shell). Vertices represent interactions. 4-momentum p must be conserved at each vertex; i ...